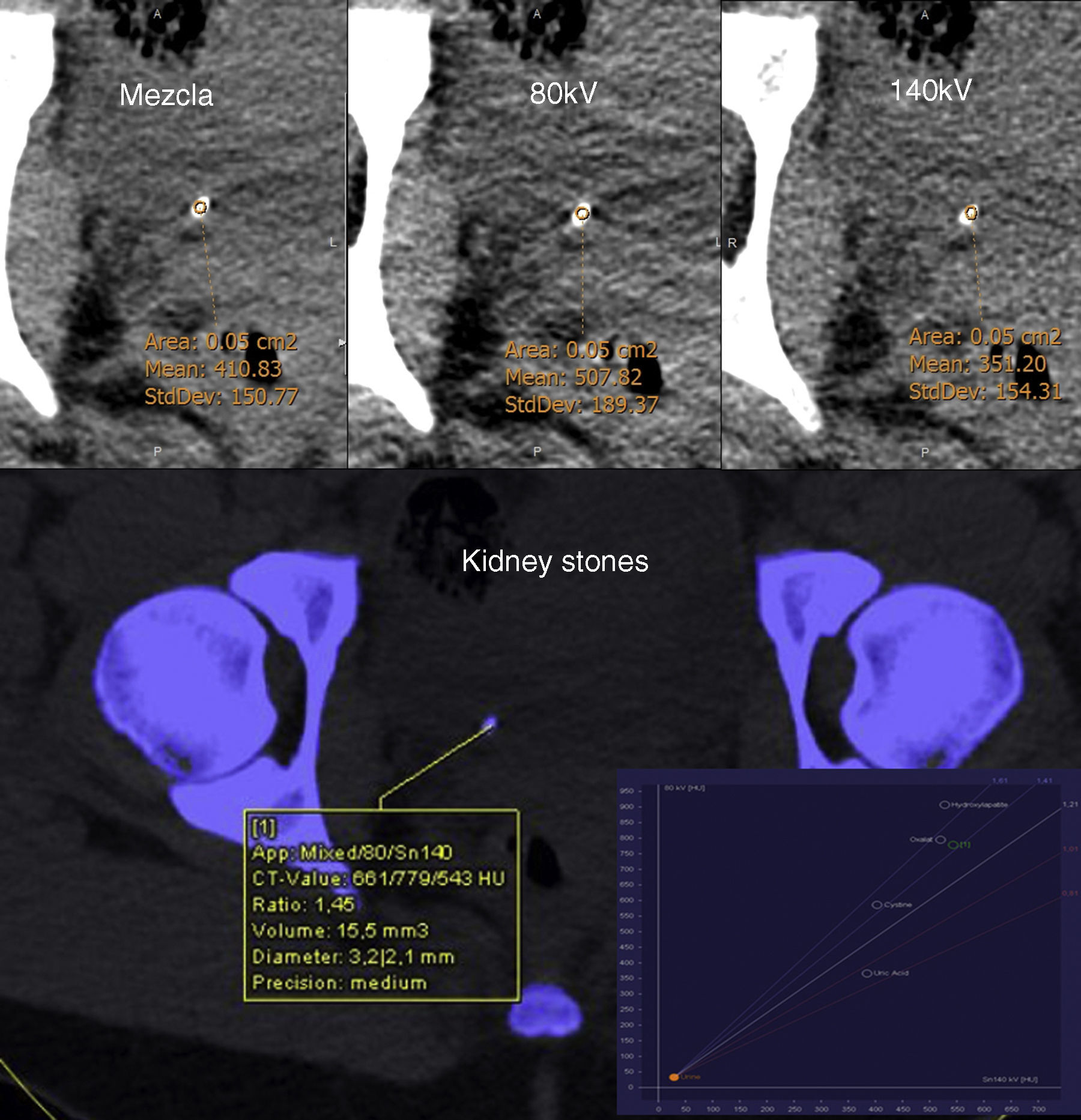
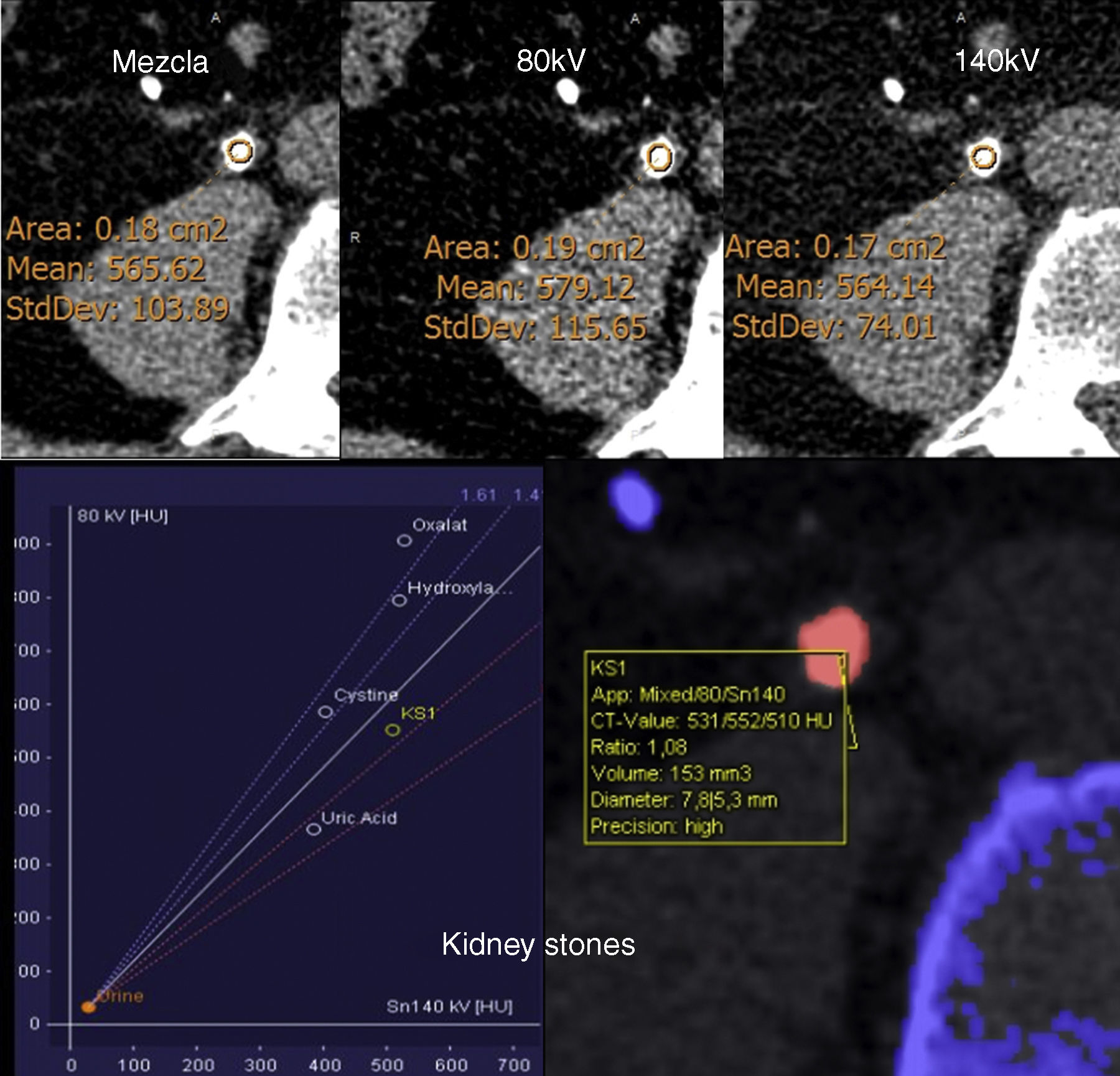
Valorar de manera prospectiva e in vivo la identificación de litiasis renales de ácido úrico con tomografía computarizada (TC) de doble energía (TCDE) con y sin software específico.
Material y métodosSe estudiaron 65 litiasis de 63 pacientes analizadas ex vivo con espectrofotometría y que habían sido estudiadas con una TCDE. Se valoró el rendimiento diagnóstico en identificar litiasis de ácido úrico con TCDE mediante el análisis de las densidades radiológicas de las litiasis utilizando el software específico, o sin utilizarlo (midiéndolo manualmente), y mediante el análisis de las ratios de densidad de las litiasis en ambas energías con o sin el software específico.
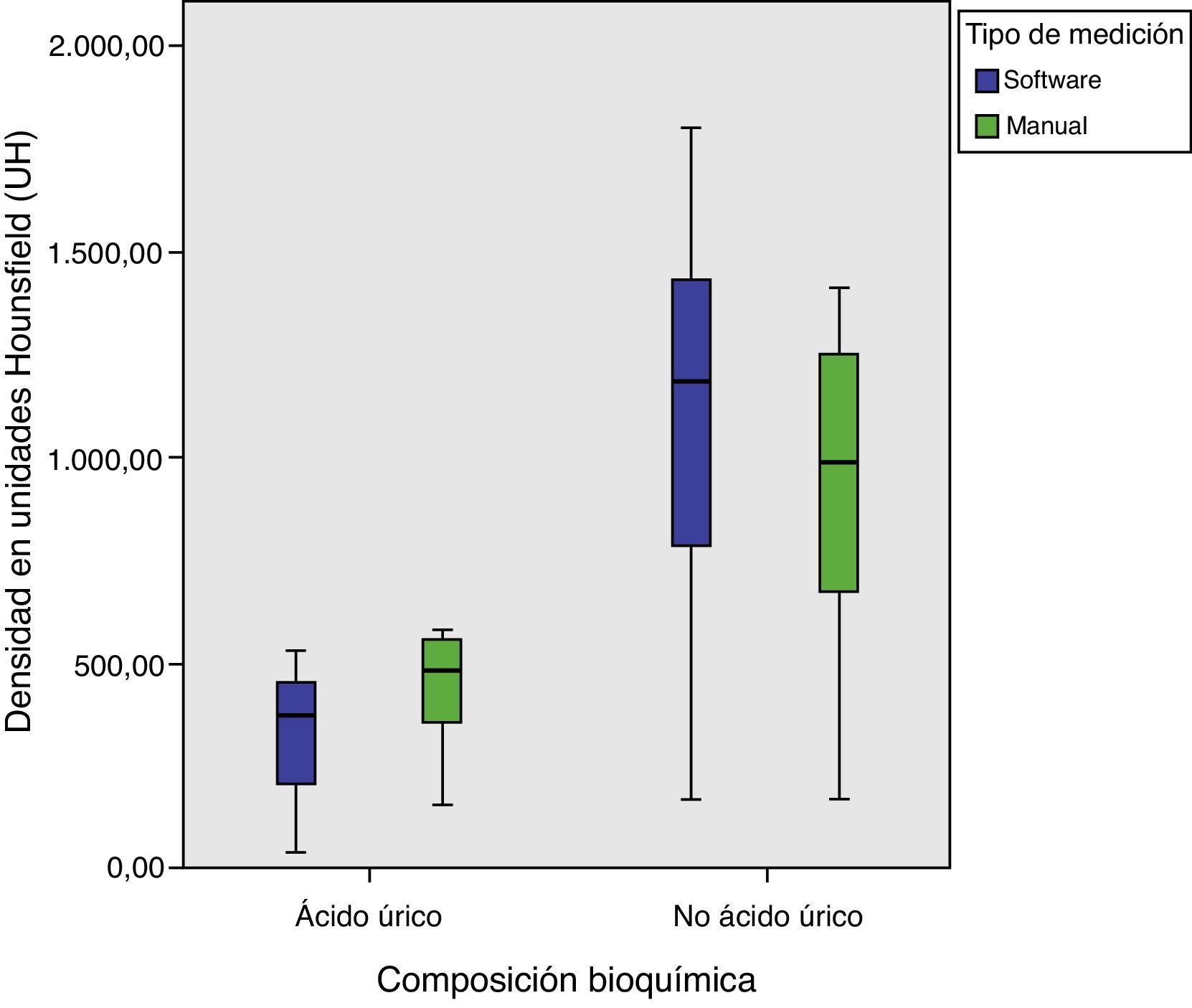
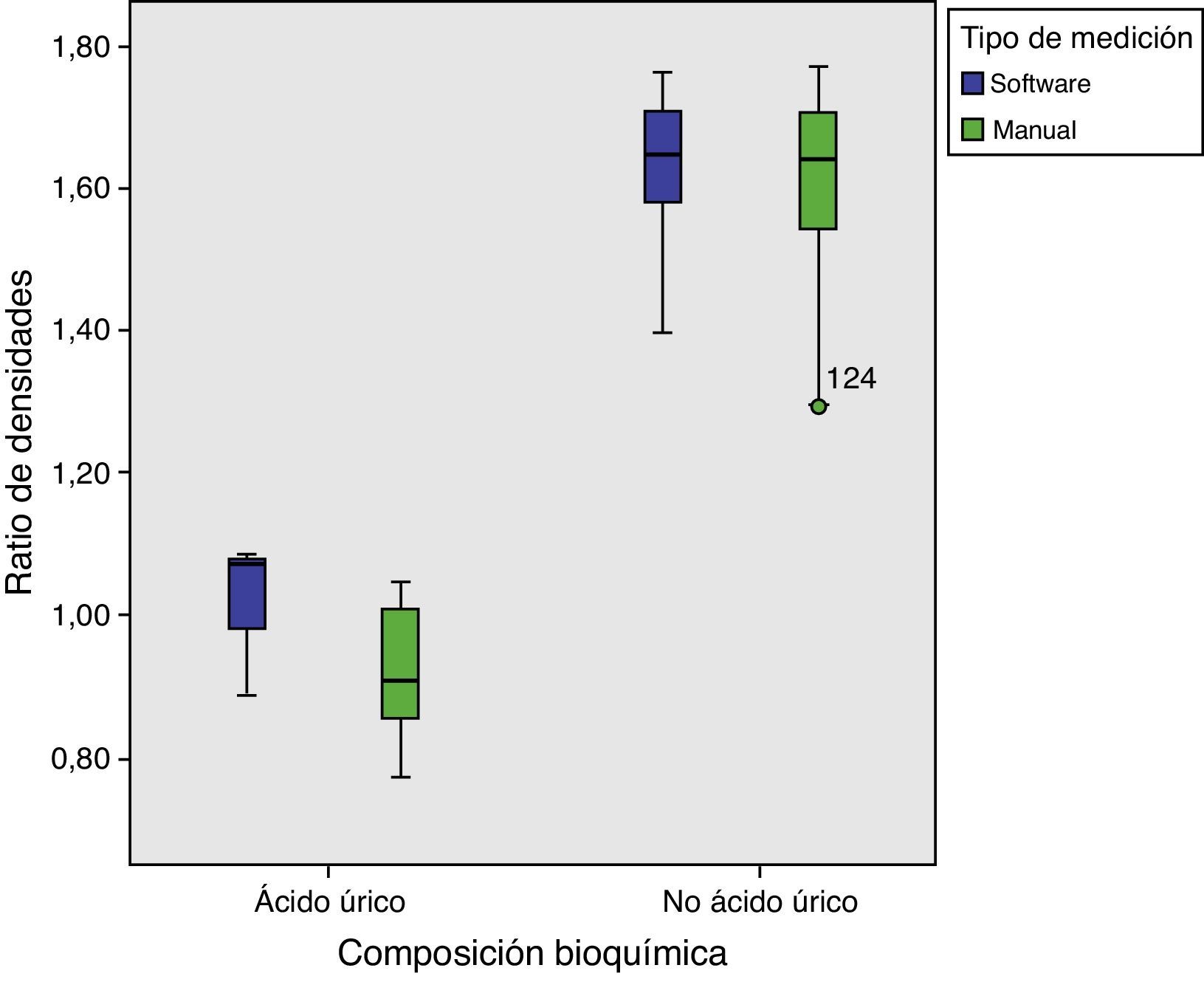
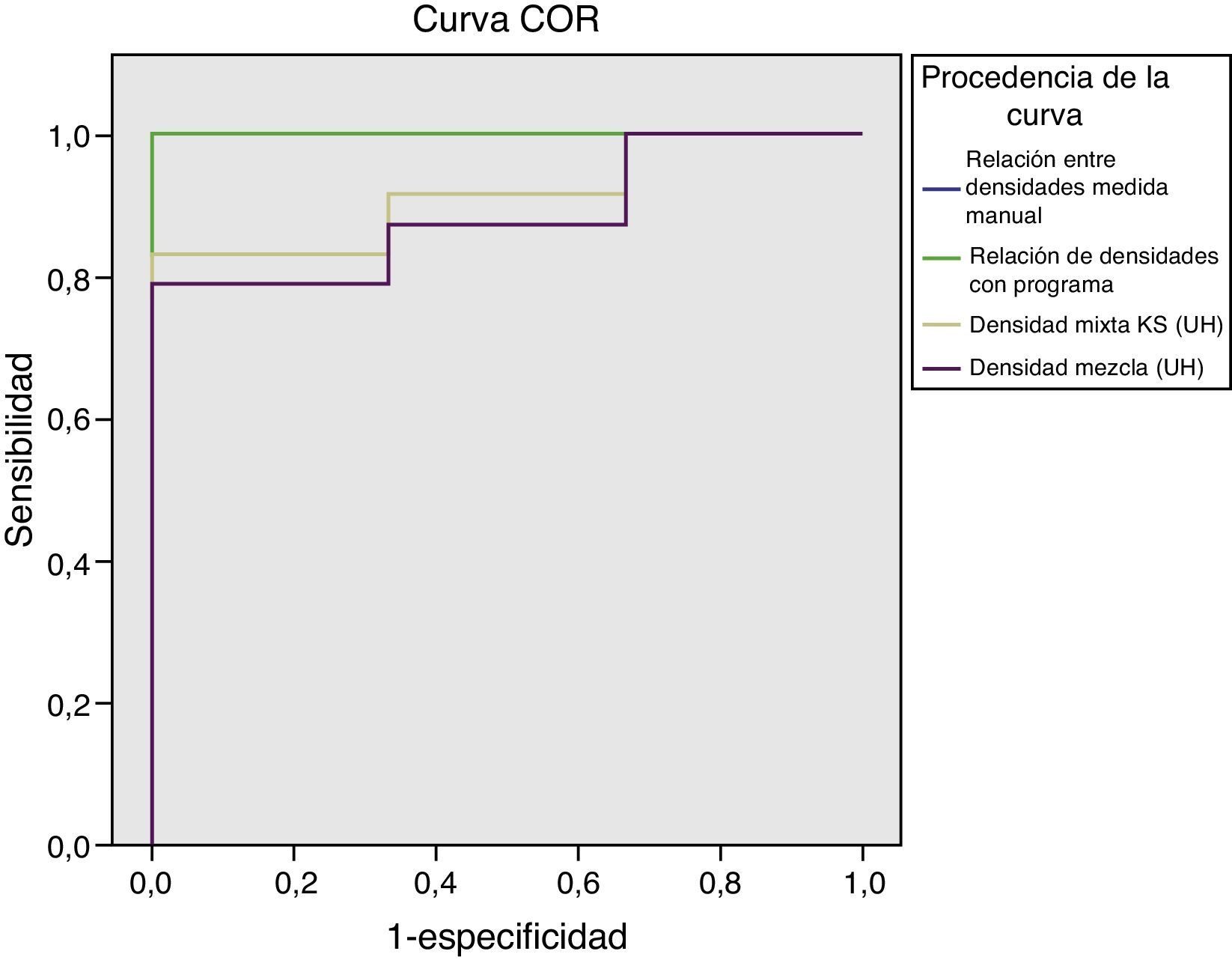
ResultadosLas seis litiasis de ácido úrico incluidas fueron correctamente identificadas mediante la valoración de la ratio de densidades con un punto de corte de 1,21, tanto con el software específico como sin él, con un rendimiento diagnóstico perfecto, sin presencia de falsos positivos ni negativos. El estudio de densidades de las litiasis obtuvo valores de las curvas COR en clasificación de litiasis de ácido úrico de 0,92 para medición con la aplicación informática y de 0,89 para las mediciones manuales y una precisión diagnóstica del 84% (42/50) con el software y del 83,1% (54/65) para las mediciones manuales para un punto de corte de 538 UH.
ConclusionesEl estudio de litiasis con TCDE permite identificar correctamente las litiasis de ácido úrico mediante el cálculo de la ratio de densidades en ambas energías. Los resultados obtenidos con y sin software específico son similares.
To prospectively evaluate the usefulness of dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) with and without dedicated software in identifying uric acid kidney stones in vivo.
Material and methodsWe studied 65 kidney stones in 63 patients. All stones were analyzed in vivo by DECT and ex vivo by spectrophotometry. We evaluated the diagnostic performance in identifying uric acid stones with DECT by analyzing the radiologic densities with dedicated software and without using it (through manual measurements) as well as by analyzing the attenuation ratios of the stones in both energies with and without the dedicated software.
ResultsThe six uric acid stones included were correctly identified by evaluating the attenuation ratios with a cutoff of 1.21, both with the dedicated software and without it, yielding perfect diagnostic performance without false positives or false negatives. The study of the attenuations of the stones obtained the following values on the receiver operating characteristic curves in the classification of the uric acid stones: 0.92 for the measurements done with the software and 0.89 for the manual measurements; a cutoff of 538 HU yielded 84% (42/50) diagnostic accuracy for the software and 83.1% (54/65) for the manual measurements.
ConclusionsDECT enabled the uric acid stones to be identified correctly through the calculation of the ratio of the attenuations in the two energies. The results obtained with the dedicated software were similar to those obtained manually.