Validar el cuestionario de satisfacción Anti-Clot Treatment Scale (ACTS) en pacientes con fibrilación auricular no valvular (FANV) en tratamiento con anticoagulantes orales atendidos en consultas de Medicina Interna y Neurología de España.
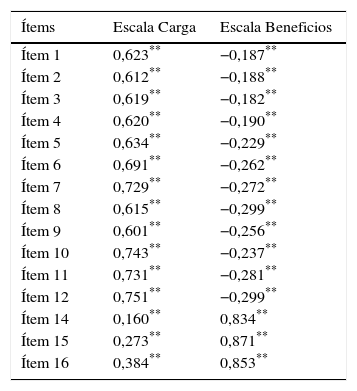
MétodosEstudio transversal, multicéntrico, en el que se incluyeron 1.337 sujetos≥18 años con FANV, en tratamiento con anticoagulantes orales≥3 meses, atendidos en consultas de Medicina Interna o Neurología en España. Los pacientes completaron los cuestionarios ACTS, Self-Assessment of Treatment Questionnaire (SAT-Q) y EuroQol-5 dimensions (5Q-5D). La escala ACTS es un instrumento de satisfacción específico para la evaluación de la carga (mayor puntuación, menor carga) y beneficios (mayor puntuación, mayor beneficio) con el tratamiento anticoagulante. Se evaluaron las propiedades psicométricas del cuestionario de acuerdo con la teoría clásica de los test.
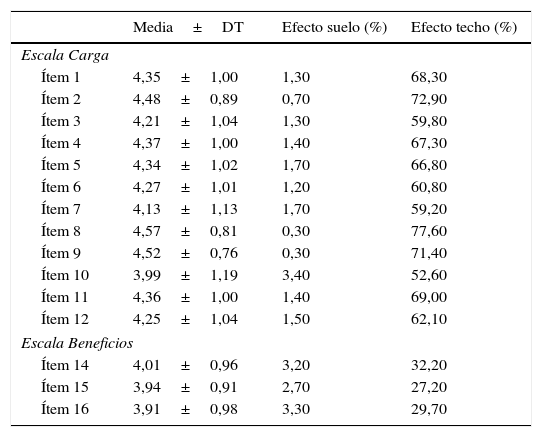
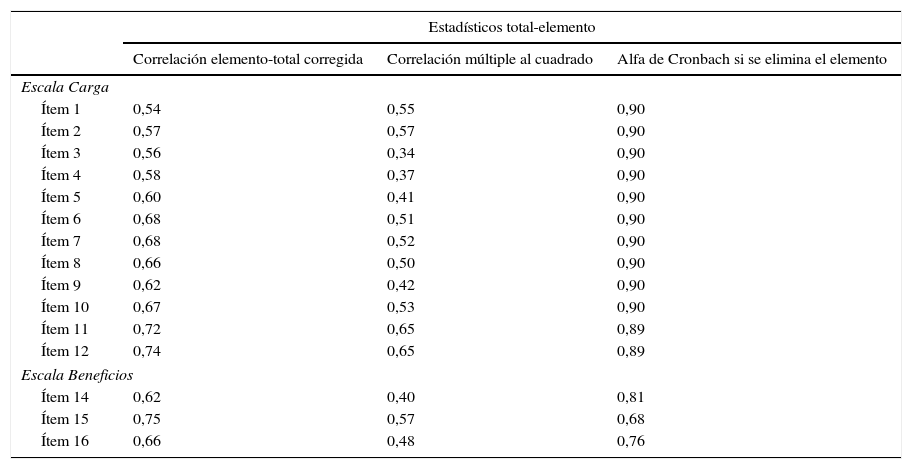
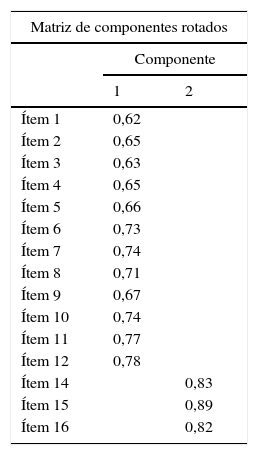
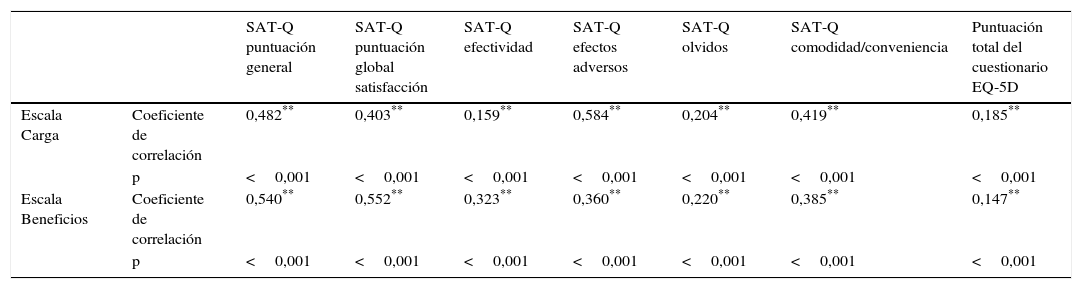
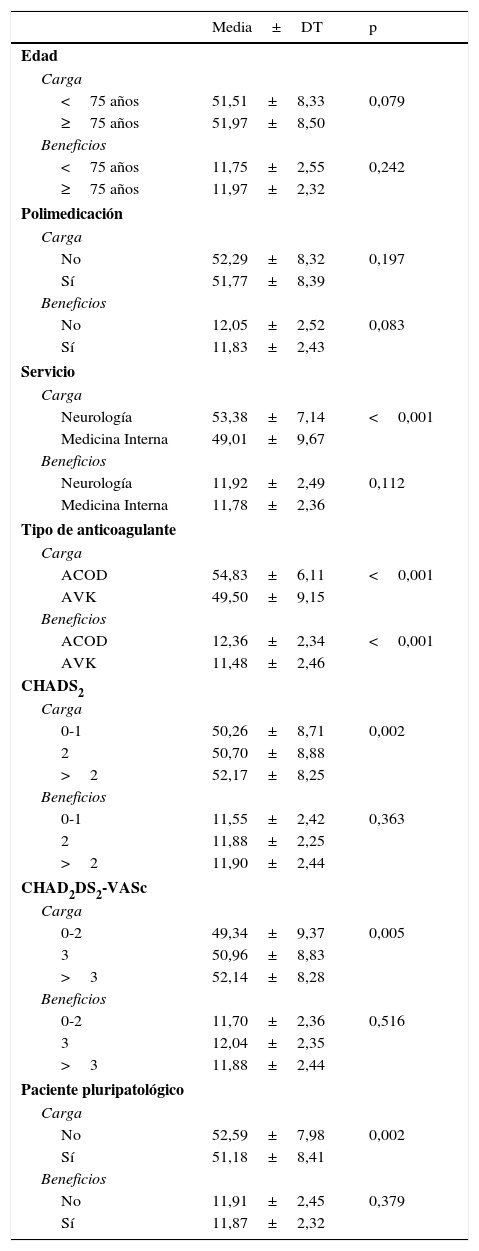
ResultadosEl tiempo medio en cumplimentar el cuestionario fue 8,99±6,06min y el 63,70% de los pacientes precisaron ayuda para la cumplimentación del mismo. Existió una elevada concordancia entre las puntuaciones del test y el retest. La fiabilidad total (alfa de Cronbach) fue 0,95 en la escala Carga y 0,82 en la escala Beneficio. El modelo factorial resultó pertinente. Todas las correlaciones con el cuestionario SAT-Q fueron positivas, moderadas y estadísticamente significativas. Con respecto al cuestionario EQ-5D-3L, estas fueron positivas, bajas y estadísticamente significativas. La satisfacción de los pacientes fue mayor cuando estaban siendo tratados con anticoagulantes orales de acción directa.
ConclusionesEn pacientes con FANV en tratamiento con anticoagulantes orales, la versión en español del cuestionario ACTS fue fiable, válida y factible.
To validate the satisfaction questionnaire Anti-Clot-Treatment Scale (ACTS) in outpatients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF) treated with oral anticoagulants attended in Internal Medicine and Neurology departments in Spain.
MethodsIn this cross-sectional and multicentrer study, 1,337 outpatients aged≥18 years, with NVAF, treated with oral anticoagulants≥3 months, attended in Internal Medicine and Neurology departments in Spain were analyzed. The patients completed ACTS, Self-Assessment of Treatment Questionnaire (SAT-Q) and EuroQol-5 dimensions (EQ-5D) questionnaires. ACTS is a satisfaction tool that specifically analyzes burdens (higher score, lesser burden) and benefits (higher score, higher benefit) with anticoagulant treatment. The psychometric properties of the questionnaire were evaluated according to the classical test theory.
ResultsThe average time to complete the questionnaire was 8.99±6.06min and 63.70% of patients needed assistance to complete it. There was a high concordance between test and retest scores. Total reliability (Cronbach's alpha) was 0.95 in the ACTS Burdens scale and 0.82 in the ACTS Benefits scale. The factorial model was pertinent. All correlations with the SAT-Q questionnaire were positive, moderate and statistically significant. With regard to the EQ-5D-3L questionnaire, correlations were positive, low and statistically significant. Patient satisfaction was higher in the individuals being treated with new direct oral anticoagulants.
ConclusionsIn patients with NVAF treated with oral anticoagulants, the Spanish version of ACTS questionnaire was reliable, valid and feasible.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora