To test a software application for the quantification of metabolic heterogeneity and to evaluate its superiority in relation to visual interpretation. To investigate if a quantitative analysis adds information to the interpretation of 18F-FDG-PET/CT.
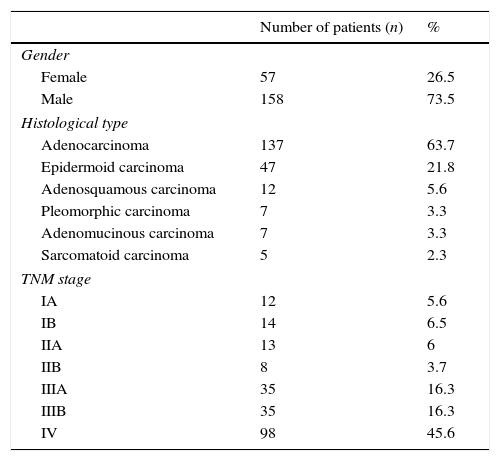
Material and methodsThe study analyzed 215 patients with a 18F-FDG-PET/CT done for the initial staging of lung cancer between March 2011 and December 2015. The study included 57 (26.5%) women and 158 (73.5%) men, with ages ranging from 34 to 88 years (mean±SD: 67.23±10.04). There were 82 surgical stages (I, II, IIIA), and 133 non-surgical stages (IIIB, IV). The primary tumour was analyzed quantitatively by obtaining the following parameters: SUVmax, metabolic active tumour volume (MATV), total lesion glycolysis (TLG), and the entropy heterogeneity index (ET). Heterogeneity was assessed visually. Death dates and/or the follow-up time were registered, ranging from 0.70 to 67.60 months (mean±SD: 23.20±17.68).
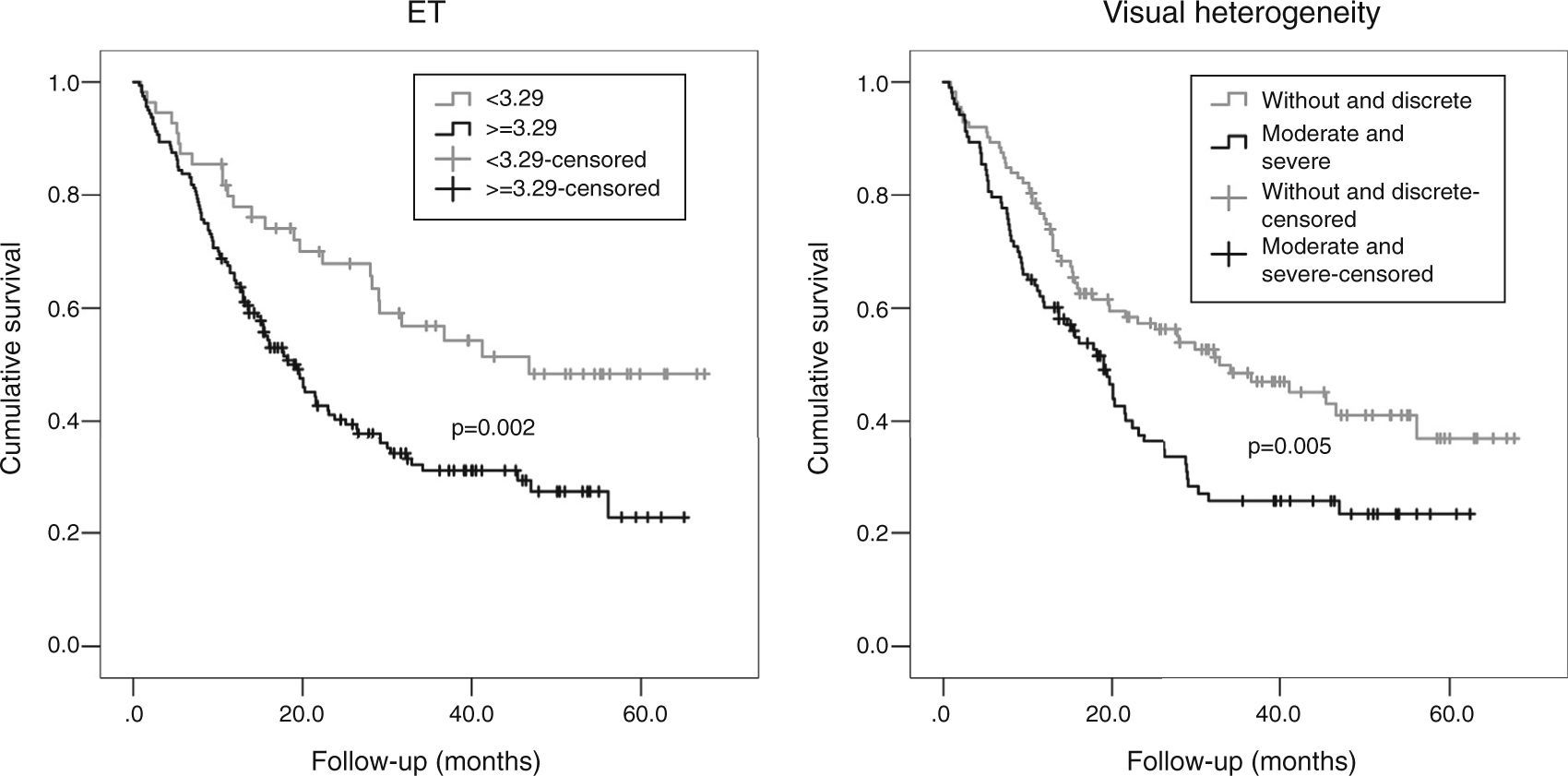
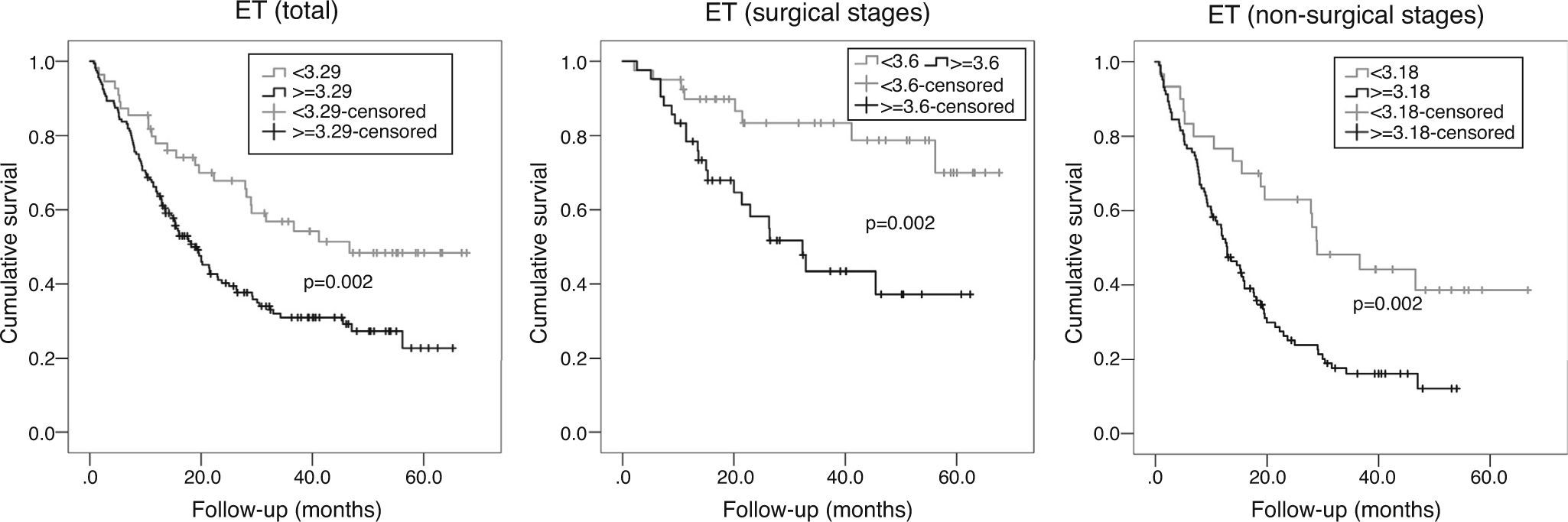
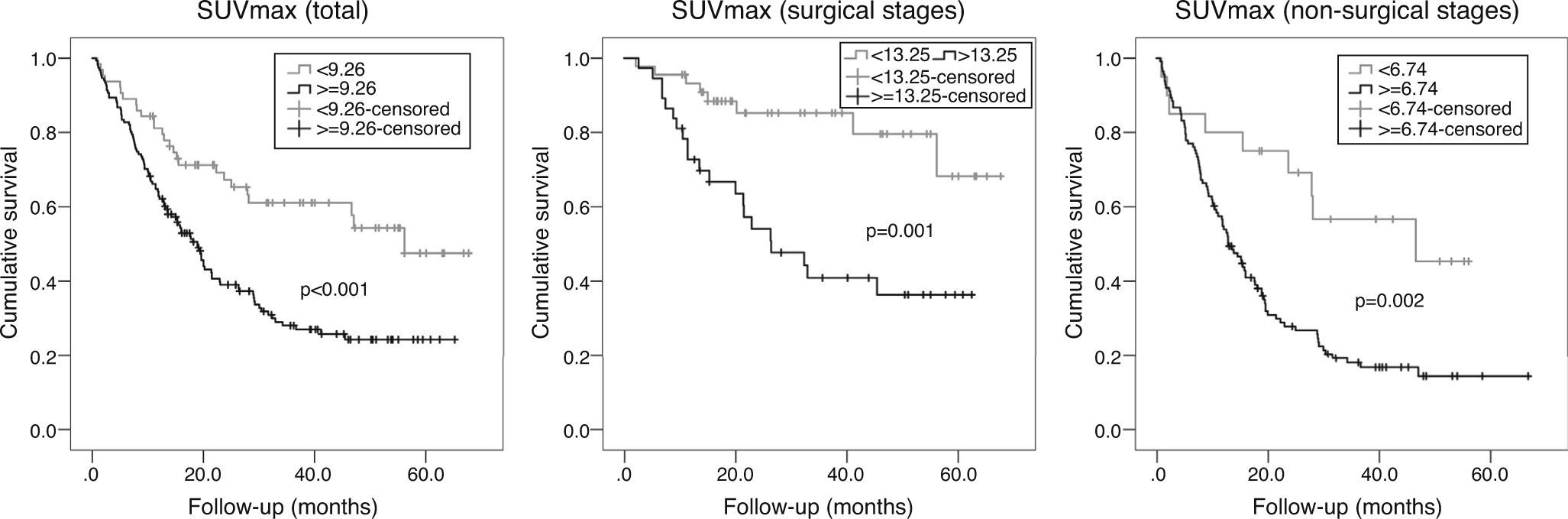
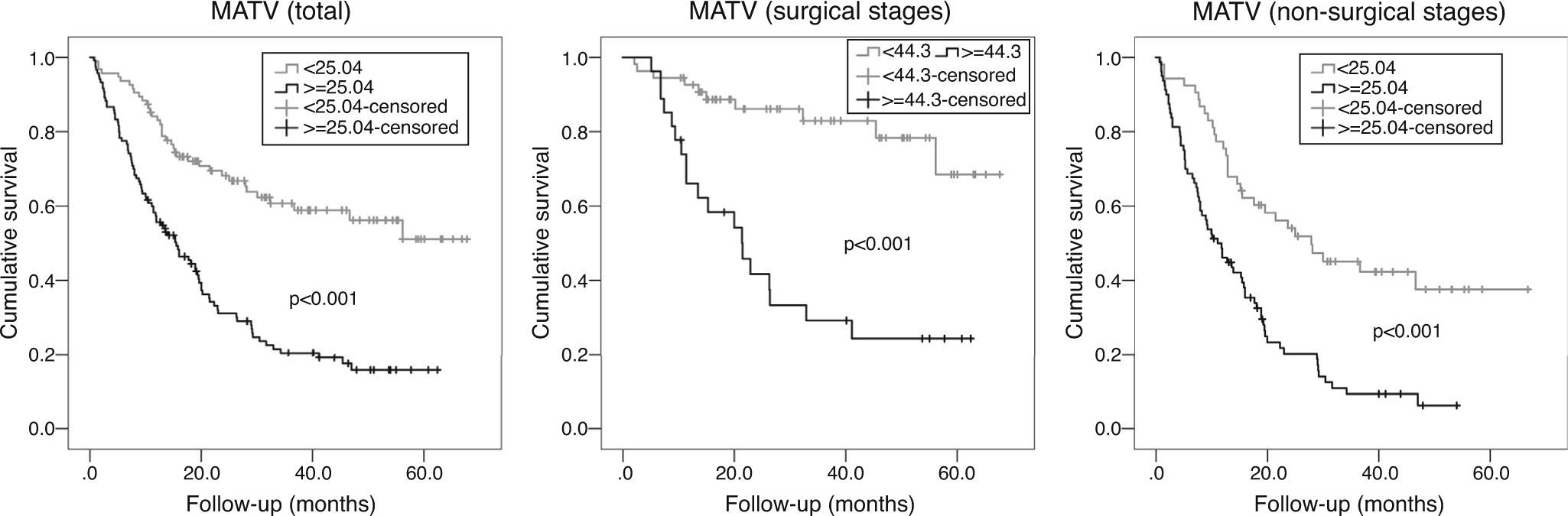
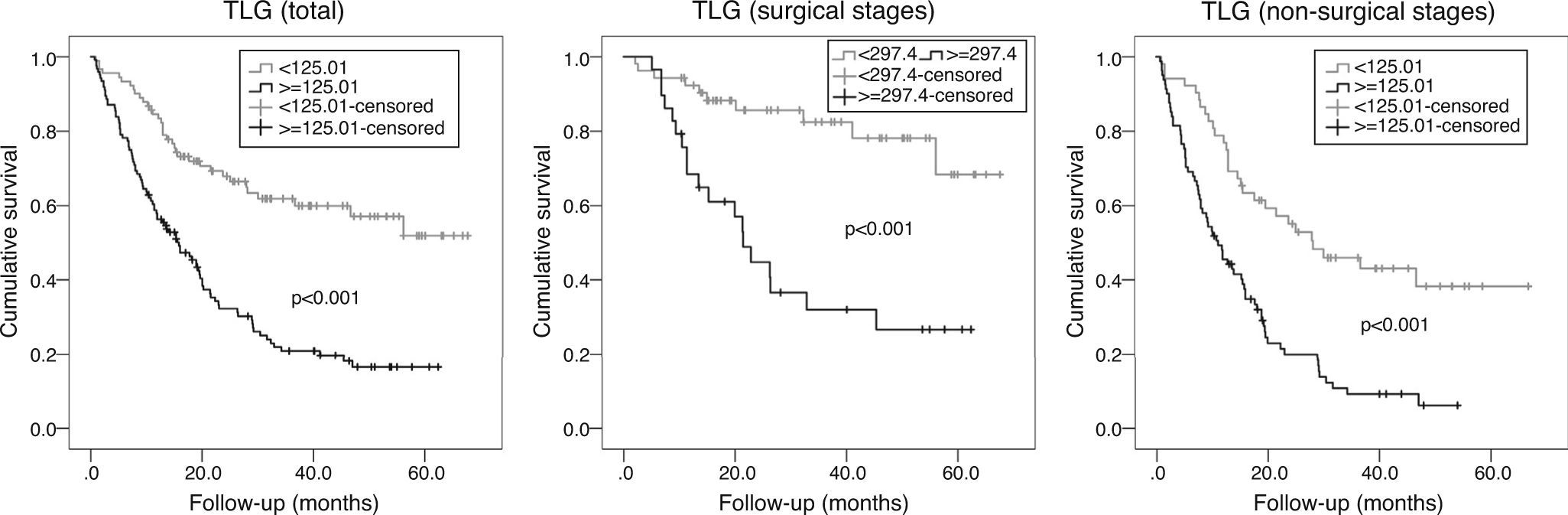
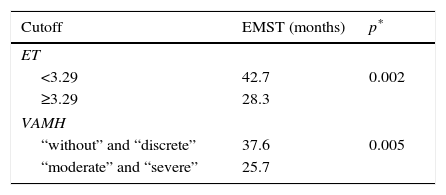
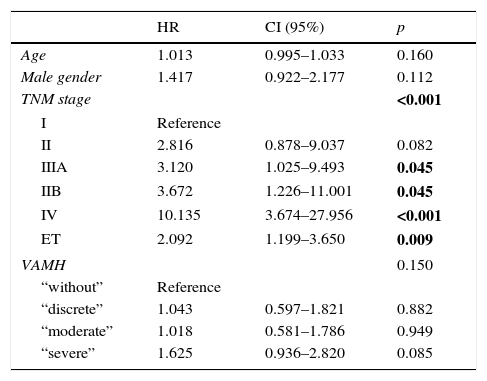
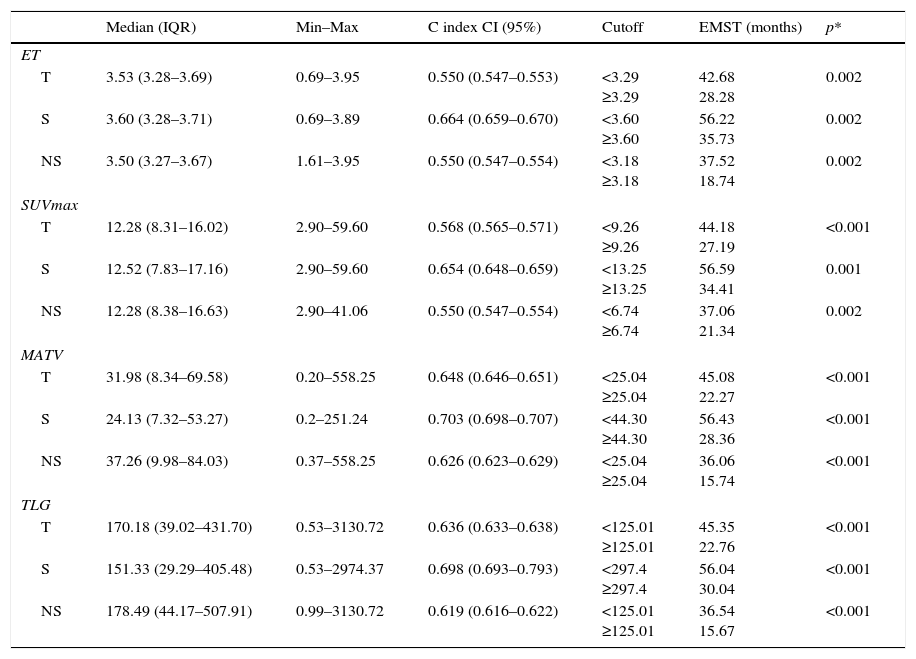
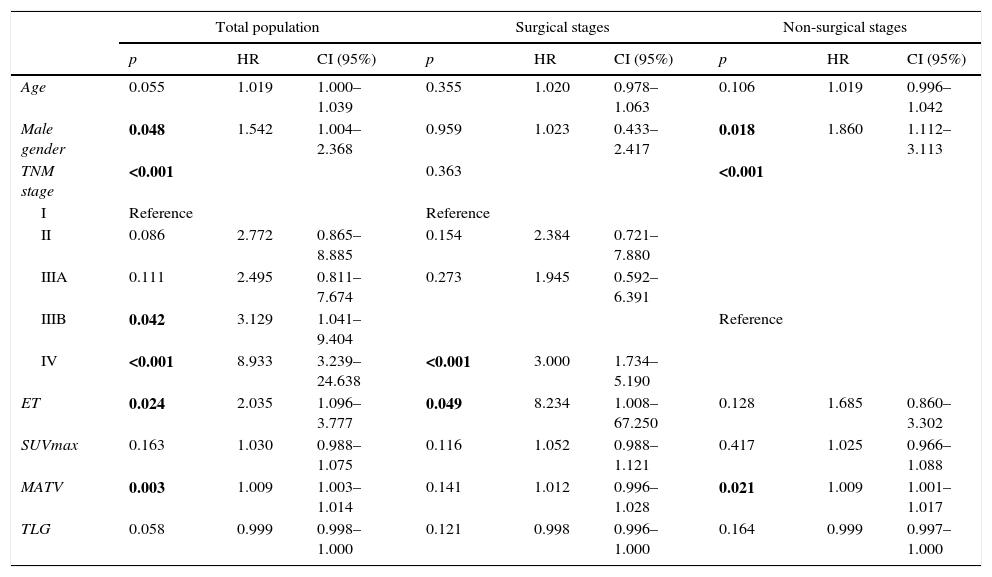
ResultsIn multivariate analysis, ET emerged as a better predictor of survival than visual analysis of heterogeneity that was not statistically significant. The C-index determination demonstrated that all quantitative parameters were statistically-significant predictors of survival. Cut-offs were obtained in order to compare survival times. A multivariate analysis was performed. In the total population, the best predictor was the TNM stage, but MATV, ET, and male gender were statistically significant and independent predictors of survival. In stages without surgical indication, the best predictor was the TNM stage, but the MATV and male gender were statistically significant and independent predictors of survival. In the surgical stages, ET was the only statistically significant and independent predictor of survival.
ConclusionsQuantification adds prognostic information to the visual analysis of 18F-FDG-PET/CT.
Valorar un software para cuantificar la heterogeneidad metabólica e investigar su superioridad en relación con la interpretación visual. Analizar si el análisis cuantitativo ofrece información adicional en la interpretación de los estudios 18F-FDG-PET/TC.
Material y métodosSe valoraron retrospectivamente 215 estudios 18F-FDG-PET/TC para estatificación inicial de cáncer de pulmón entre marzo de 2011 y diciembre de 2015; se incluyeron 57(26,5%) mujeres y 158(73,5%) hombres, con edades de 34 a 88 años (media±DE: 67,23±10,04); hubo 82 estadios quirúrgicos (I, II, IIIA) y 133 no quirúrgicos (IIIB, IV). El tumor primario fue analizado obteniendo los parámetros SUVmax, metabolic active tumour volume (MATV), total lesion glycolisys (TLG) y el índice de heterogeneidad entropía (ET). La heterogeneidad fue valorada visualmente. Se registró la fecha de fallecimiento y/o el tiempo de seguimiento, que osciló entre 0,70 y 67,60 meses (media±DE: 23,20±17,68).
ResultadosEn el análisis multivariante, la ET se mostró mejor predictor de supervivencia que el análisis visual de heterogeneidad, el cual no fue estadísticamente significativo. La determinación del C-index demostró que todos los parámetros cuantitativos fueron predictores de supervivencia estadísticamente significativos. Se obtuvieron puntos de corte para comparar los tiempos de supervivencia. En el análisis multivariante, el mejor predictor fue el TNM, pero el MATV, el ET y el género masculino demostraron ser predictores de supervivencia independientes estadísticamente significativos. En los estadios no quirúrgicos, el mejor predictor fue el TNM, pero el MATV y el género masculino demostraron ser predictores de supervivencia estadísticamente significativos e independientes. En los estadios quirúrgicos, la ET fue el único predictor de supervivencia estadísticamente significativo e independiente.
ConclusionesLa cuantificación ofrece información pronóstica adicional al análisis visual del 18F-FDG-PET/TC.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora