Evaluar los resultados de las colecistostomías percutáneas realizadas como tratamiento urgente de colecistitis aguda, en busca de predictores de supervivencia. Valorar la recurrencia de colecistitis tras la retirada del catéter en pacientes descartados para cirugía diferida, y buscar factores predictores de recurrencia.
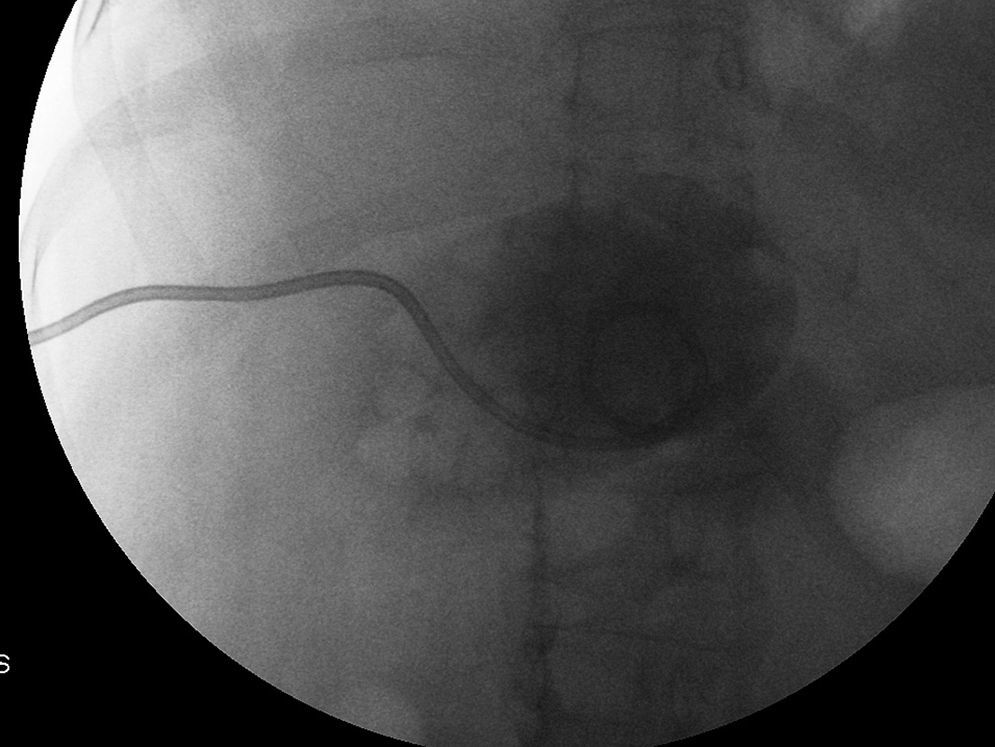
Material y métodosSe revisan retrospectivamente 40 pacientes sometidos a colecistostomía durante dos años. Se analiza la relación de la supervivencia durante el periodo de hospitalización con la evolución de fiebre, dolor abdominal, leucocitosis y proteína C reactiva después del procedimiento. Se analiza la recurrencia de colecistitis tras la retirada del catéter en pacientes descartados para colecistectomía diferida por alto riesgo quirúrgico, así como la influencia de la colangiografía no permeable, la edad, el sexo y las comorbilidades en el porcentaje de recurrencias.
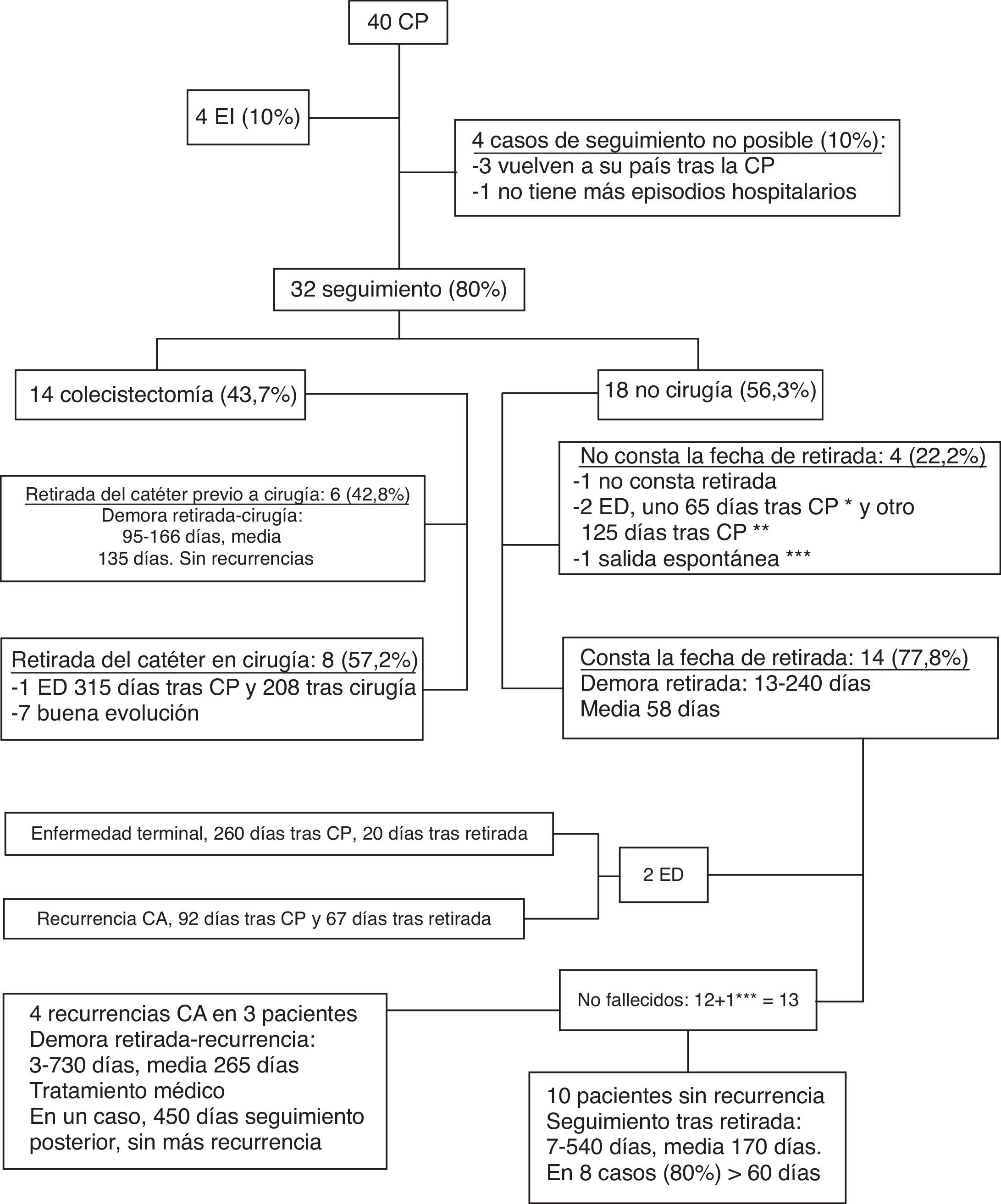
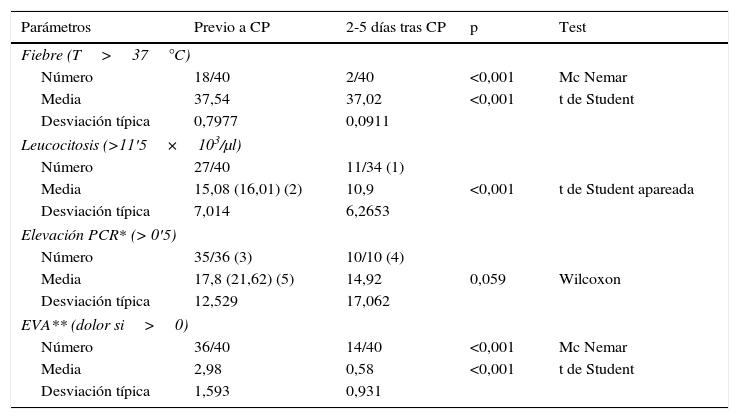
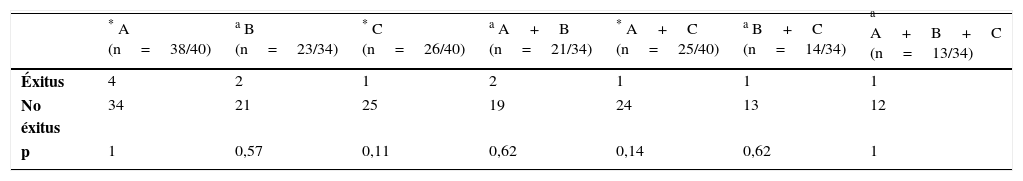
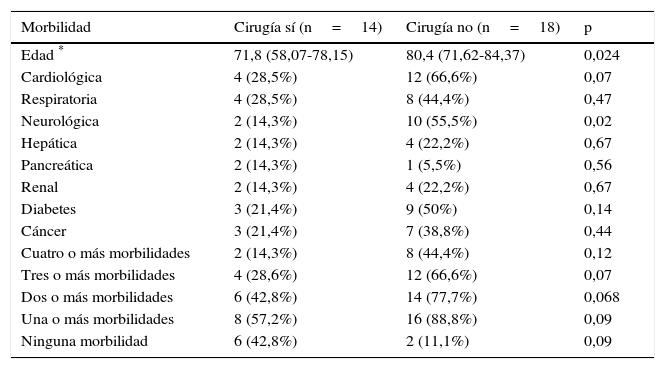
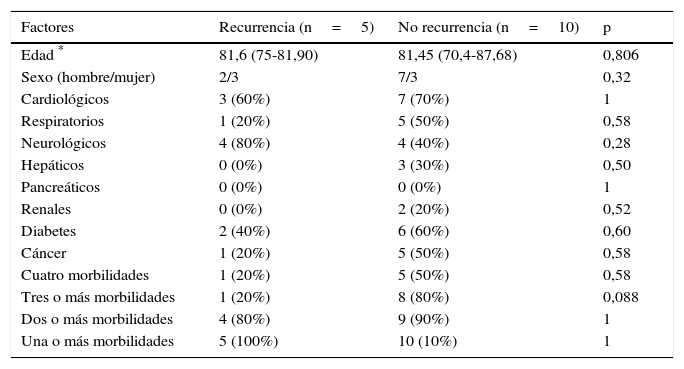
ResultadosDurante la hospitalización fallecieron cuatro pacientes por shock séptico (10%). La colecistostomía mejoró significativamente la fiebre, la leucocitosis y el dolor abdominal en un máximo de 5 días tras el procedimiento, pero estas mejoras no tuvieron un efecto estadísticamente relevante sobre la supervivencia, por lo que no se consideran útiles como factores pronósticos. Entre los 15 pacientes descartados para cirugía hubo seis recurrencias de colecistitis (40%) con un seguimiento medio de 6,7 meses tras la retirada del catéter. Un paciente falleció por recurrencia. No se encontró asociación de recurrencia con los parámetros analizados.
ConclusionesLa colecistostomía ofrece resultados similares a los obtenidos en otras series como tratamiento urgente de la colecistitis aguda en pacientes con alto riesgo quirúrgico. La retirada del catéter en pacientes descartados para cirugía con colecistitis litiásica es una opción desaconsejable debido al elevado riesgo de recurrencia de colecistitis en comparación con otras series.
To evaluate the results of percutaneous cholecystostomy for urgent treatment of acute cholecystitis, with the aim of identifying factors that predict survival. To analyze the recurrence of cholecystitis after catheter withdrawal in patients considered unsuitable candidates for delayed surgery, with the aim of identifying factors that predict recurrence.
Material and methodsWe reviewed 40 patients who underwent percutaneous cholecystostomy in a two-year period. We analyzed survival during hospitalization in relation with fever, abdominal pain, leukocytosis, and C-reactive protein before and after the procedure. We analyzed the recurrence of cholecystitis after catheter withdrawal in patients considered unsuitable candidates for delayed surgery, as well as the influence of obstruction seen on cholangiography, age, sex, and comorbidities on the recurrence rate.
ResultsDuring the hospital stay, 4 (10%) patients died of septic shock. Cholecystostomy improved fever, leukocytosis, and abdominal pain within five days of the procedure, but these improvements did not have a statistically significant effect on survival and were not therefore considered useful prognostic factors. Among the 15 patients considered unsuitable candidates for delayed surgery, 6 (40%) had recurrences of cholecystitis during a mean follow-up period of 6.7 months after catheter withdrawal. We found no association between recurrence and any of the parameters analyzed.
ConclusionsOutcomes in our series of patients with high risk for surgery who underwent cholecystostomy for urgent treatment of acute cholecystitis were similar to those reported in other series. Withdrawing the catheter in patients considered unsuitable candidates for delayed surgery is not recommended due to the high risk of recurrence of cholecystitis in comparison with other series.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora