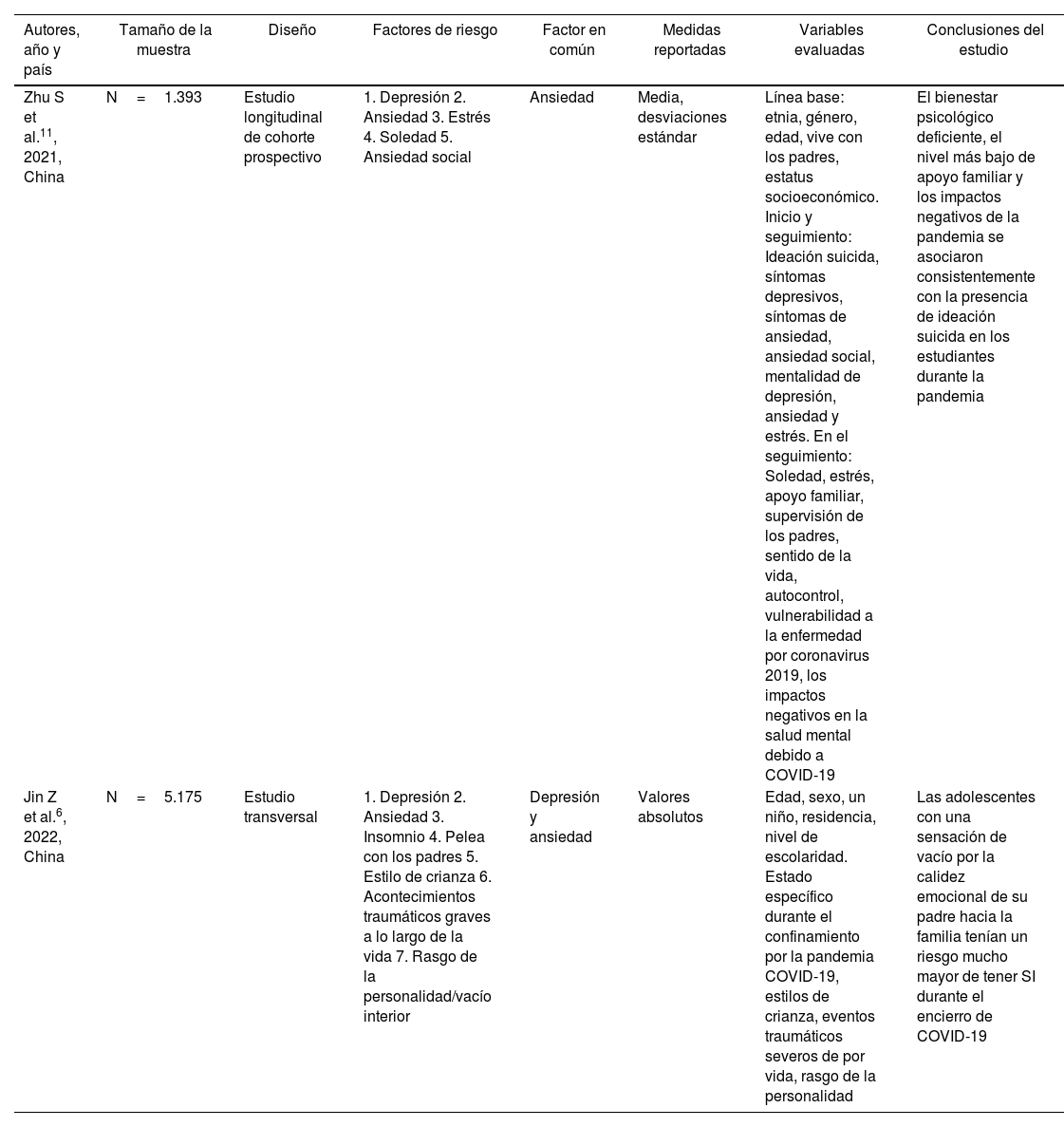
Niños y adolescentes podían presentar mayor riesgo de intento o ideación suicida durante la pandemia COVID-19.
ObjetivoEstablecer los factores de riesgo asociados al intento e ideación suicida en niños y adolescentes durante la pandemia COVID-19.
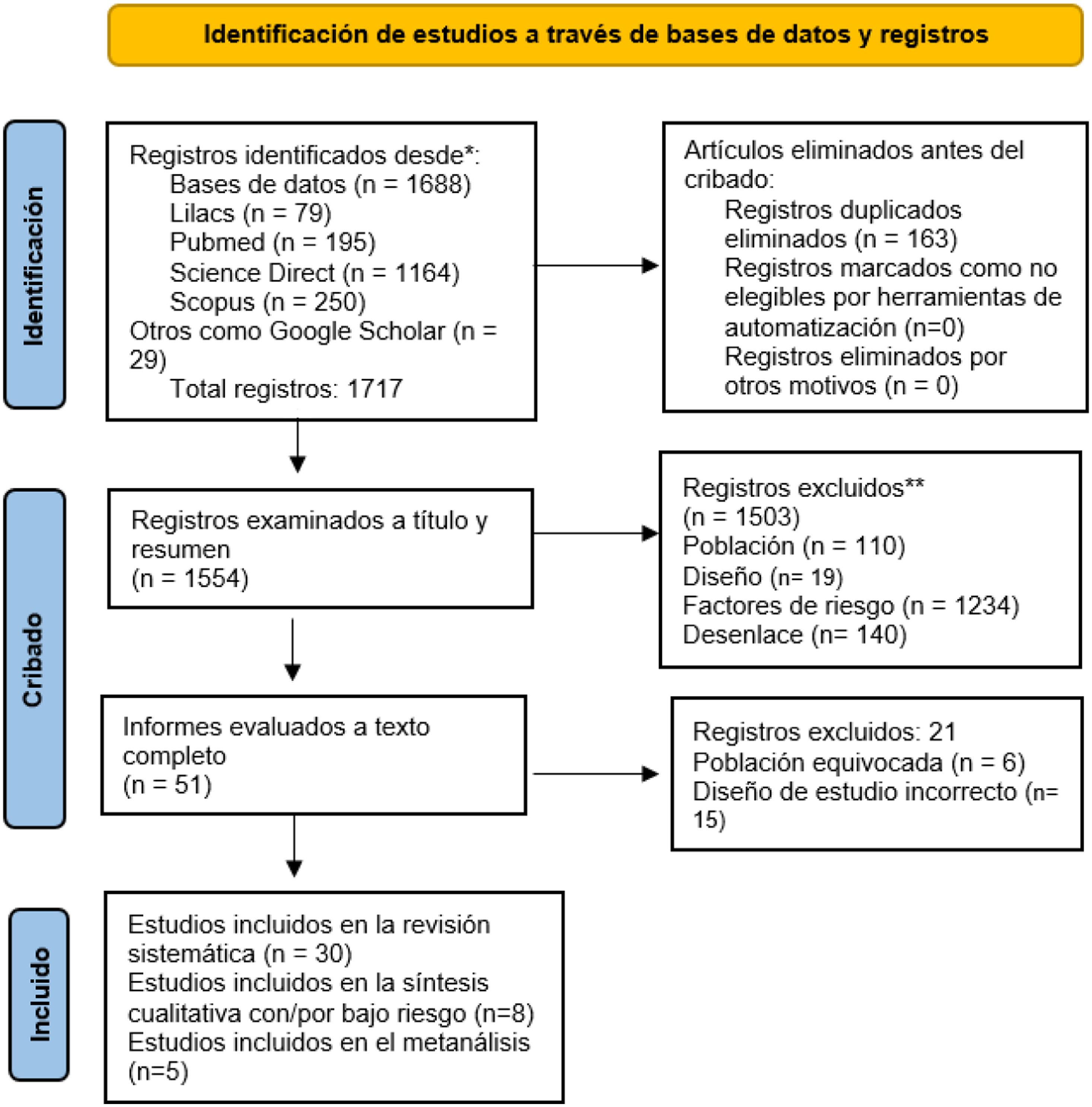
MétodosRevisión sistemática de la literatura y metaanálisis. La búsqueda se hizo en PubMed, LILACS, Science Direct, Scopus y Google Scholar de mayo a agosto de 2022. Se evaluó la calidad con Newcastle-Ottawa y STROBE. El metaanálisis se hizo con el modelo de efectos aleatorios para datos dicotómicos.
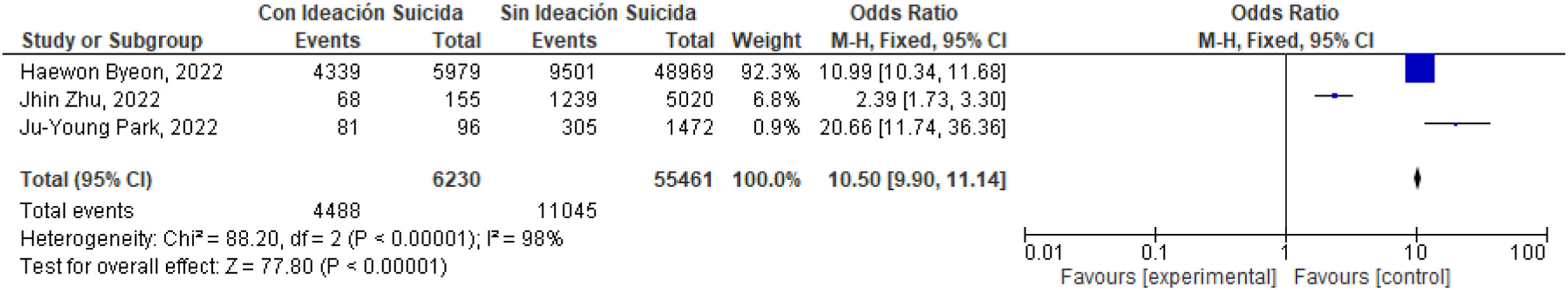
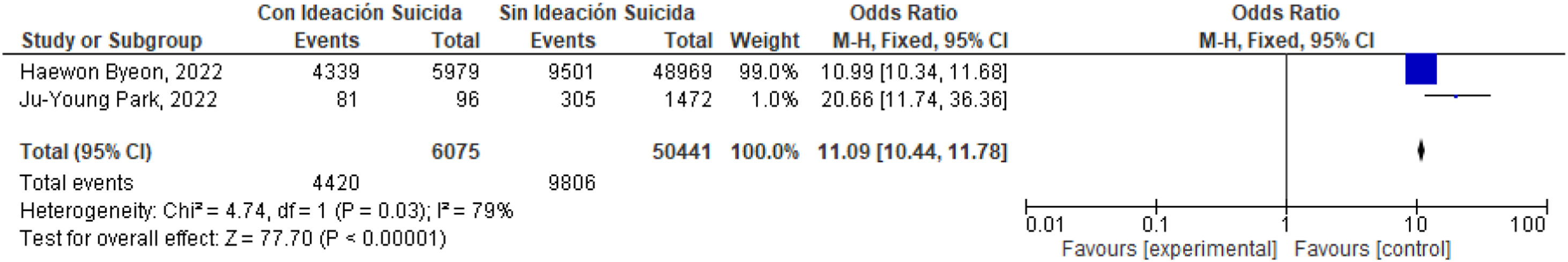
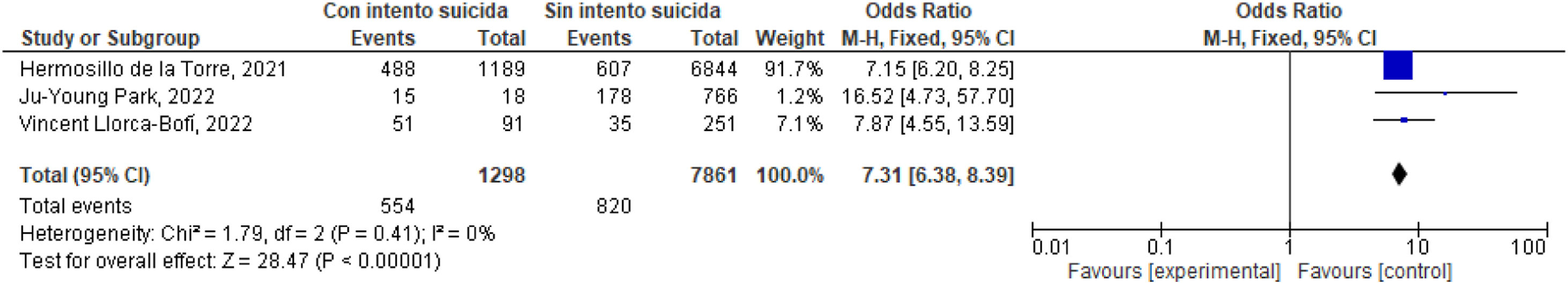
ResultadosSe encontró relación entre depresión e ideación suicida e intento suicida estimador global OR: 10,50 (9,90-11,14); I2=98%; OR: 7,31 (6,38-8,39); I2=0%.
Children and adolescents could be at greater risk of suicidal ideation or attempts during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Objectiveestablish risk factors associated with suicidal attempt and ideation in children and adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic.
MethodsSystematic literature review and meta-analysis. The search was conducted in PubMed, LILACS, Science Direct, Scopus and Google Scholar from May to August 2022. Quality was assessed with Newcastle-Ottawa and STROBE. The meta-analysis was done with the random effects model for dichotomous data.
ResultsA relationship was found between depression and suicidal ideation and suicide attempt: Global estimator OR: 10.50 (9.90-11.14); I2=98%; OR: 7.31 (6.38-8.39); I2=0%.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora