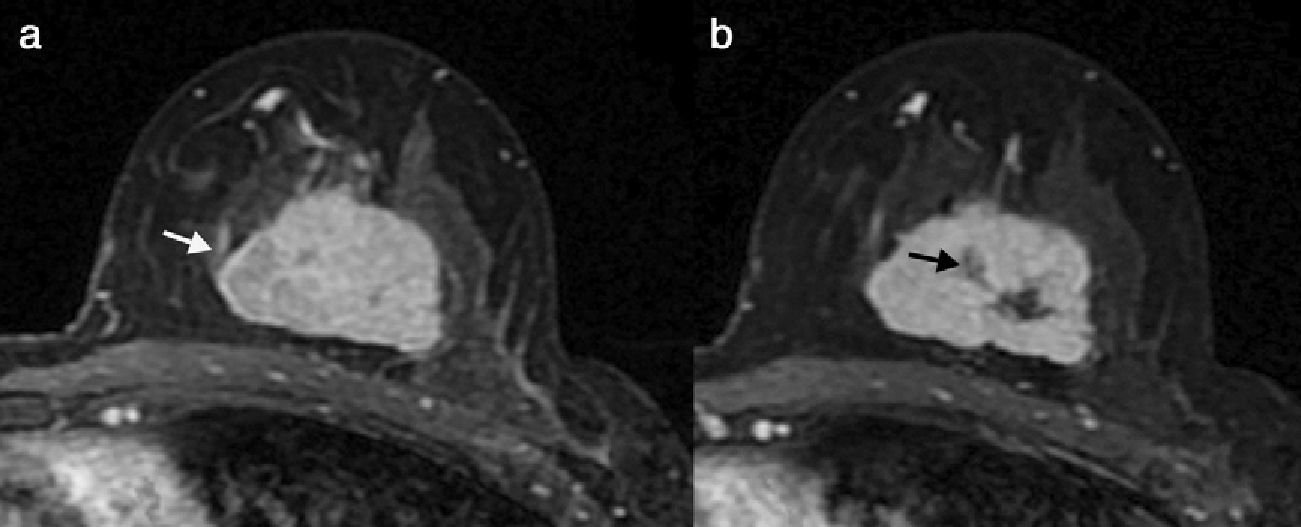
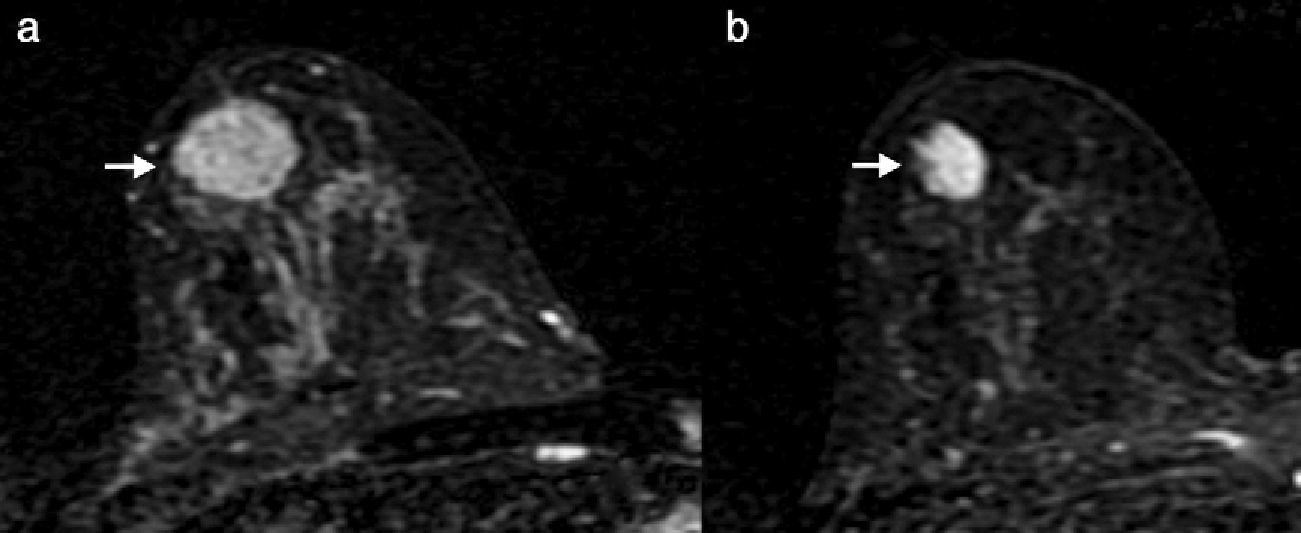
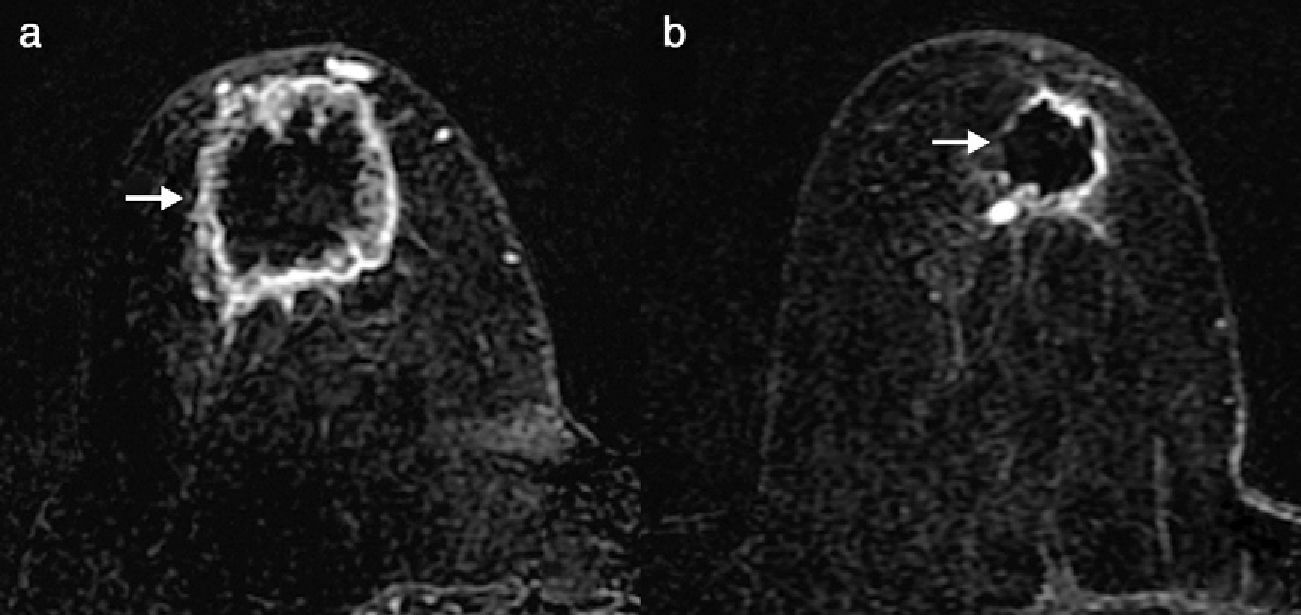
To evaluate the radiologic and pathologic responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and their correlation in the molecular subtypes of breast cancer and to analyze their impact in disease-free survival.
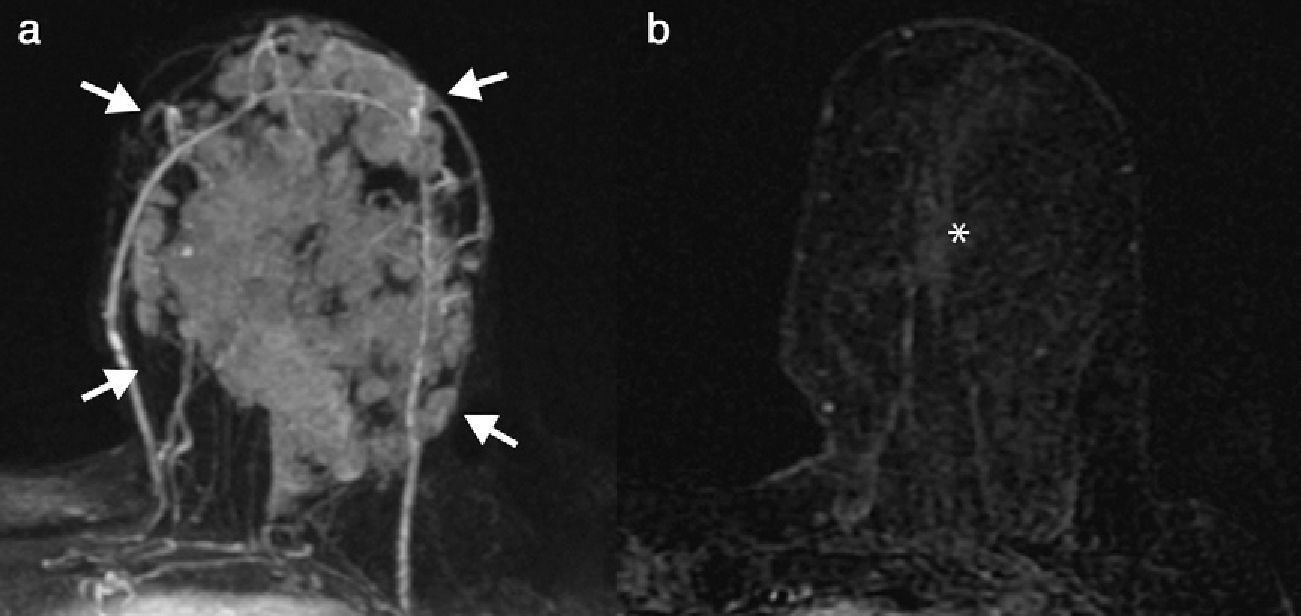
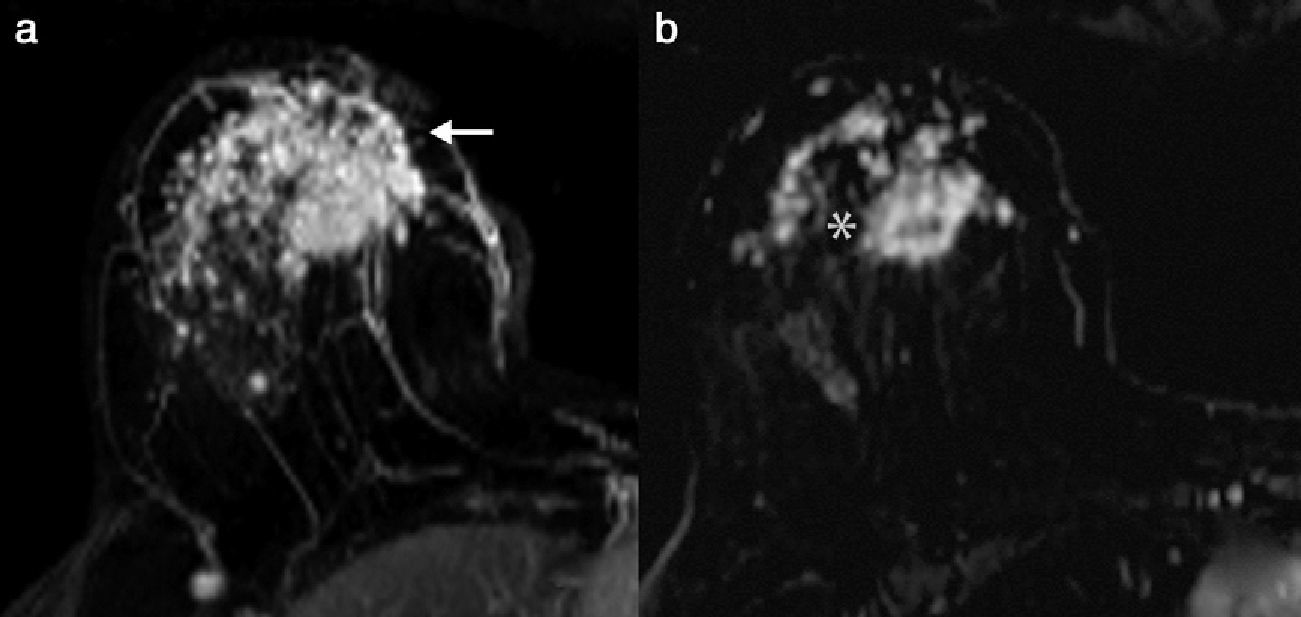
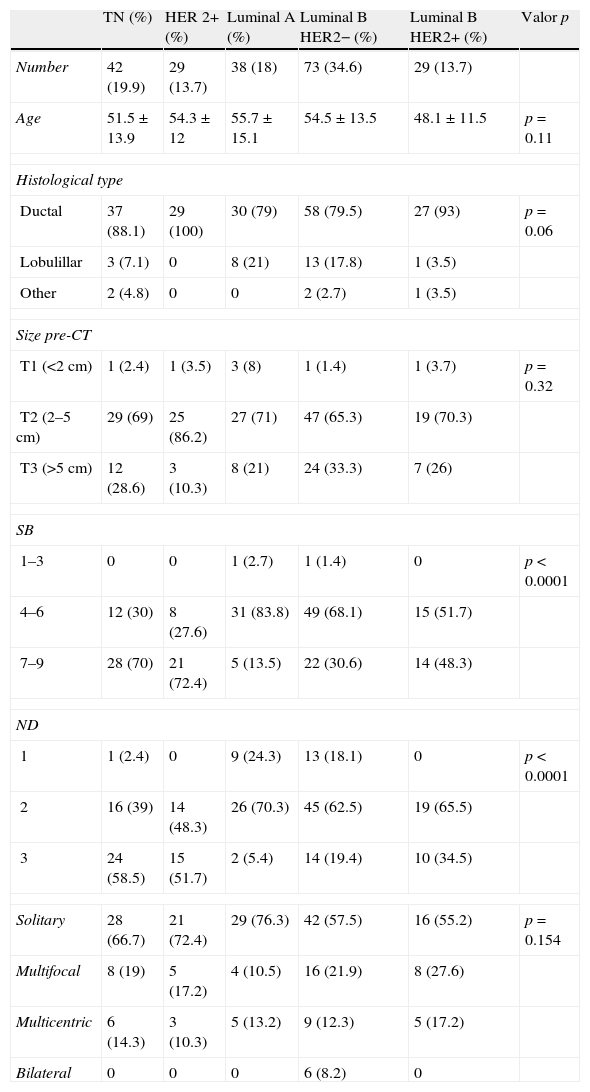
Materials and methodsWe included 205 patients with breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. We evaluated the radiologic response by comparing MRI images acquired before and after chemotherapy. The pathologic response was classified on the Miller and Payne scale. For each subtype (HER2+, TN, luminal A, luminal B HER2−, and luminal B HER2+), we used the χ2 test, Student's t-test, ANOVA, and Kendall's Tau-b to evaluate the radiologic response and the pathologic response, the radiologic–pathologic correlation, and the disease-free survival.
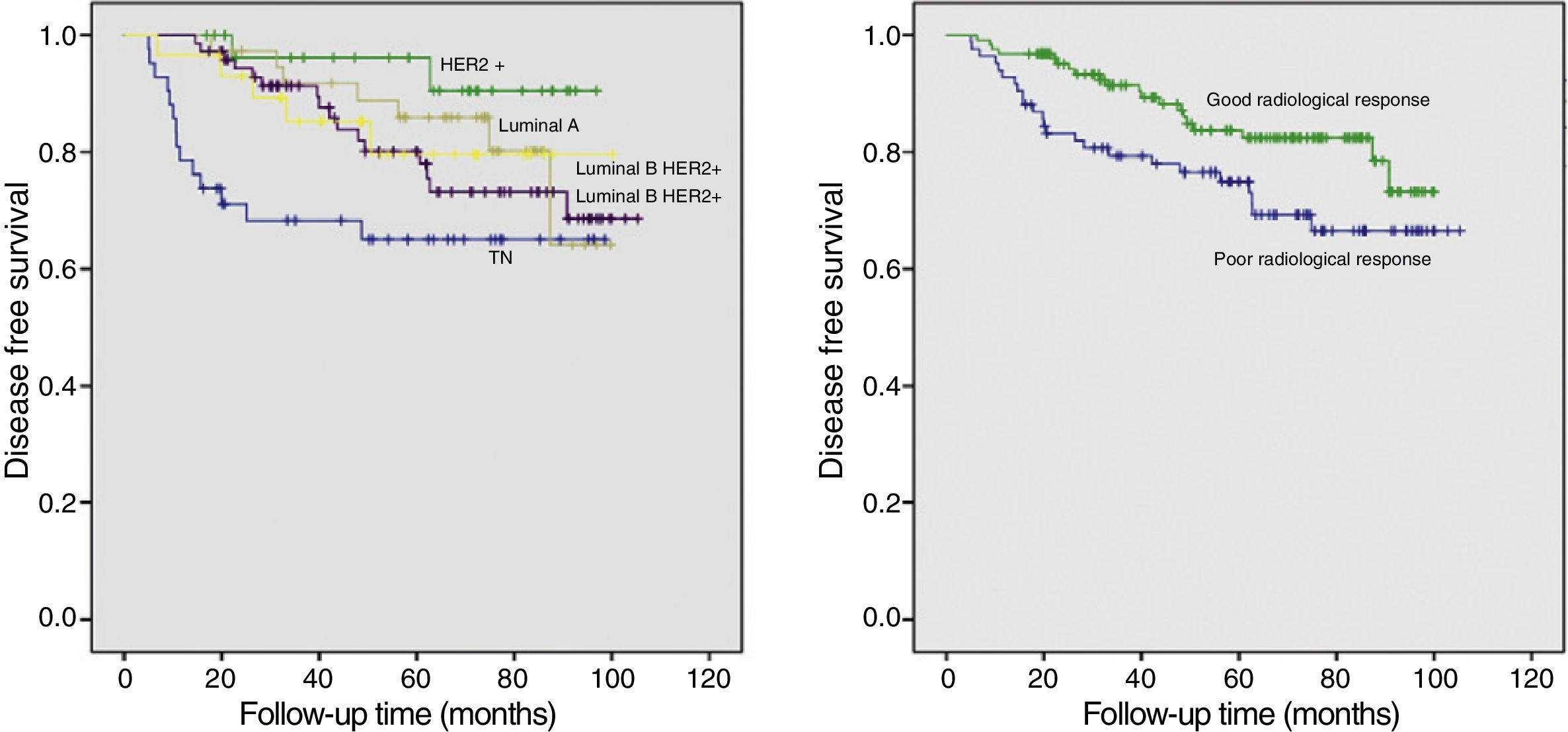
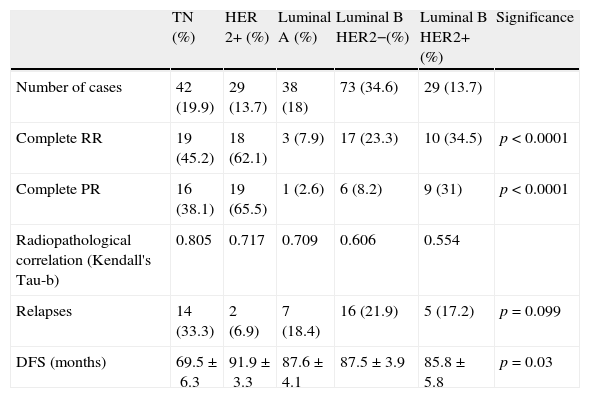
ResultsThe subtypes HER2+ (62.1%) and TN (45.2%) had higher rates of complete radiologic response. The pathologic response was 65.5% in the HER2+ subtype, 38.1% in the TN subtype, 2.6% in the luminal A subtype, 8.2% in the luminal B HER2− subtype, and 31% in the luminal B HER2+ subtype. The rate of radiologic–pathologic correlation was significant in all subtypes, higher in TN and HER2 (Tau-b coefficients 0.805 and 0.717, respectively). Disease-free survival was higher in HER2+ (91.9±3.3 months) and lower in TN (69.5±6.3 months), with significant differences between the cases with poor and good radiologic responses (p=0.040). Survival was greater in cases with good radiologic response, except in cases with luminal A subtype.
ConclusionMRI can be a useful tool that provides information about the evolution of breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy, which varies with the immunohistochemical subtype.
Valorar la respuesta radiológica, patológica y su correlación en los subtipos moleculares del cáncer de mama y analizar su implicación en la supervivencia libre de enfermedad.
Material y métodosSe incluyeron 205 pacientes con cáncer de mama tratadas con quimioterapia neoadyuvante. Se valoró la respuesta radiológica con RM pre y posquimioterapia. La respuesta patológica se clasificó según la escala de Miller y Payne. Se valoró la respuesta radiológica y patológica en cada subtipo (HER2+, TN, luminal A, luminal B HER2– y luminal B HER2+), la correlación radiopatológica y la supervivencia libre de enfermedad mediante las pruebas χ2, t de Student, ANOVA y Tau-b de Kendall.
ResultadosLos subtipos HER2+ (62,1%) y TN (45,2%) mostraron mayor tasa de respuesta radiológica completa. La respuesta patológica fue del 65,5% en el HER2+, 38,1% en el TN, 2,6% en los luminales A, 8,2% en los luminales B HER2– y 31% en los luminales B HER2+. El índice de correlación radiopatológico fue significativo en todos los subtipos, mayor en los TN y HER2 (coeficientes Tau-b 0,805 y 0,717 respectivamente). La supervivencia libre de enfermedad fue mayor para HER2+ (91,9±3,3 meses) y menor en el TN (69,5±6,3 meses), con diferencias significativas entre los casos de mala y buena respuesta radiológica (p=0,040). La supervivencia fue superior en los casos de buena respuesta radiológica a excepción del subtipo luminal A.
ConclusiónLa RM puede ser una herramienta que aporta información de la evolución del CM tratado con neoadyuvancia, variable según el subtipo inmunohistoquímico.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora