To investigate the association between positive lesions detected by 99mTc-PSMA SPECT/CT and blood levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in patients with prostate cancer (PCa) and bone metastasis undergoing endocrine therapy.
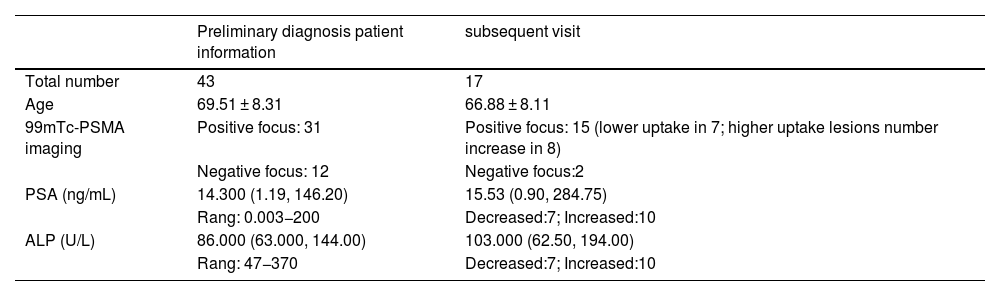
MethodsA retrospective analysis was performed on 43 patients diagnosed with PCa bone metastasis who underwent endocrine therapy. PSA, ALP, whole body bone imaging and 99mTc-PSMA SPECT/CT imaging were collected from all patients (Among them, 17 cases were re-examined 99mTc-PSMA SPECT/CT imaging). According to the results of the first 99mTc-PSMA SPECT/CT imaging for detecting bone metastasis, all cases were divided into two groups: positive group and negative group. The relationship between 99mTc-PSMA imaging and PSA and ALP was analyzed by ROC curve. Fisher exact probability method was used to examine the changes in imaging radioactivity uptake, PSA, and ALP levels in 17 patients after treatment, and P < 0.05 was statistically significant.
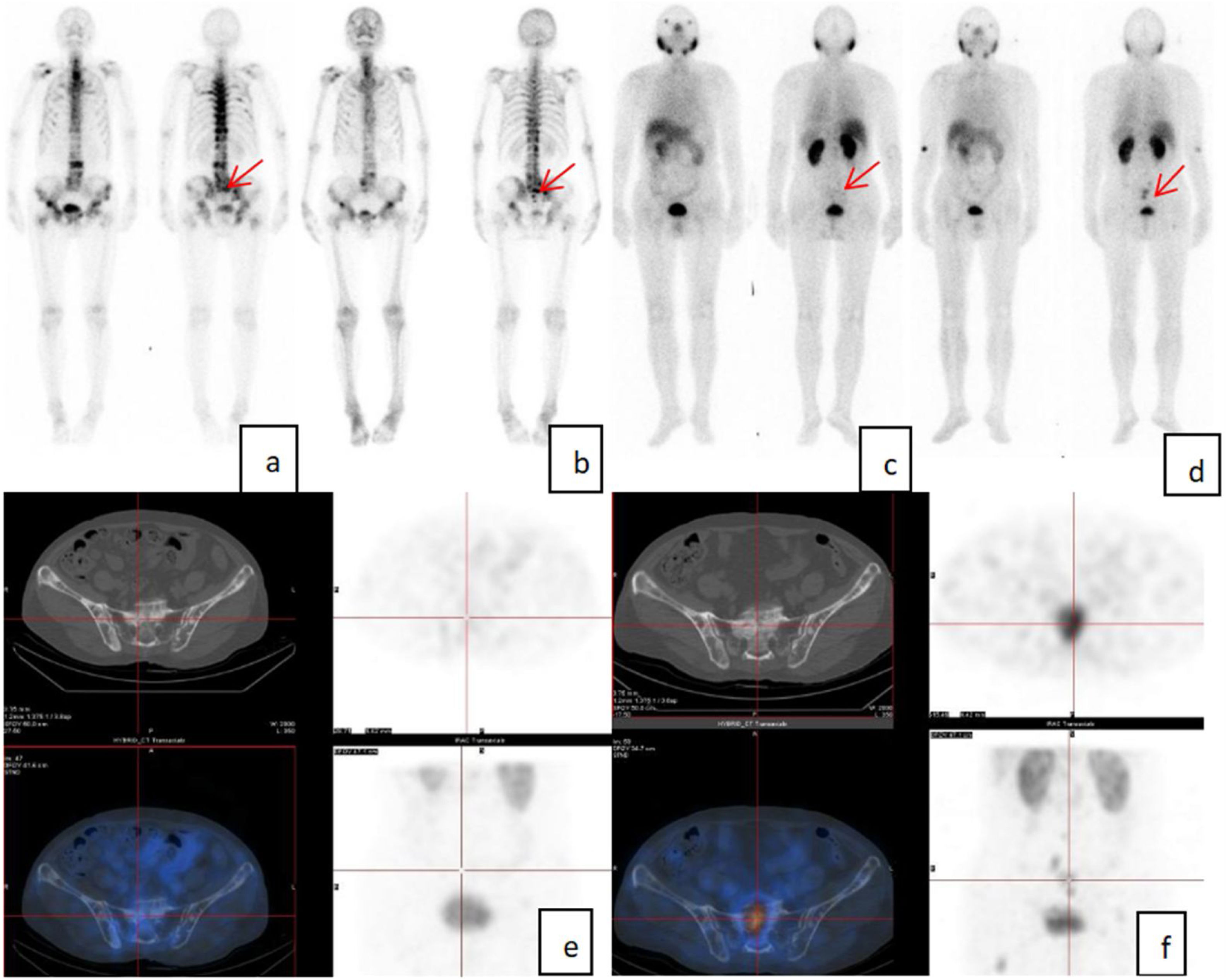
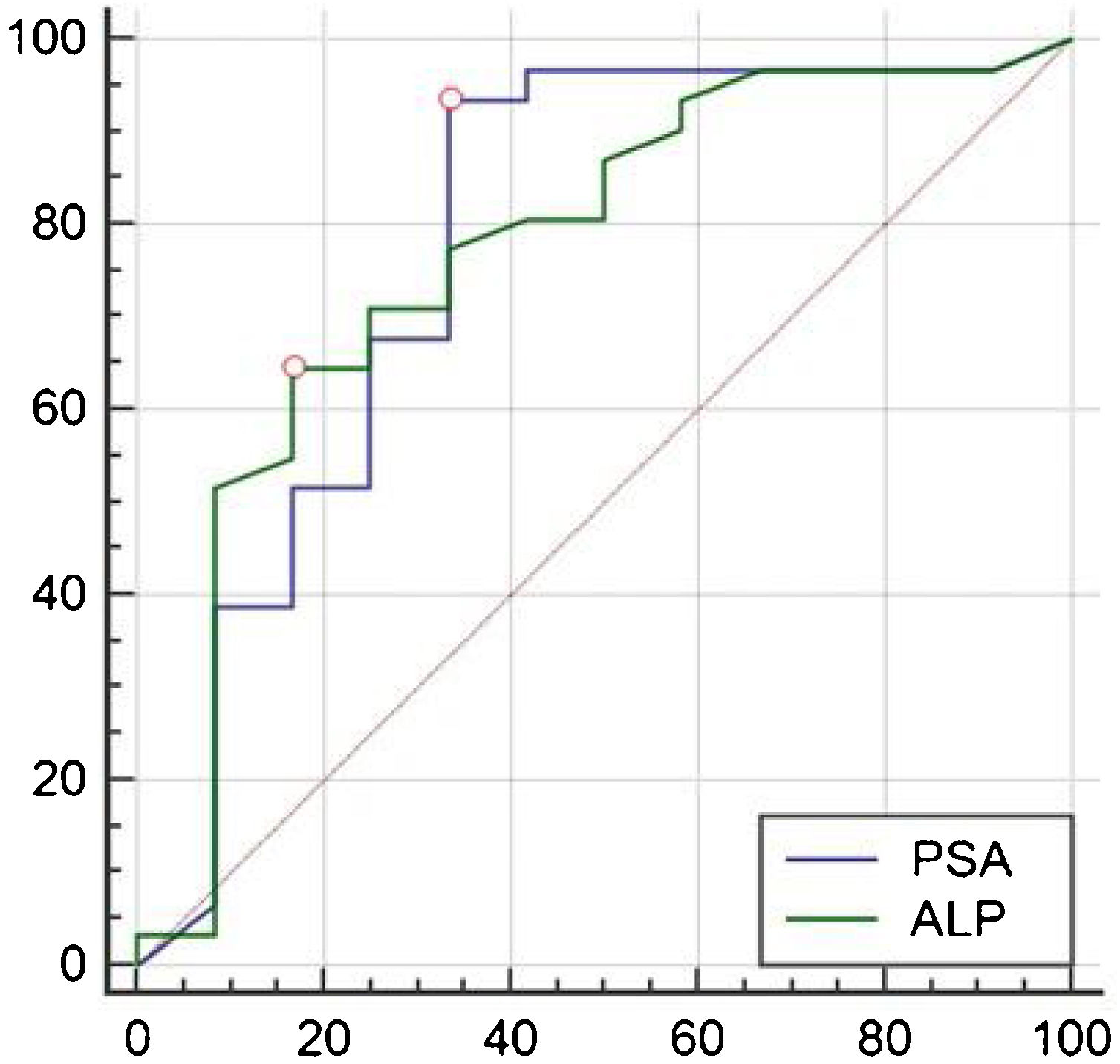
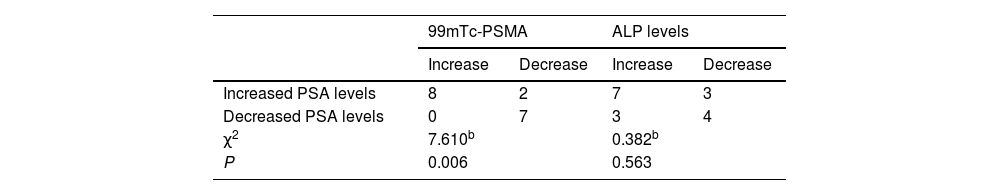
ResultsAll 43 patients had different degrees of radioactive concentrations on whole-body bone imaging. The first 99mTc-PSMA SPECT/CT imaging showed positive bone metastases in 31 cases and negative bone metastases in 12 cases. ROC curve analysis of PSA and ALP, AUC were 0.778 and 0.770, respectively. When PSA > 1.13 ng/mL, 99mTc-PSMA SPECT/CT imaging diagnostic sensitivity was 93.55%, and specificity was 66.67%. When ALP was >86U/L, the diagnostic sensitivity of 99mTc-PSMA SPECT/CT imaging was 64.52%, and the specificity was 83.33%. In 17 cases, the PSA level decreased in 7 and increased in 10. There were 10 cases of increased ALP and 7 cases of decreased ALP levels. In the second 99mTc-PSMA imaging lesion, there were 9 cases with decreased or no uptake, and 8 cases with increased uptake or number of lesions. The changes in 99mTc-PSMA uptake by Fisher’s exact probability method were statistically significant (P < 0.05, P = 0.006, and P = 0.006, respectively), and ALP level was not statistically significant (P = 0.563).
Conclusion99mTc-PSMA SPECT/CT imaging can detect PCa bone metastases, which are related to PSA levels. When PSA > 1.13 ng/mL, the sensitivity of diagnosis and detection of positive bone metastases is higher, and when ALP is >86U/L, 99mTc-PSMA imaging has higher specificity.
Investigar la asociación entre las lesiones positivas detectadas por 99mTc-PSMA SPECT/CT y los niveles sanguíneos de antígeno prostático específico (PSA) y fosfatasa alcalina (ALP) en pacientes con cáncer de próstata (CaP) y metástasis óseas sometidos a terapia endocrina.
MétodosSe realizó un análisis retrospectivo de 43 pacientes diagnosticados de metástasis ósea de CaP que fueron sometidos a terapia endocrina. Se obtuvieron imágenes de PSA, ALP, imágenes óseas de todo el cuerpo e imágenes de SPECT/CT con 99mTc-PSMA de todos los pacientes (entre ellos, 17 casos fueron reexaminados con imágenes de SPECT/CT con 99mTc-PSMA). Según los resultados de la primera imagen SPECT/TC con 99mTc-PSMA para detectar metástasis óseas, todos los casos se dividieron en dos grupos: grupo positivo y grupo negativo. La relación entre las imágenes de 99mTC-PSMA y el PSA y la FA se analizó mediante la curva ROC. Se utilizó el método de probabilidad exacta de Fisher para examinar los cambios en la captación de radiactividad por imágenes, los niveles de PSA y ALP en 17 pacientes después del tratamiento, y P < 0,05 fue estadísticamente significativo.
ResultadosLos 43 pacientes tenían diferentes grados de concentraciones radiactivas en las imágenes óseas de todo el cuerpo. Las primeras imágenes SPECT/TC con 99mTc-PSMA mostraron metástasis óseas positivas en 31 casos y metástasis óseas negativas en 12 casos. En el análisis de la curva ROC de PSA y ALP, el AUC fue 0,778 y 0,770, respectivamente. Cuando el PSA > 1,13 ng/mL, la sensibilidad diagnóstica por imágenes SPECT/CT con 99mTc-PSMA fue del 93,55 % y la especificidad fue del 66,67 %. Cuando la FA era >86 U/L, la sensibilidad diagnóstica de la SPECT/CT con 99mTc-PSMA fue del 64,52 % y la especificidad fue del 83,33 %. En 17 casos, el nivel de PSA disminuyó en 7 y aumentó en 10. Hubo 10 casos de aumento de ALP y 7 casos de disminución de los niveles de ALP. En la segunda lesión por imágenes con 99mTc-PSMA, hubo 9 casos con captación disminuida o nula y 8 casos con captación aumentada o número de lesiones. Los cambios en la captación de 99mTc-PSMA mediante el método de probabilidad exacta de Fisher fueron estadísticamente significativos (P < 0,05, P = 0,006 y P = 0,006, respectivamente), y el nivel de ALP no fue estadísticamente significativo (P = 0,563).
ConclusiónLas imágenes SPECT/CT con 99mTc-PSMA pueden detectar metástasis óseas de CaP, que están relacionadas con los niveles de PSA. Cuando el PSA es >1,13 ng/mL, la sensibilidad del diagnóstico y la detección de metástasis óseas positivas es mayor, y cuando la FA es >86 U/L, las imágenes con 99mTc-PSMA tienen una mayor especificidad.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)