Headache after carotid artery stenting is a headache with onset during the procedure or in the first few hours after it, and where there is no evidence to suggest a complication of that procedure. The purpose of this study is to describe the main features of these headaches based on our clinical experience.
Patients and methodsObservational prospective study of a sample of patients undergoing carotid artery stenting at Hospital Clínico Universitario Lozano Blesa, in Zaragoza, Spain. We recorded sociodemographic characteristics, cardiovascular risk factors, carotid artery disease, and history of primary headache; data were gathered using structured interviews completed before and 24hours after the procedure.
ResultsWe included 56 patients (mean age 67±9.52 years); 84% were men. Twelve patients (21.4%) experienced headache, 83.3% of whom were men; mean age was 60.58±9.31 years. Headache appeared within the first 6hours in 7 patients (58.4%) and during the procedure in 4 (33.3%). Pain lasted less than 10minutes in 4 patients (33.3%) and between 10 and 120minutes in 5 (41.7%). Headache affected the frontotemporal area in 7 patients (58.3%); 7 patients (58.3%) described pain as unilateral. It was oppressive in 8 patients (66.7%) and of moderate intensity in 6 (50%). Nine patients (75%) required no analgesics. We found no statistically significant associations with any of the variables except for age (P=.007; t test).
ConclusionsIn our sample, headache after carotid artery stenting was mild to moderate in intensity, unilateral, oppressive, and short-lasting. Further studies are necessary to gain a deeper knowledge of its characteristics and associated risk factors.
La cefalea post-stent carotídeo es aquella cefalea de aparición durante el procedimiento o en las horas posteriores, sin que haya datos de la existencia de una complicación del mismo. El objetivo de este estudio es definir las características de esta cefalea a partir de nuestra experiencia clínica.
Pacientes y métodoEstudio transversal prospectivo observacional de una muestra de pacientes sometidos a stenting carotídeo en el Hospital Clínico Universitario Lozano Blesa. Se estudiaron variables sociodemográficas, factores de riesgo cardiovascular, afectación carotídea y antecedentes de cefalea primaria. Se realizó una entrevista estructurada antes del procedimiento y en las siguientes 24h.
ResultadosSe incluyeron un total de 56 pacientes con una media de edad de 67±9,52 años; un 84% eran hombres. La cefalea apareció en 12 pacientes (21,4%), siendo el 83,3% hombres con una media de edad de 60,58±9,31 años. En el 58,4% (n=7) comenzó en las primeras 6h y en el 33,3% (n=4) durante el procedimiento. En el 33,3% (n=4) la duración fue menor de 10min, y en el 41,7% (n=5) osciló entre 10-120min. Localizaron el dolor en la región frontotemporal el 58,3% (n=7); el 58,3% (n=7) lo describe como unilateral. Es opresivo en un 66,7% (n=8), de intensidad moderada en un 50% (n=6) y el 75% de los pacientes no precisó analgesia. No se observó ninguna relación estadísticamente significativa con las variables estudiadas, excepto la edad (p=0,007).
ConclusionesEn nuestra serie, la cefalea post-stent carotídeo es de intensidad leve-moderada, unilateral, opresiva y de breve duración. Si bien son necesarios más estudios para poder definir mejor sus características y factores de riesgo.
In Spain, cerebrovascular diseases constitute the leading cause of mortality in women and the third most frequent in men, as well as the greatest cause of disability. Around 28% of ischaemic strokes are atherothrombotic, and most are caused by carotid artery stenosis.1 The diagnostic protocol for stroke should therefore include a neurosonology study. Duplex/Doppler ultrasonography is used to detect atheromatosis of the supra-aortic trunks and/or large intracranial arteries as a possible cause of stroke.2
Patients with significant stenosis, detected by either Doppler ultrasonography of the supra-aortic trunks, CT angiography, or MRI angiography, may also undergo a cerebral angiography study, the gold standard for diagnosing and quantifying stenosis. The technique is both diagnostic and therapeutic, as it enables carotid artery stenting. Indicating cerebral angiography over thromboendarterectomy depends on numerous factors, including patient characteristics and the type of atheromatous plaque.3
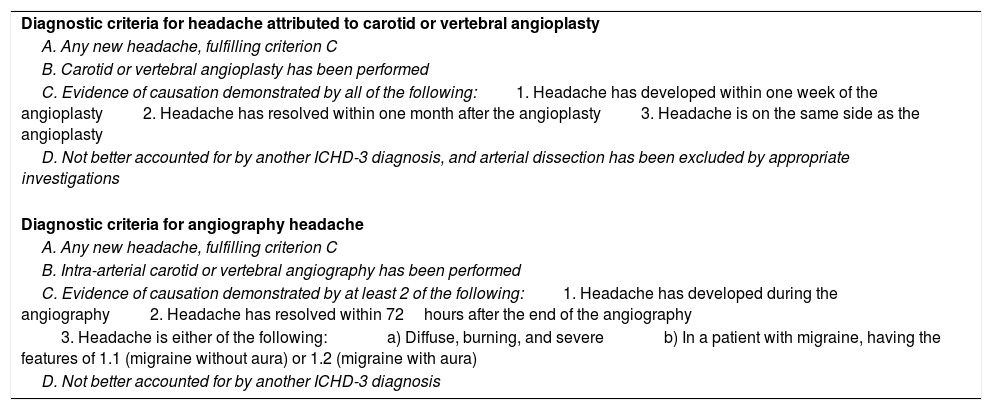
Patients may experience headache during or after carotid artery stenting. This type of headache is classified as an independent entity (G44.810) in the second edition of the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD); the diagnostic criteria were later modified in the third edition, beta version, published in 2013 (6.5.3).4,5 The ICHD-3 Beta diagnostic criteria for headache attributed to carotid or vertebral angioplasty (6.5.3) and for angiography headache (6.7.2) are described in Table 1. The classification defines this type of headache as “headache caused by the surgical procedure of cervical angioplasty. Pain can also involve the neck and face. It can remain isolated or be a warning symptom preceding the focal deficits of (mostly haemorrhagic) stroke.”4
Diagnostic criteria for headache attributed to carotid or vertebral angioplasty (6.5.3) and angiography headache (6.7.2) according to the third edition of the International Classification of Headache Disorders, beta version.
| Diagnostic criteria for headache attributed to carotid or vertebral angioplasty |
| A. Any new headache, fulfilling criterion C |
| B. Carotid or vertebral angioplasty has been performed |
| C. Evidence of causation demonstrated by all of the following:1. Headache has developed within one week of the angioplasty2. Headache has resolved within one month after the angioplasty3. Headache is on the same side as the angioplasty |
| D. Not better accounted for by another ICHD-3 diagnosis, and arterial dissection has been excluded by appropriate investigations |
| Diagnostic criteria for angiography headache |
| A. Any new headache, fulfilling criterion C |
| B. Intra-arterial carotid or vertebral angiography has been performed |
| C. Evidence of causation demonstrated by at least 2 of the following:1. Headache has developed during the angiography2. Headache has resolved within 72hours after the end of the angiography |
| 3. Headache is either of the following:a) Diffuse, burning, and severeb) In a patient with migraine, having the features of 1.1 (migraine without aura) or 1.2 (migraine with aura) |
| D. Not better accounted for by another ICHD-3 diagnosis |
From a clinical viewpoint, headache after carotid artery stenting is a type of headache with onset during or within 2hours of the procedure with no evidence of other complications. Pain resolves within one month. This type of headache must present different characteristics from those of previous headache episodes experienced by the patient. Despite the well-defined diagnostic criteria for headache after carotid artery stenting, pain localisation, intensity, quality, and duration are highly non-specific; a spatial and temporal association between the procedure and headache onset is therefore the only definitive diagnostic criterion.
This study aims to define the characteristics of headache after carotid artery stenting based on our clinical experience.
Patients and methodsWe performed a prospective, cross-sectional study of a series of consecutively recruited patients assessed at the stroke unit of Hospital Clínico Universitario Lozano Blesa (Zaragoza, Spain), and indicated for diagnostic angiography and, where appropriate, carotid artery stenting. Patients were gathered between November 2012 and May 2015. All patients showed carotid artery stenoses > 50%, whether symptomatic or asymptomatic.
We established the following inclusion criteria:
- -
Age≥18 years
- -
Participating voluntarily and signing an informed consent form.
The exclusion criteria were as follows:
- -
Declining to give informed consent
- -
Aphasia or other language alterations considerably limiting patients’ ability to complete an interview
- -
Cognitive impairment or any other difficulties limiting patients’ ability to complete an interview
- -
Intracranial stenosis or carotid artery dissection
- -
Displaying cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome after carotid artery stenting.
- -
A neurologist administered a questionnaire to candidate patients on 3 occasions:
- -
Initial visit: 24hours before the procedure, to gather clinical and demographic data (using the patient’s clinical history) and to obtain informed consent
- -
Visit 1: personal interview within 24hours of the procedure
- -
Visit 2: telephone interview a month after the procedure
We gathered data on the following clinical and demographic variables: personal data, age, sex, body mass index, weight, height, cardiovascular risk factors (current or former smoker, diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, dyslipidaemia), location of stenosis (left internal carotid artery [ICA], right ICA, or both), degree of stenosis (NASCET criteria6: mild, 50%-69%; moderate, 70%-89%; severe, ≥ 90%), stent location, symptoms prior to diagnosis (transient ischaemic attack, stroke, asymptomatic), and history of primary headache according to the ICHD-3 Beta criteria5 (migraine without aura, migraine with aura, tension-type headache, other).
During the interview performed after angiography and/or carotid artery stenting, patients were asked whether they had experienced headache. If they had, we inquired about the characteristics of the headache: time of onset, duration, localisation, laterality, pain characteristics and intensity, associated symptoms, and whether the patient required analgesics.
Description of the procedureIn accordance with our hospital’s protocol, carotid artery angiography and carotid artery stenting are performed percutaneously using transfemoral access with local anaesthesia. Patients receive medication for the procedure at 2 different time points: 24hours before angioplasty, and again several hours before the procedure. The previous day, patients receive dual antiplatelet therapy (100mg acetylsalicylic acid+75mg clopidogrel [30mg if the patient was not taking the drug previously]). On the day of the procedure, patients received an additional, 75-mg dose of clopidogrel, 100mg acetylsalicylic acid, 1000mg acetylcholine, 60mg nimodipine, 80mg atorvastatin, and 12mg intravenous dexamethasone.7
Statistical analysisQuantitative variables are expressed as means±standard deviation and range; qualitative variables are expressed as percentages. We performed a descriptive bivariate and multivariate analysis. The t test was used to compare means and the parametric chi-square test to compare qualitative variables. Statistical significance was set at P<.05; the analysis was performed using the SPSS statistical software, version 15.
ResultsThe study included a total of 56 patients; mean age was 67.04±9.52 years (range, 44-83). Men accounted for 83.9% of the sample (n=47); 16.1% were women (n=9). Twenty-eight patients (67.8%) undergoing carotid artery angiography and/or stenting were above the healthy BMI range (> 25).
Regarding cardiovascular risk factors, 47 patients had arterial hypertension (83.9%), 40 dyslipidaemia (71.4%), and 22 diabetes mellitus (39.3%); only 23.2% were current smokers, and 44.6% were former smokers. Twelve patients (21.8%) reported history of primary headache: 3 had migraine with aura (5.4%) and 9 had tension-type headache (16.1%). Stenosis affected the right ICA in 46 patients (82.1%) and the left ICA in 43 (78.2%). Stenoses in the right ICA were severe in 43.5% of cases, moderate in 37%, and mild in 19.6%; in the left ICA, 48.8% of stenoses were severe, 30.2% moderate, and 20.9% mild.
Although right ICA stenoses were more severe, stents were placed in the right ICA in 50.9% of cases (n=28) and in the left ICA in 49.1% (n=27); 10 patients (17.9%) underwent diagnostic angiography only. In our sample, the initial manifestation of carotid artery stenosis was transient ischaemic attack in 15 patients (27.3%) and stroke in 33 (60%), whereas 7 (12.7%) showed no symptoms; in these cases, diagnosis was established based on non-vascular neurological symptoms.
Twelve patients (21.4%) experienced headache, 10 of whom were men; the mean age of this subgroup was 60.6±9.31 years. Headache onset occurred during the procedure in 4 cases (33.3%), within 6hours in 7 (58.4%), and 6 to 24hours after the study in one case (8.3%). Pain lasted less than 24hours in all but one case: duration was < 10minutes in 4 patients (33.3%), < 2hours in 5 (41.7%), and between 2 and 24hours in 2 (16.7%). Pain was always ipsilateral to the angioplasty: frontotemporal in 7 patients (58.3%), hemicranial in 2 (16.7%), facial in 2 (16.7%), and occipital in one (8.3%). Pain was unilateral in 7 patients (58.3%) and bilateral in 5 (41.7%). Headache was oppressive in 8 (66.7%), burning in 2 (16.7%), and stabbing and pulsatile in one (8.3%). No patient described headache as disabling; headache was mild (n=6) or moderate (n=6) in all cases, and 9 patients (75%) required no analgesics.
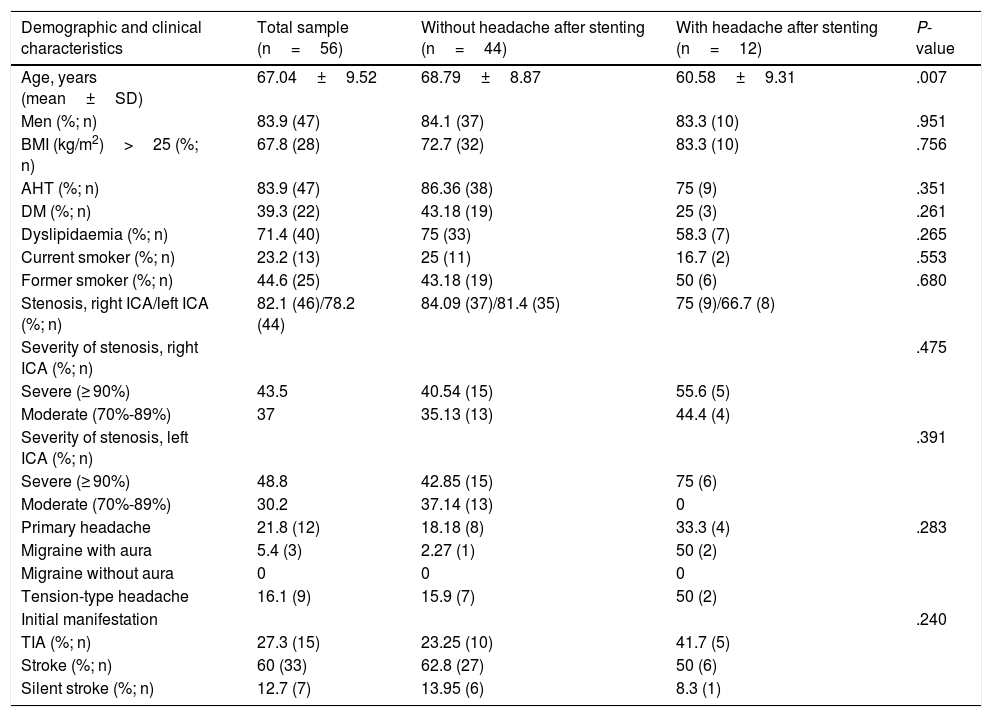
Only one patient experienced headache on the second day; pain was mild, lasted less than 6hours, and was unilateral, occipital, and oppressive. Table 2 compares the clinical and demographic characteristics of the patients with and without headache.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with and without headache after carotid artery stenting.
| Demographic and clinical characteristics | Total sample (n=56) | Without headache after stenting (n=44) | With headache after stenting (n=12) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years (mean±SD) | 67.04±9.52 | 68.79±8.87 | 60.58±9.31 | .007 |
| Men (%; n) | 83.9 (47) | 84.1 (37) | 83.3 (10) | .951 |
| BMI (kg/m2)>25 (%; n) | 67.8 (28) | 72.7 (32) | 83.3 (10) | .756 |
| AHT (%; n) | 83.9 (47) | 86.36 (38) | 75 (9) | .351 |
| DM (%; n) | 39.3 (22) | 43.18 (19) | 25 (3) | .261 |
| Dyslipidaemia (%; n) | 71.4 (40) | 75 (33) | 58.3 (7) | .265 |
| Current smoker (%; n) | 23.2 (13) | 25 (11) | 16.7 (2) | .553 |
| Former smoker (%; n) | 44.6 (25) | 43.18 (19) | 50 (6) | .680 |
| Stenosis, right ICA/left ICA (%; n) | 82.1 (46)/78.2 (44) | 84.09 (37)/81.4 (35) | 75 (9)/66.7 (8) | |
| Severity of stenosis, right ICA (%; n) | .475 | |||
| Severe (≥ 90%) | 43.5 | 40.54 (15) | 55.6 (5) | |
| Moderate (70%-89%) | 37 | 35.13 (13) | 44.4 (4) | |
| Severity of stenosis, left ICA (%; n) | .391 | |||
| Severe (≥ 90%) | 48.8 | 42.85 (15) | 75 (6) | |
| Moderate (70%-89%) | 30.2 | 37.14 (13) | 0 | |
| Primary headache | 21.8 (12) | 18.18 (8) | 33.3 (4) | .283 |
| Migraine with aura | 5.4 (3) | 2.27 (1) | 50 (2) | |
| Migraine without aura | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Tension-type headache | 16.1 (9) | 15.9 (7) | 50 (2) | |
| Initial manifestation | .240 | |||
| TIA (%; n) | 27.3 (15) | 23.25 (10) | 41.7 (5) | |
| Stroke (%; n) | 60 (33) | 62.8 (27) | 50 (6) | |
| Silent stroke (%; n) | 12.7 (7) | 13.95 (6) | 8.3 (1) |
AHT: arterial hypertension; BMI: body mass index; DM: diabetes mellitus; ICA: internal carotid artery; SD: standard deviation; TIA: transient ischaemic attack.
Carotid artery stenting always increases cerebral perfusion and blood flow (20%-40% above the baseline value); this effect lasts several hours. Hyperperfusion is defined as an increase of over 100% in cerebral blood flow compared to preoperative values.8 Cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome, a complication of carotid artery stenting and endarterectomy, is characterised by decreased level of consciousness, confusion, headache, and focal neurological signs.
Carotid artery revascularisation causes cerebral haemodynamic changes; the severity of these changes varies from patient to patient. In patients without preoperative cerebral hypoperfusion, flow velocity peaks on postoperative day 1 and normalises on day 4-5. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion, in contrast, is associated with abnormally high flow velocities lasting several weeks. Cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome develops in patients showing hyperperfusion during the postoperative period and rarely appears in patients with increases in perfusion of below 100%; it is known in this case as “cerebral reperfusion syndrome.”
The main risk factors for cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome are reduced cerebrovascular reserve, post-stenting arterial hypertension, and hypoperfusion lasting several hours after the intervention. Diagnosis is established according to clinical symptoms and neuroimaging and neurosonology findings (Doppler and duplex ultrasound to study flow velocity in intracranial arteries).7
Our results show that headache following carotid artery angiography and/or stenting is a relatively frequent occurrence (21.4%). In our sample, headache usually appeared within 6hours of the procedure, lasted between 10minutes and 24hours (up to 2hours in most cases), and was located in the frontotemporal region unilaterally. Pain was oppressive and of mild to moderate intensity, rarely requiring analgesics. A statistically significant association was identified between age and development of headache after stenting (P=.007).
Numerous articles have addressed the association between headache and carotid artery stenting in the context of cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome. In these cases, headache should be regarded as a symptom of the syndrome. Few studies have focused on headache after carotid artery stenting, however. Gündüz et al.9 studied a sample of 64 patients, with headache presenting in 39.1% of those undergoing stenting and 21.9% in those undergoing diagnostic angiography exclusively. In the patients undergoing stenting, headache was ipsilateral to the carotid artery treated, of moderate intensity, oppressive (headache after angiography was characterised by burning pain), and fully resolved after approximately 10minutes. These results are similar to our own, although the incidence is higher.
Our results should be interpreted with caution due to the small size of our sample. Only one patient developed headache over 24hours after the procedure; we therefore cannot analyse the differences between this type of headache and headaches developing within 24hours of the procedure. However, we may hypothesise that different pathophysiological mechanisms are involved. Further research is necessary to better define this entity's aetiology, pathogenesis, clinical characteristics, and predisposing factors.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Please cite this article as: Suller Marti A, Bellosta Diago E, Velázquez Benito A, Tejero Juste C, Santos Lasaosa S. Cefalea post-stent carotídeo. Neurología. 2019;34:445–450.