Our aim is to evaluate if different metabolic parameters obtained by 18F-FDG PET/CT and diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) can aid in neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy (RCT) response assessment in locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) patients.
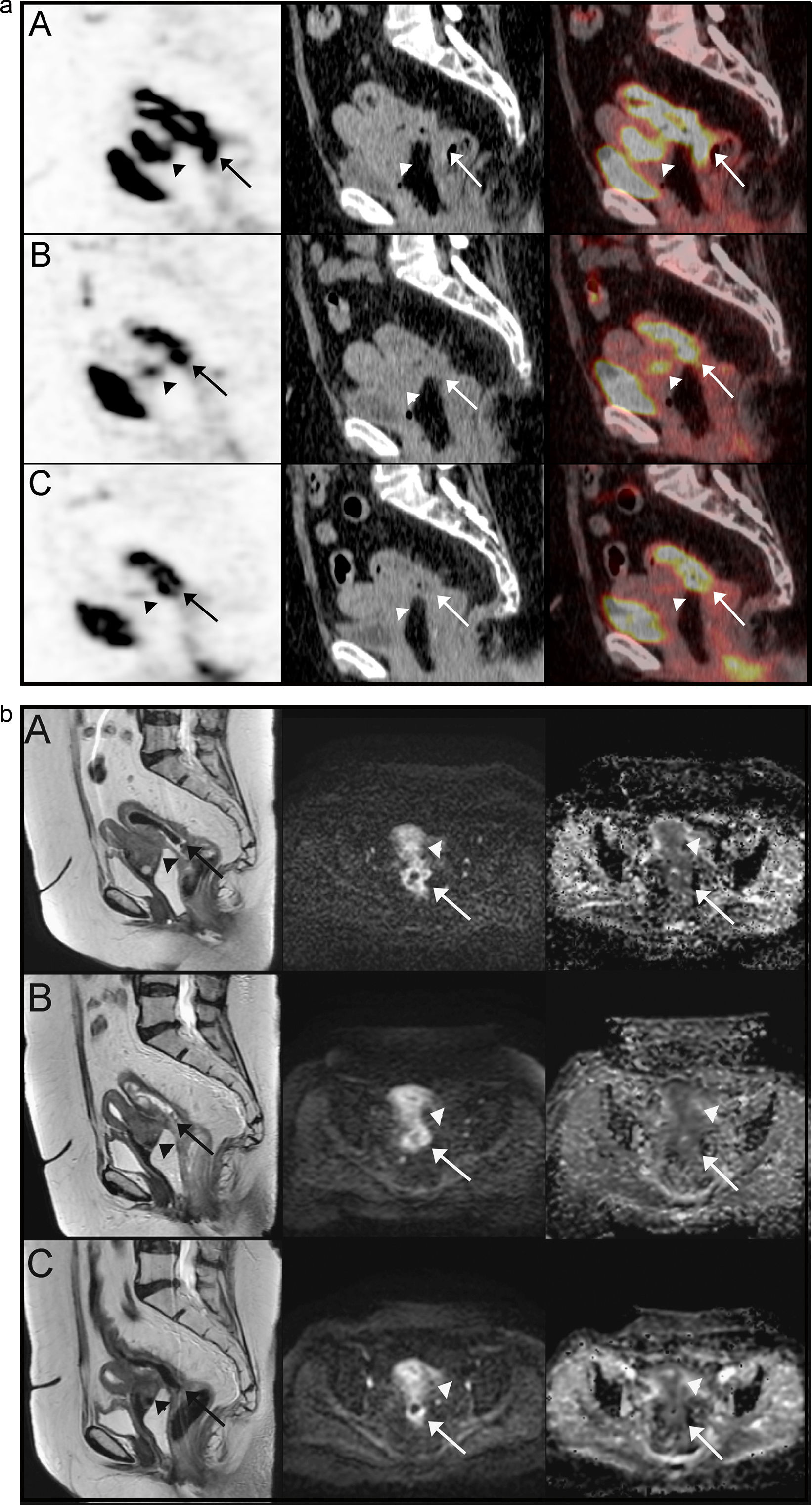
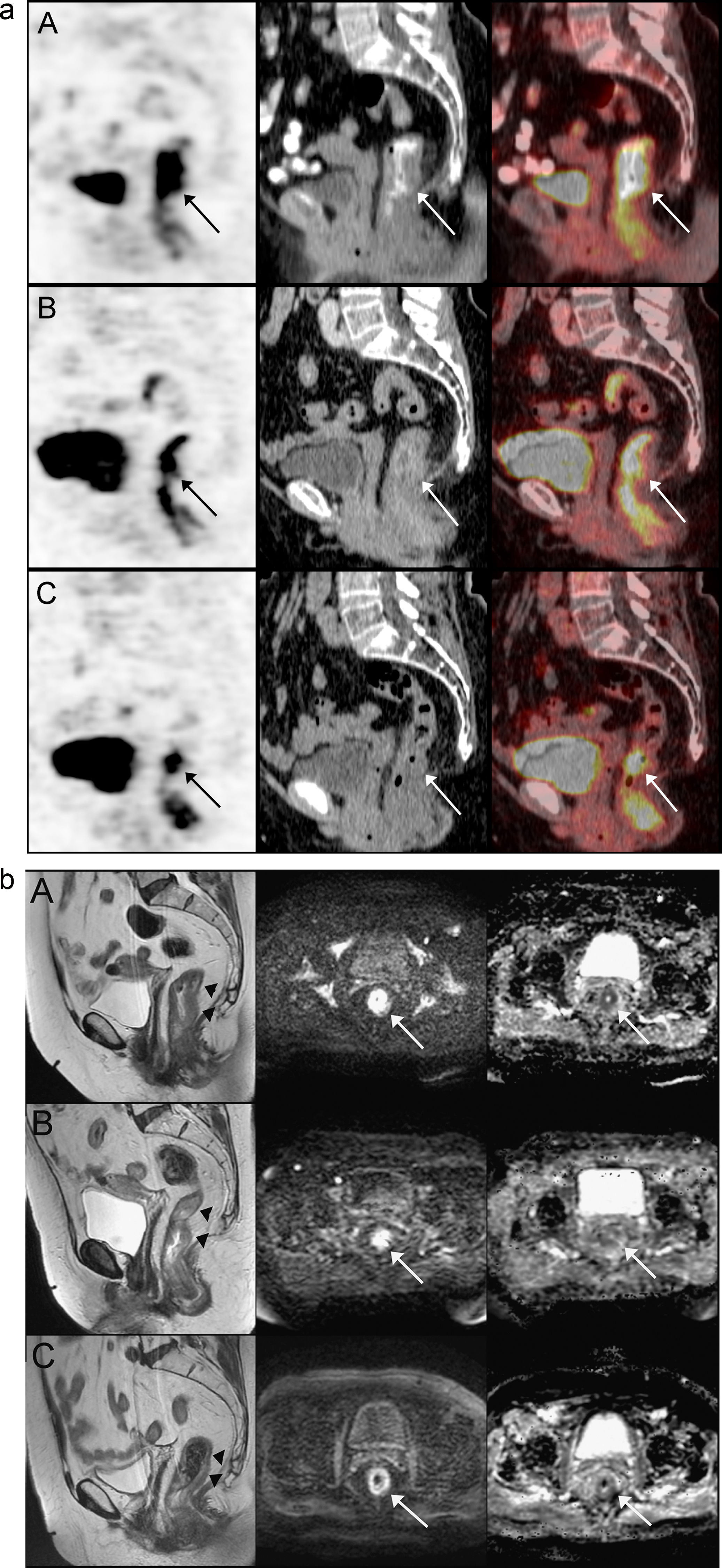
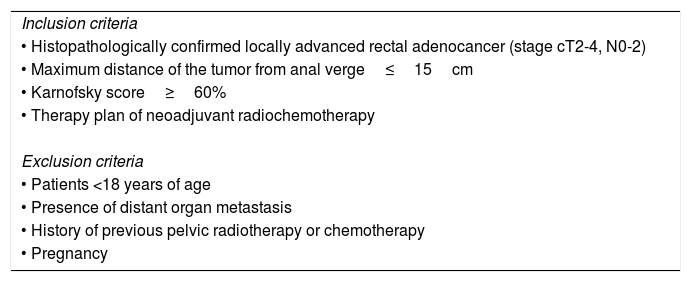
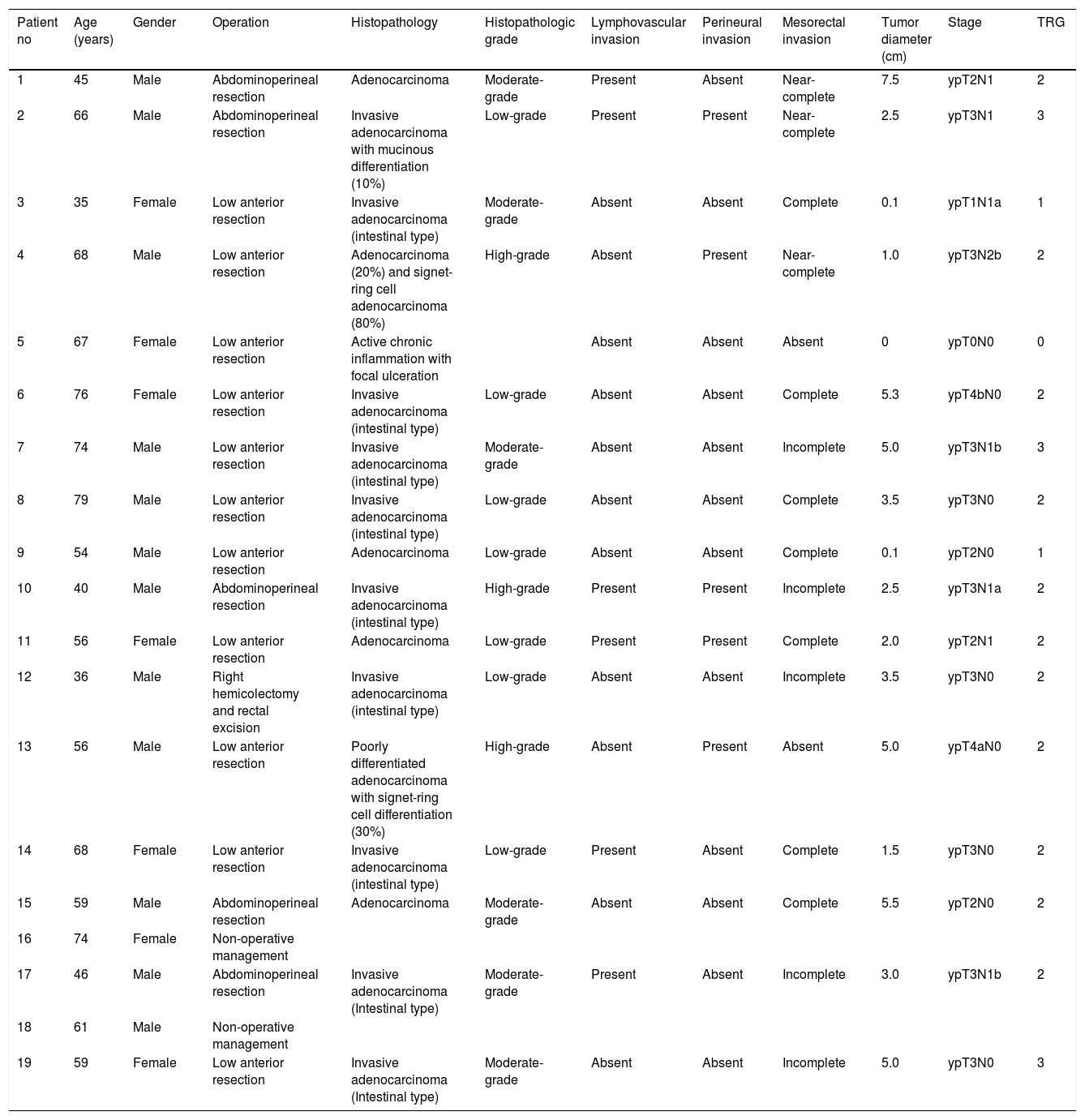
MethodsOut of 20 LARC patients, who were planned to receive neoadjuvant RCT, 19 were included in this prospective study. Patients had 18F-FDG PET/CT and DW-MRI at initial staging, interim (2 weeks after onset of RCT) and after completion of RCT (post-therapy). Standardized uptake value (SUV) parameters (SUVmax, SUVmean, SUVpeak, SULpeak), metabolic tumor volume (MTV) and tumor lesion glycolysis (TLG) detected on PET images and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values (for b=400 and b=1000s/mm2) obtained from DW-MRI were recorded. Postoperative tumor regression grade (TRG) was used as gold-standard, except for 2 patients who were under complete remission with non-operative management 19 months post-therapy and scored as responders.
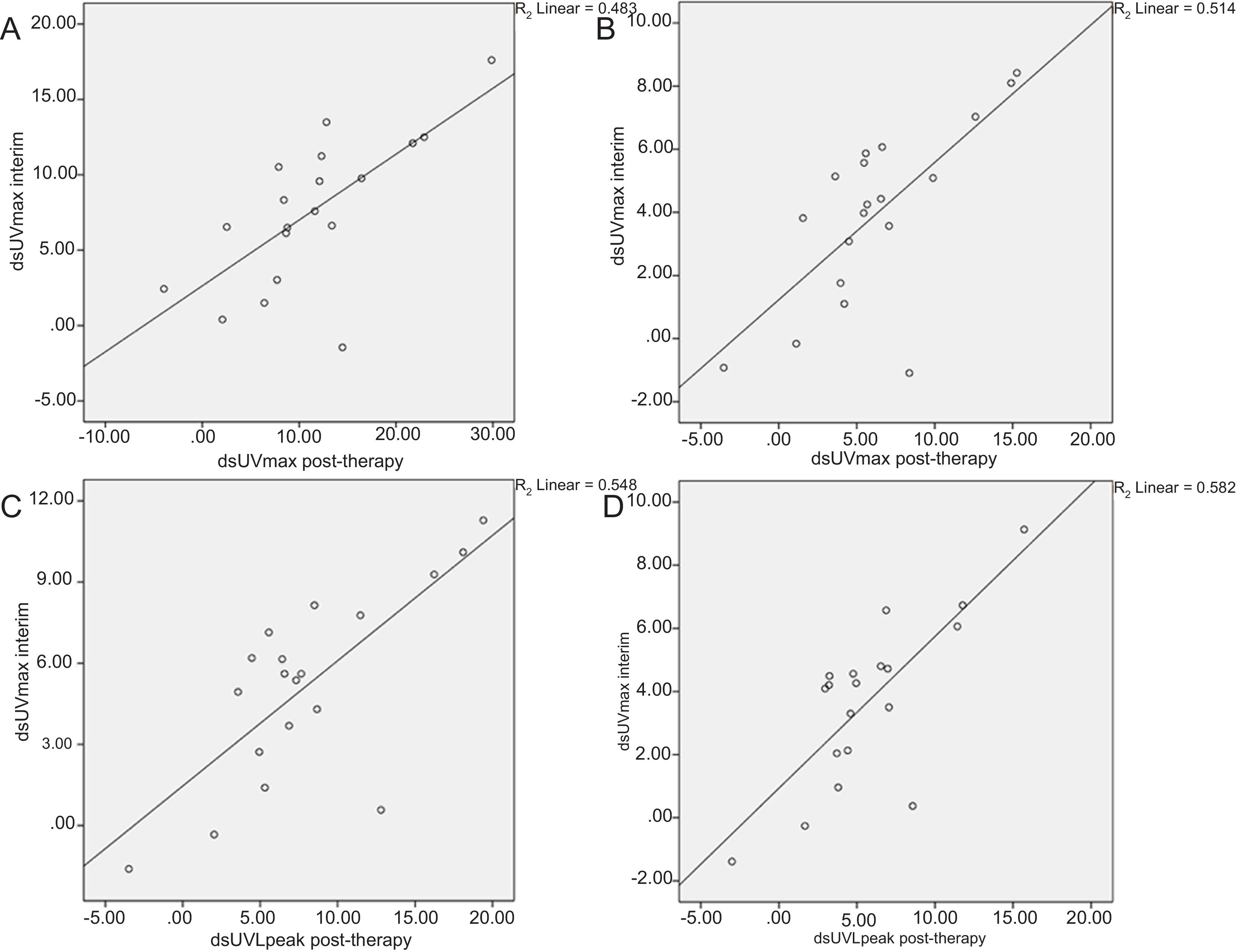
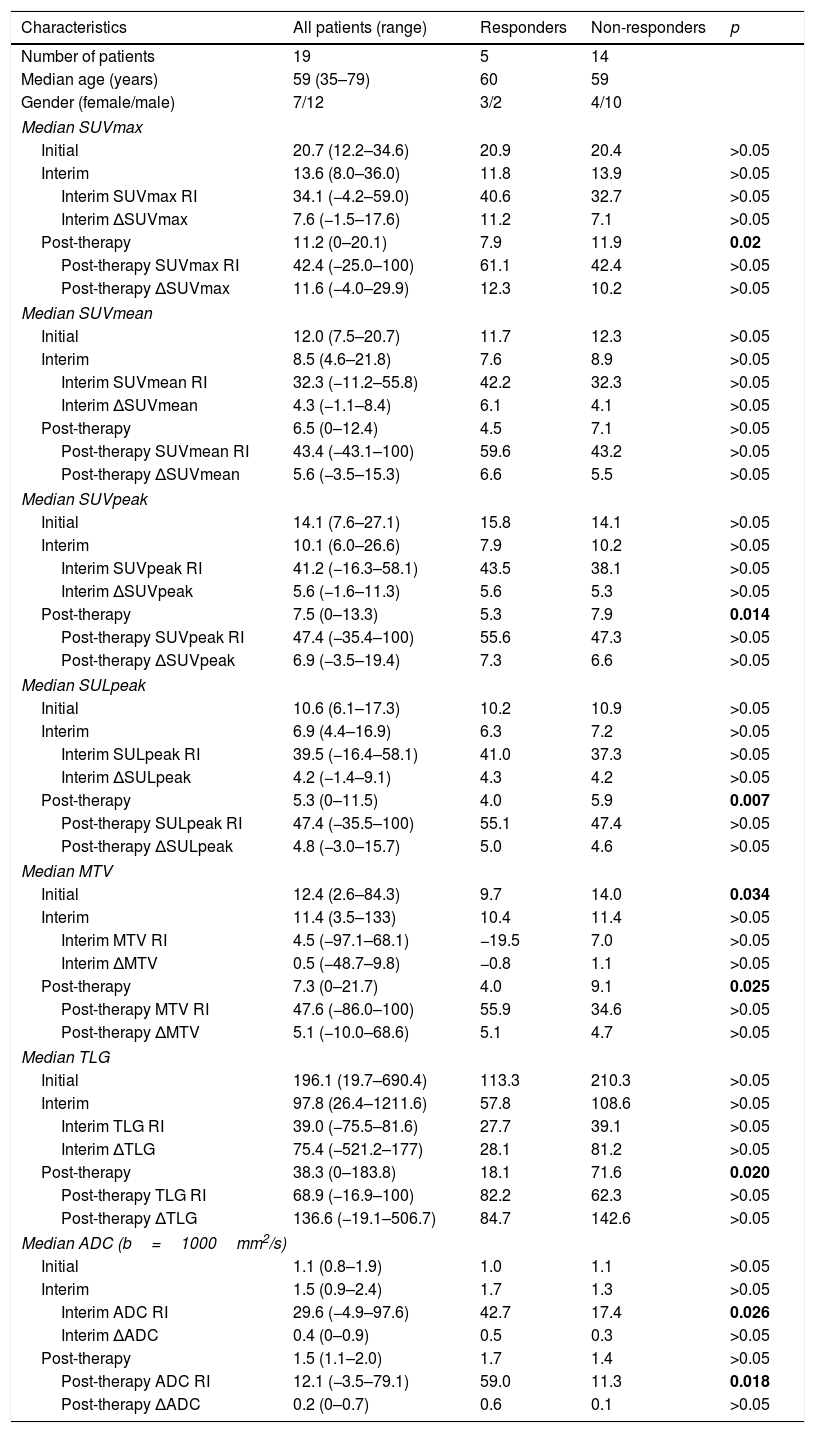
ResultsOn interim PET/CT, no significant difference was found among PET parameters between responders and non-responders, whereas post-therapy SUVmax, SUVpeak, MTV, SULpeak, TLG (p=0.02, p=0.014, p=0.025, p=0.007, p=0.02, respectively) and initial MTV (p=0.034) were significantly lower in responders. ADC response index (RI) was higher in responders (interim p=0.026; post-therapy: p=0.018) and ROC analysis revealed that a threshold of ADC RI>41.6% for interim MRI and >44.6% for post-therapy MRI had sensitivity and specificity of 75.0% and 90.9%, respectively.
ConclusionsWhile interim 18F-FDG PET/CT failed to predict therapy response during RCT, post-therapy PET could accurately differentiate responders. DW-MRI was found to be more promising in interim detection of RCT response.
El objetivo fue evaluar si diferentes parámetros metabólicos obtenidos con PET-TC 18F-FDG y la RM con técnica de difusión (DW-RM), pueden ayudar a evaluar la respuesta a la radioquimioterapia neoadyuvante en pacientes con cáncer de recto localmente avanzado.
MétodosDe 20 pacientes con cáncer rectal localmente avanzado que se planificaron para recibir radioquimioterapia neoadyuvante, 19 fueron incluidos en este estudio prospectivo. Se les realizó PET-TC 18F-FDG y RM de difusión en la estadificación inicial, interim PET (a las dos semanas de inicio de tratamiento) y al finalizar el tratamiento (post-tratamiento). Se calcularon valores de Standardized Uptake Value (SUVmax, SUVmean, SULpeak, volumen tumoral metabólico (MTV) y tasa de glicólisis (TLG) y valores de coeficiente de difusión aparente (ADC) obtenidos de la RM (para b=400 y para b=1000s/mm2). El grado de regresión tumoral tras la cirugía fue el patrón oro, excepto para dos pacientes que alcanzaron la remisión completa con manejo no operatorio, tras 19 meses de tratamiento y se consideraron respondedores.
ResultadosEn interim PET-TC no se encontraron diferencias significativas en los parámetros de PET entre respondedores y no respondedores, mientras que en el PET post-tratamiento, el SUVmax, SUVpeak, MTV, SULpeak, TLG (p=0.02, p=0.014, p=0.025, p=0.007, p=0.02, respectivamente) y MTV inicial (p=0.034) fueron significativamente inferiores en los respondedores. El índice de respuesta ADC fue mayor en los respondedores (interim p=0.026, post-tratamiento p=0.018) y el análisis de curvas ROC mostró que un valor umbral de ADC RI>41.6% para interim RM y >44.6% para la RM post-tratamiento, presentaban una sensibilidad y especificidad del 75 y 90.9%, respectivamente.
ConclusionesSi bien el interim PET-TC 18F-FDG no logra predecir la respuesta al tratamiento durante la quimiorradioterapia, el PET post-tratamiento podría diferenciar adecuadamente a los respondedores. La RM de difusión parece más prometedora en la respuesta precoz al tratamiento.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora