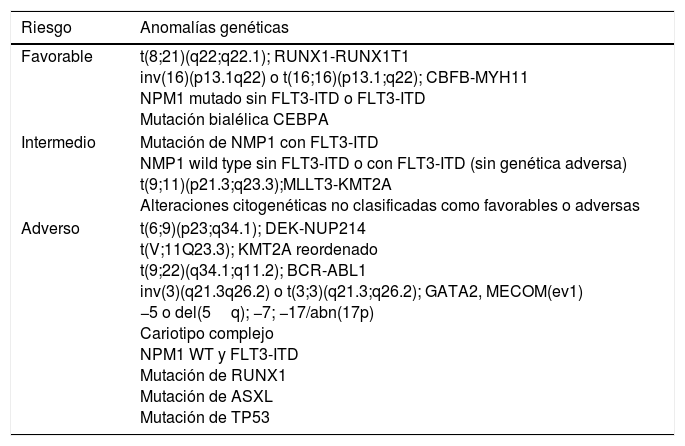
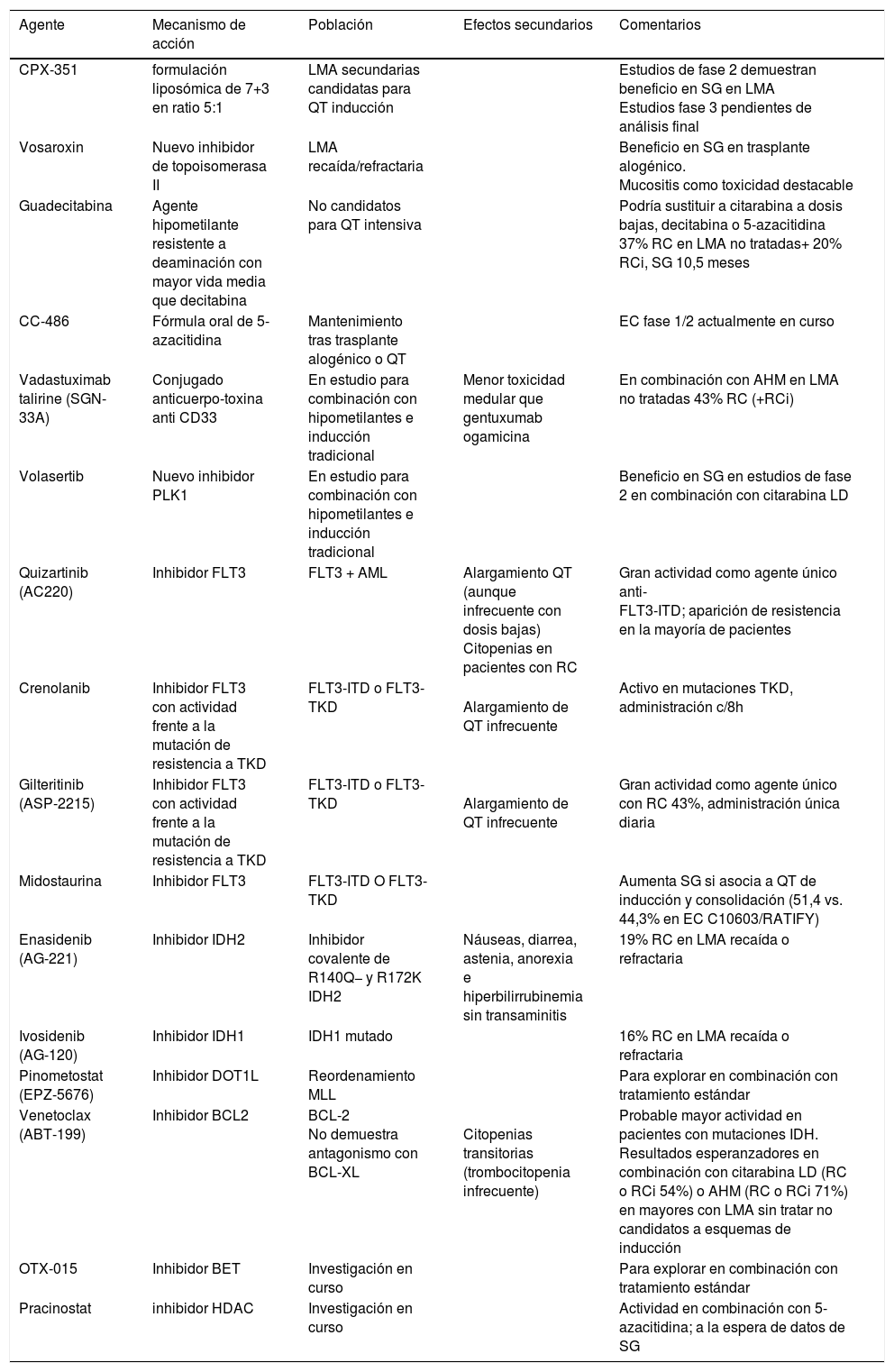
La leucemia mieloide aguda es la forma más frecuente de leucemia aguda, cuya incidencia aumenta con la edad. La enfermedad deriva de una stem cell hematopoyética maligna multipotente transformada que adquiere alteraciones genómicas sucesivas. La identificación de anomalías citogenéticas recurrentes asociadas a distintos patrones de presentación clínica de leucemia mieloide aguda ha llevado a la incorporación de diversos marcadores genéticos que influyen en la toma de decisiones clínicas. Además, las implicaciones que dichas anomalías pueden tener en las respuestas a los tratamientos y en las tasas de recaída y de supervivencia se han incorporado en la reciente clasificación molecular y de la Organización Mundial de la Salud y de la European Leukemia Net, con el objetivo de crear categorías pronósticas que ayuden a racionalizar mejor el diagnóstico, pronóstico, la reevaluación de la enfermedad y la combinación de protocolos terapéuticos, con la finalidad de aumentar la supervivencia.
Acute myeloid leukaemia is the most common form of acute leukaemia, and its incidence increases with age. The disease derives from a transformed multipotent malignant haematopoietic stem cell that acquires consequent genomic alterations. The identification of recurrent cytogenetic anomalies associated with different patterns of acute myeloid leukaemia clinical presentation has led to the incorporation of genetic markers in clinical decision-making. In addition, the observation that these anomalies may mark therapeutic responses and relapse and survival rates have been incorporated into the World Health Organisation's recent molecular classification and stratification and the European Leukaemia Net, with the aim of creating prognostic categories that help rationalise better diagnosis, prognosis, re-evaluation of the disease and the combination of therapeutic protocols in order to increase the survival rate of these patients.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora