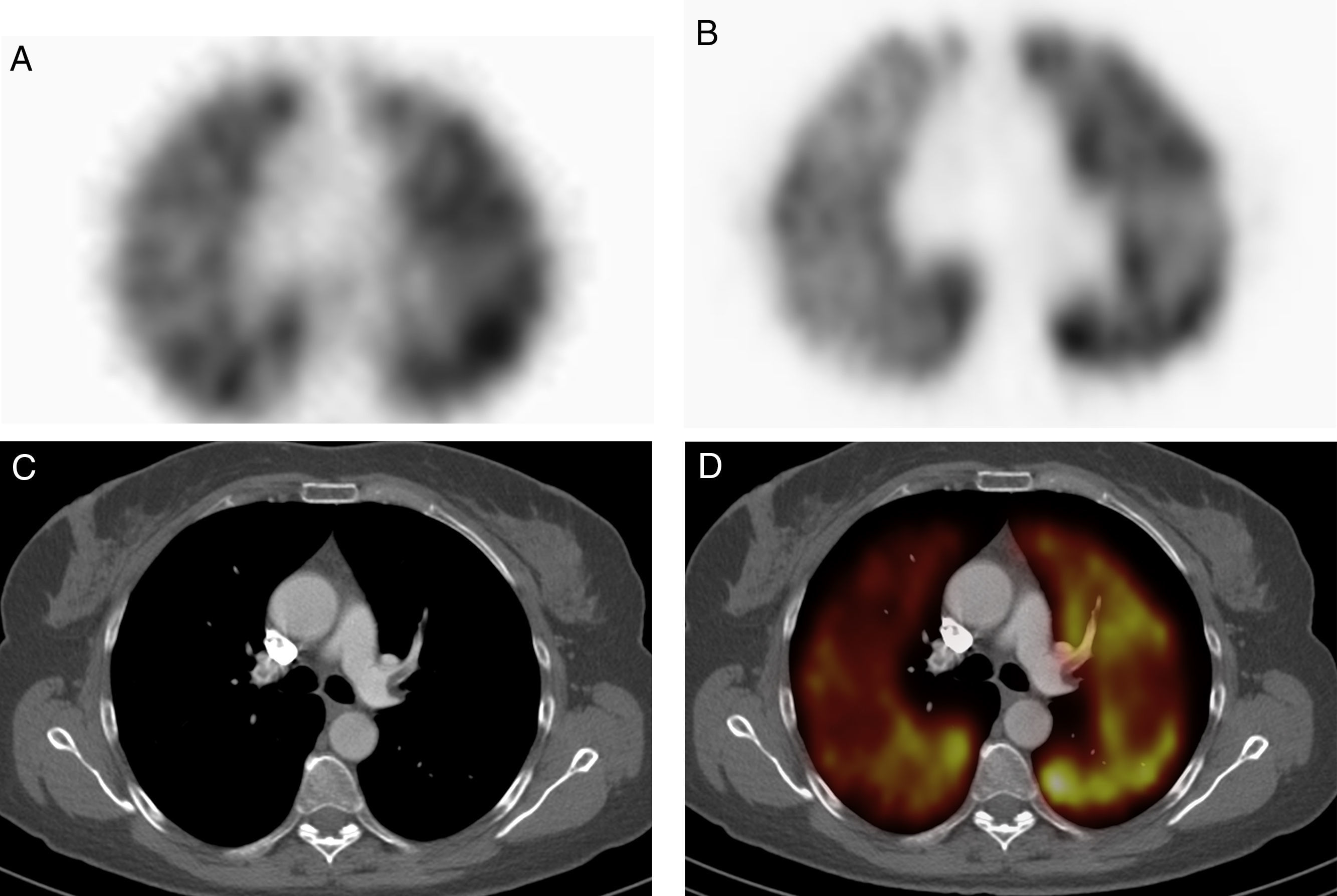
To compare diagnostic accuracy of Ventilation/Perfusion (V/P) single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) combined with simultaneous full-dose CT with a hybrid SPECT/CT scanner versus planar ventilation/perfusion (V/P) SPECT and CT angiography (CTA) in patients suspected with acute pulmonary embolism (PE).
MethodsBetween 2009 and 2011, consecutive patients suspected of acute PE were referred for V/P SPECT/CT (reviewed board approved study). A contrast agent was administered to patients who had no contraindications. Non-contrast V/P SPECT/CT was performed on the remaining patients. All patients were followed-up for at least 3 months.
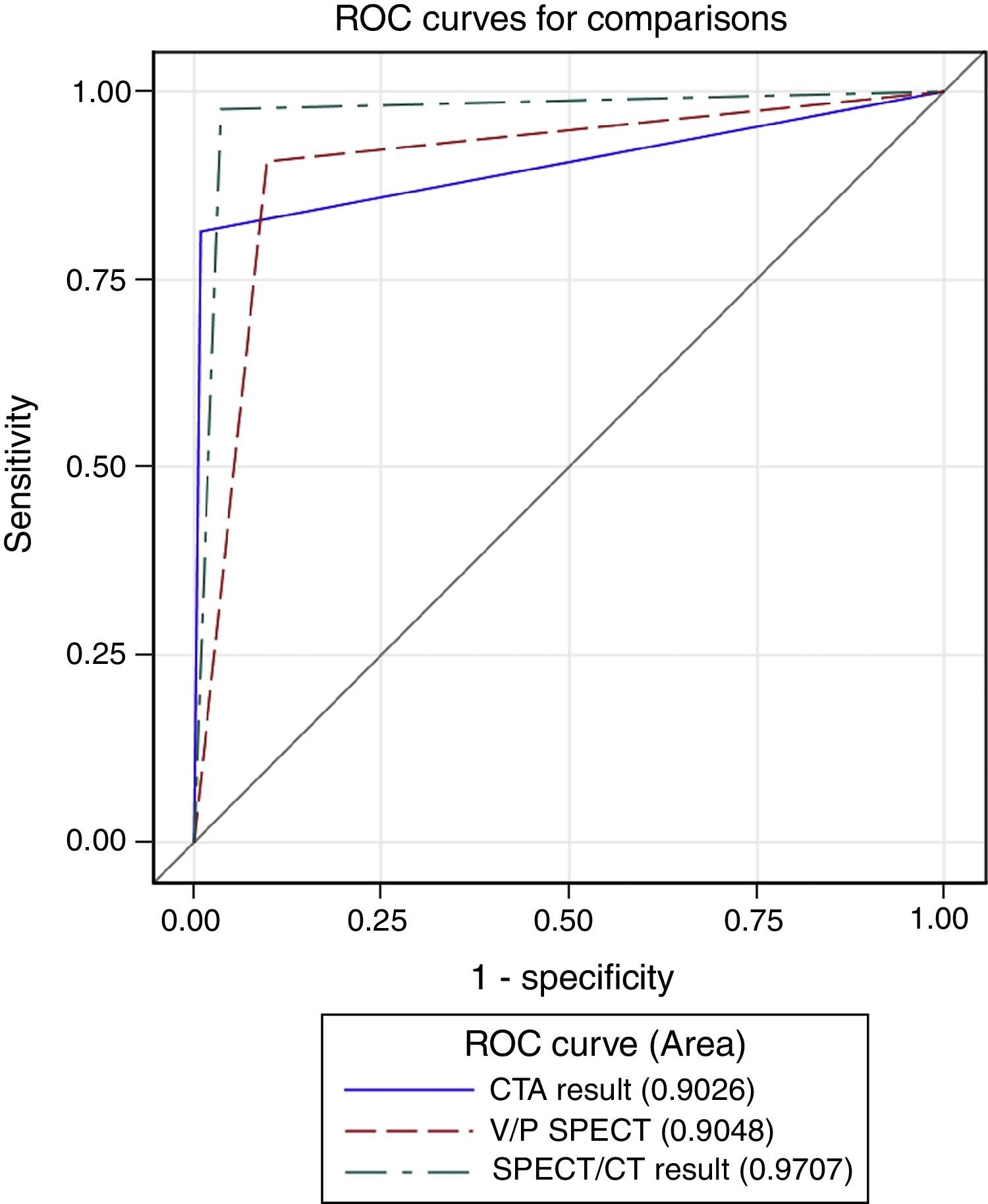
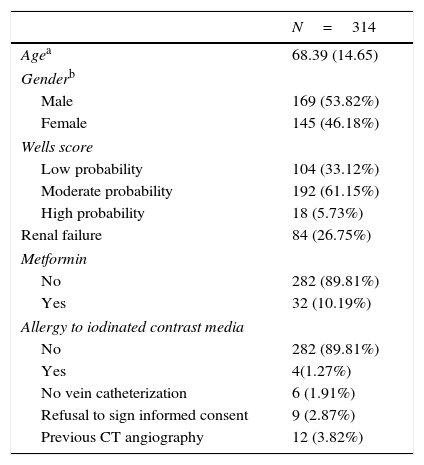
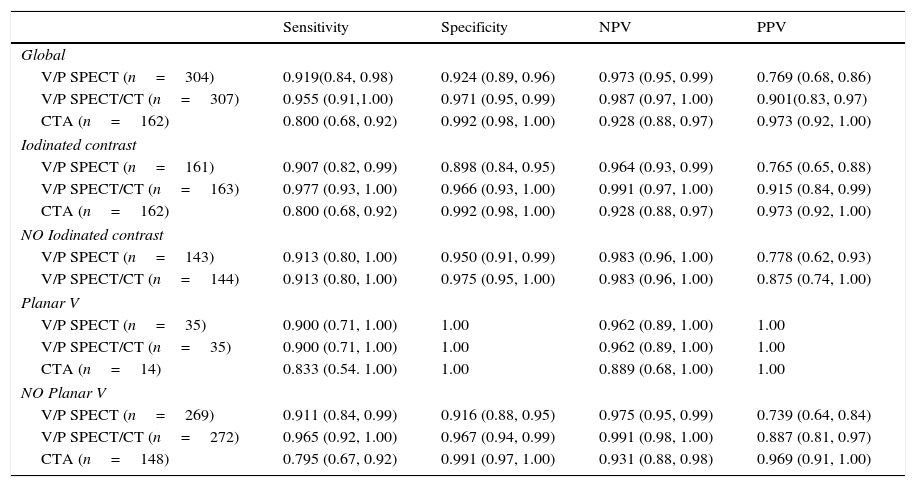
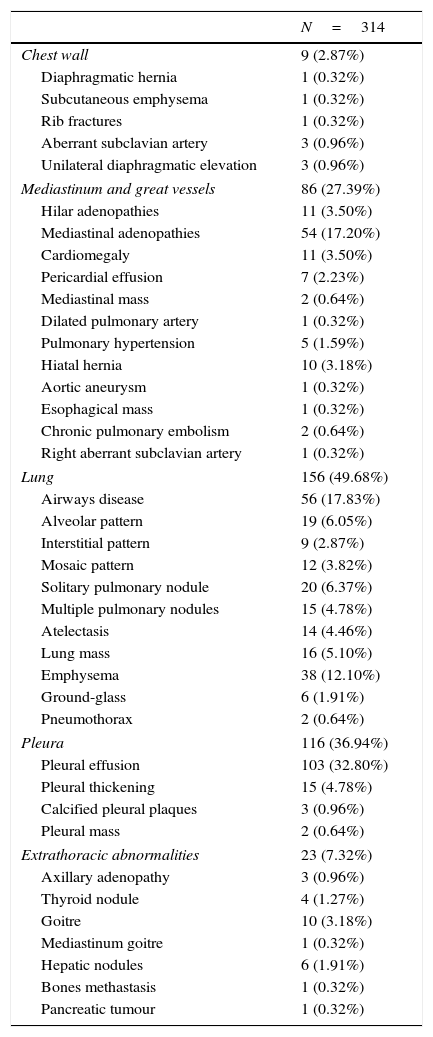
ResultsA total of 314 patients were available during the study period, with the diagnosis of PE confirmed in 70 (22.29%) of them. The overall population sensitivity and specificity was 90.91% and 92.44%, respectively for V/P SPECT, 80% and 99.15%, respectively, for CTA, and 95.52% and 97.08% for V/P SPECT/CT. SPECT/CT performed better than V/P SPECT (AUC differences=0.0419, P=0.0043, 95% CI; 0.0131–0.0706) and CTA (AUC differences=0.0681, P=0.0208, 95% CI; 0.0103–0.1259)). Comparing imaging modalities when contrast agent could be administered, sensitivity and specificity increased and V/P SPECT/CT was significantly better than CTA (AUC differences=0.0681, P=0.0208, 95% CI; 0.0103–0.1259) and V/P SPECT (AUC differences=0.0659, P=0.0052, 95% CI; 0.0197–0.1121). In case of non-contrast enhancement, there was non-significant increase of specificity. Secondary findings on CT impacted patient management in 14.65% of cases.
ConclusionOur study shows that combined V/P SPECT/CT scanning has a higher diagnostic accuracy for detecting acute PE than V/P SPECT and CTA alone. When feasible, V/P SPECT/CT with contrast enhancement is the best option.
Valorar la exactitud diagnóstica de la SPECT/TC de ventilación-perfusión (V/P) pulmonar de alta dosis mediante un equipo híbrido SPECT/TC frente a la SPECT de V/P pulmonar y a la angiografía por TC (CTA) en pacientes con sospecha de tromboembolismo pulmonar (TEP) agudo.
MetodologíaEntre 2009 y 2011, se estudiaron de forma consecutiva con SPECT/TC de V/P pulmonar los pacientes con sospecha de TEP agudo que acudieron a nuestro centro (estudio aprobado por el comité de ética hospitalaria). A los pacientes que no presentaban contraindicaciones se les administró contraste yodado (CI) por vía intravenosa. En el resto se realizó un estudio SPECT/TC de V/P pulmonar sin CI. Los pacientes fueron seguidos durante un período de 3 meses.
ResultadosSe estudiaron un total de 314 pacientes. En 70 (22,29%) se confirmó el diagnóstico de TEP. La sensibilidad y especificidad para la población global fue: 90,91 y 92,44% respectivamente para la SPECT de V/P; 80 y 99.15% para la CTA; y 95.52 y 97.08% para la SPECT/TC de V/P pulmonar. La SPECT/TC presentaba una exactitud diagnóstica superior a la SPECT de V/P (diferencias AUC=0,0419; p=0,0043; IC95%: 0,0131-0,0706) y la CTA (diferencias AUC=0,0681, p=0,0208; IC95%: 0,0131-0,1259). Comparando las diferentes modalidades cuando se administró CI, observamos un aumento de la sensibilidad y la especificidad de la SPECT/TC de V/P superior a la CTA (diferencias AUC=0,0681; p=0,0208; IC95%: 0,0131-0,1259) y a la SPECT de V/P (diferencias AUC=0,0659; p=0,0052; IC95%: 0,0197-0,1121). En el caso de no administrar CI se observó un aumento no estadísticamente significativo de la especificidad. Los hallazgos secundarios de la TC provocaron un cambio en el manejo del paciente en un 14,65% de los casos.
ConclusiónNuestro estudio demuestra que el estudio combinado SPECT/TC de V/P pulmonar tiene una mayor exactitud diagnóstica para detectar el TEP agudo que la SPECT de V/P pulmonar o la CTA por sí solos. Cuando es factible, la SPECT/TC de V/P pulmonar con CI es la mejor opción diagnóstica.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora