Understanding the effects of natural remedies and alternative therapies on animal behavior is crucial for both scientific research and potential therapeutic applications. Aloe vera, a succulent plant known for its medicinal properties, has been widely studied for its potential benefits in various health conditions. Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine practice, involves the stimulation of specific points on the body to promote healing and balance. By assessing the behavioral changes in rats exposed to Aloe vera and acupuncture, this study aims to shed light on the potential benefits and mechanisms underlying these interventions.
Aim of the studyThis study aims to investigate the impact of Aloe vera and acupuncture on rat behavior using an experimental approach. The findings from this research may contribute to our understanding of alternative treatments and their potential applications in both human and veterinary medicine.
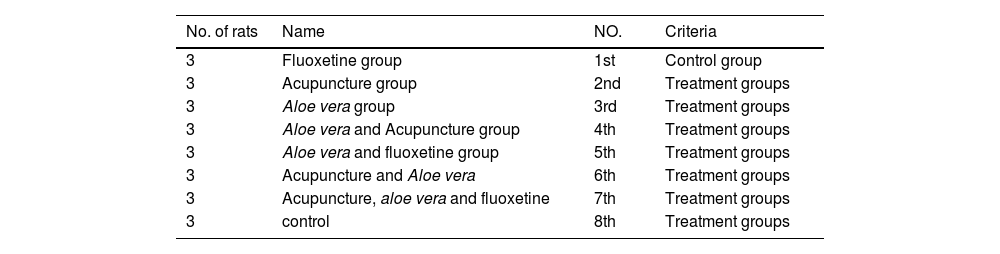
MethodIn this experiment, rats were divided into eight groups: one control and seven treatment groups. The rats received drugs, Aloe vera extract, or acupuncture once daily orally for 2 weeks. Their behavior was evaluated using the Open Field Test and The Forced Swim Test on days 1, 7, and 14. Blood samples were collected from the rats' hearts and analyzed to assess kidney and liver function.
ResultThe results of the study showed that Aloe Vera extract, particularly at a dose of 150 mg/kg, exhibited significant antidepressant effects. The combination of Aloe Vera extract, fluoxetine, and acupuncture therapy yielded the highest antidepressant effects compared to other groups. Additionally, the Aloe Vera extract showed positive effects on kidney and liver function.
Conclusionthe study suggests that Aloe Vera extract may have potential as an alternative or complementary treatment for depression. Its antidepressant effects were demonstrated, particularly at a dose of 150 mg/kg, and were further enhanced when combined with fluoxetine and acupuncture therapy. Further research is needed to determine the optimal dosage and understand the mechanisms behind these effects.
Entender los efectos de los remedios naturales y las terapias alternativas en el comportamiento animal es crucial tanto para la investigación científica como para posibles aplicaciones terapéuticas. El aloe vera, una planta suculenta conocida por sus propiedades medicinales, ha sido ampliamente estudiada por sus posibles beneficios en diversas condiciones de salud. La acupuntura, una práctica de medicina tradicional china, implica la estimulación de puntos específicos en el cuerpo para promover la curación y el equilibrio. Mediante la evaluación de los cambios de comportamiento en las ratas expuestas al aloe vera y la acupuntura, este estudio tiene como objetivo arrojar luz sobre los posibles beneficios y mecanismos subyacentes de estas intervenciones.
Objetivo del estudioeste estudio tiene como objetivo investigar el impacto del aloe vera y la acupuntura en el comportamiento de las ratas utilizando un enfoque experimental. Los hallazgos de esta investigación pueden contribuir a nuestra comprensión de los tratamientos alternativos y sus posibles aplicaciones en la medicina humana y veterinaria.
MétodoEn este experimento, las ratas se dividieron en 8 grupos: un grupo de control y 7 grupos de tratamiento. Las ratas recibieron medicamentos, extracto de aloe vera o acupuntura una vez al día por vía oral durante 2 semanas. Se evaluó su comportamiento utilizando la Prueba de campo abierto y la Prueba de nado forzado en los días 1, 7 y 14. Se recolectaron muestras de sangre de los corazones de las ratas y se analizaron para evaluar la función renal y hepática.
Resultadolos resultados del estudio mostraron que el extracto de aloe vera, especialmente a una dosis de 150 mg/kg, mostró efectos antidepresivos significativos. La combinación de extracto de aloe vera, fluoxetina y terapia de acupuntura produjo los mayores efectos antidepresivos en comparación con otros grupos. Además, el extracto de aloe vera mostró efectos positivos en la función renal y hepática.
Conclusiónel estudio sugiere que el extracto de aloe vera puede tener potencial como tratamiento alternativo o complementario para la depresión. Se demostraron sus efectos antidepresivos, especialmente a una dosis de 150 mg/kg y se mejoraron aún más cuando se combinaron con fluoxetina y terapia de acupuntura. Se necesita más investigación para determinar la dosis óptima y comprender los mecanismos detrás de estos efectos.
Acupuncture is a part of Traditional Chinese Medicine that aims to restore and maintain health by stimulating specific points on the body using fine needles.1 It is generally considered safe, with few adverse effects such as soreness, pain, bruising, and mild bleeding at the needle site. Acupuncture may mediate signals that control information exchange in the body, helping to restore balance. Psychiatric symptoms of depression and anxiety are associated with neurotransmitters like serotonin, norepinephrine, dopamine, and endorphins, as well as dysregulation of the HPA axis.2 Research suggests that acupuncture can have physiological effects, potentially regulating these neurotransmitters and influencing the neuroendocrine and immune systems. However, it's important to note that acupuncture should not replace conventional treatments and consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended.3
Aloe vera is a medicinal plant with a gel-like substance found in its leaves. It has been traditionally used to treat various skin conditions such as burns and wounds. Aloe vera also has potential health benefits, including anticancer, antioxidant, antidiabetic, and antihyperlipidemic effects.4 It contains a range of compounds, including vitamins, enzymes, minerals, sugars, anthraquinones, fatty acids, hormones, and other beneficial substances.5
Material and methodThe current study was conducted in the Pharmacy College, University of Kerbala, following all the instructions of the Animal Ethics Committee of the college and university and complies with ethical guidelines for animal experimentation.
AnimalTwenty-four adult rats weighing approximately 200–230 g were obtained from the animal house of the Pharmacy Department in the college. All the rats were housed in normal light/dark cycles and fed with a standard laboratory diet. They had open access to water to ensure standard rat growth and performance.
Experimental designThe rats were subdivided into eight groups (Table 1): one control group and seven treatment groups. The administration of drugs and extracts was done once daily orally for 2 weeks in each group. The rats were evaluated after receiving the drug and extract on days 1, 7, and 14 using the Open Field Test (OFT). The results were then compared among the different groups and time points. The acupuncture was done daily on animal site shown in Fig. 1 by mean of insulin needles6. the dose of fluoxetine used was 0.05 mg\rat after it was diluted with distilled water. At the end of the experiment, 14 samples were collected from the seven groups. Blood samples were drawn from the heart of the rats and placed in gel tubes. After sample collection, the tubes were centrifuged for a few minutes and then transferred to the laboratory for analysis of kidney function (represented by serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen) and liver function (represented by GPT and GOT levels).
Experimental groups.
| No. of rats | Name | NO. | Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | Fluoxetine group | 1st | Control group |
| 3 | Acupuncture group | 2nd | Treatment groups |
| 3 | Aloe vera group | 3rd | Treatment groups |
| 3 | Aloe vera and Acupuncture group | 4th | Treatment groups |
| 3 | Aloe vera and fluoxetine group | 5th | Treatment groups |
| 3 | Acupuncture and Aloe vera | 6th | Treatment groups |
| 3 | Acupuncture, aloe vera and fluoxetine | 7th | Treatment groups |
| 3 | control | 8th | Treatment groups |
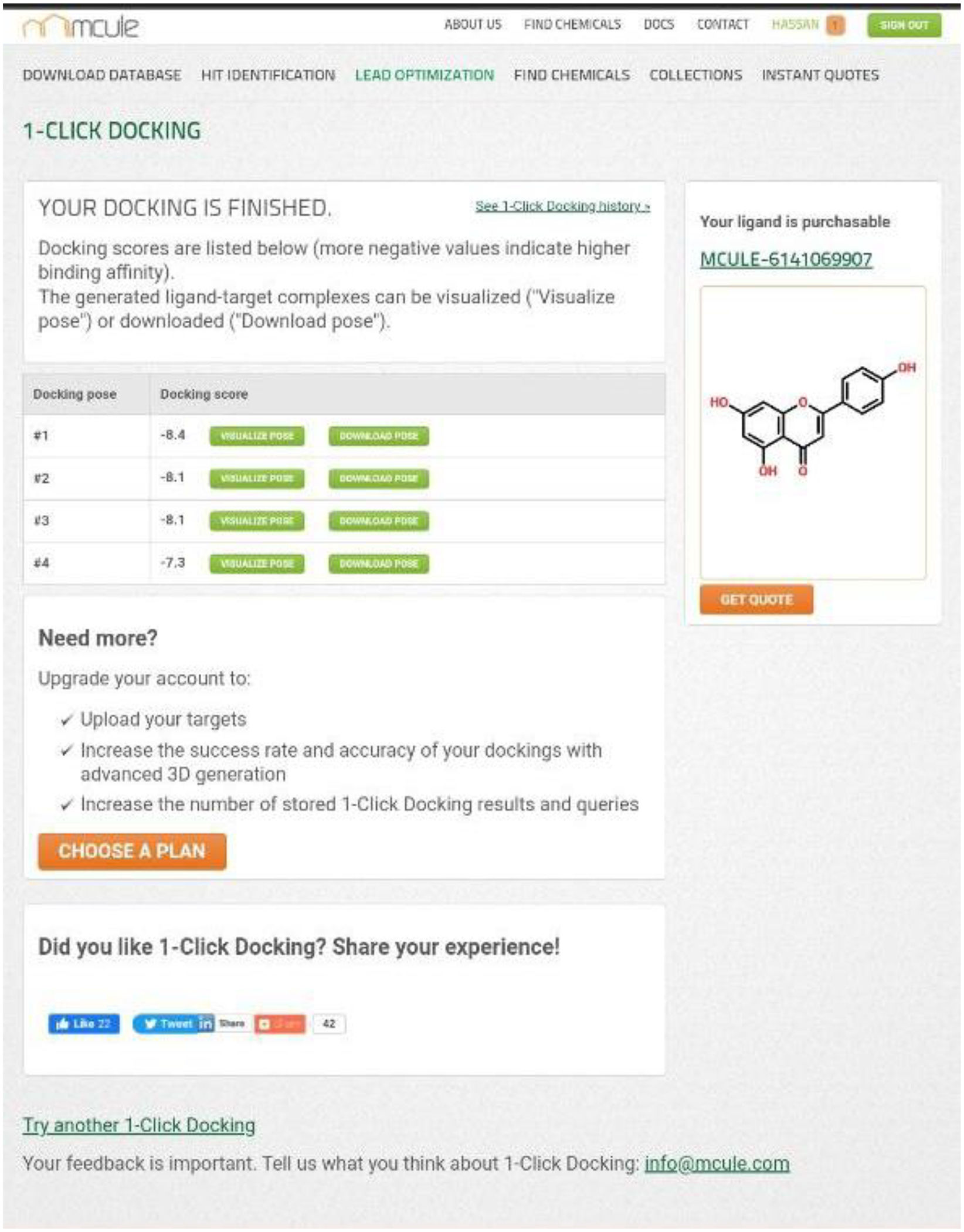
The choice of Aloe Vera as a potential alternative treatment for depression was based on the results of the MCULE docking study. Among the compounds tested, Aloe Vera extract showed the highest score and maximum affinity to fluoxetine receptors. This indicates that it has the potential to interact effectively with these receptors, similar to fluoxetine (Fig. 2, 3).
Preparation of hydro alcoholic extract of Aloe Verathe hydro alcoholic extract of Aloe Vera plant was prepared by washing and cutting the plant into small pieces. It is then boiled in 70% ethanol for 6 h per day for 2 days. After cooling, the extract is filtered to remove impurities. The liquid extract is then dried in a controlled environment for about 2 weeks. The resulting solid extract is weighed and stored in a sealed container away from sunlight and heat.7 Safety precautions should be followed during the process. The dose given for each rat in the selected groups is 30 mg after it was diluted with distilled water.
The Open Field Testis a commonly used method to assess the behavior of rats in a controlled environment. To conduct the test, a suitable open field arena is prepared, ensuring proper lighting and cleanliness. The rat is habituated to the testing room and introduced to the empty arena for a short period.8 The actual testing begins by placing the rat in the center of the arena and observing its behavior for a set time. Various parameters such as locomotion, exploration, rearing, grooming, and freezing are recorded.9 The data collected is then analyzed to compare and quantify the behaviors exhibited by different rats or experimental groups. The OFT in this experiment was performed on the 1st, 7th, and 14th day of the experiment.
The Forced Swim TestThe Forced Swim Test (FST) is a commonly used test in research to evaluate depressive-like behavior in animals, specifically rodents. It involves placing the animal in a water-filled container and observing their behaviors. The test is conducted in two sessions: a pre-test to acclimate the animal to the environment and a test session where their behaviors are recorded. During the test, active behaviors like swimming and struggling, as well as passive behaviors like immobility and floating, are monitored.10 The duration of each behavior is measured and analyzed to assess depressive-like behavior.
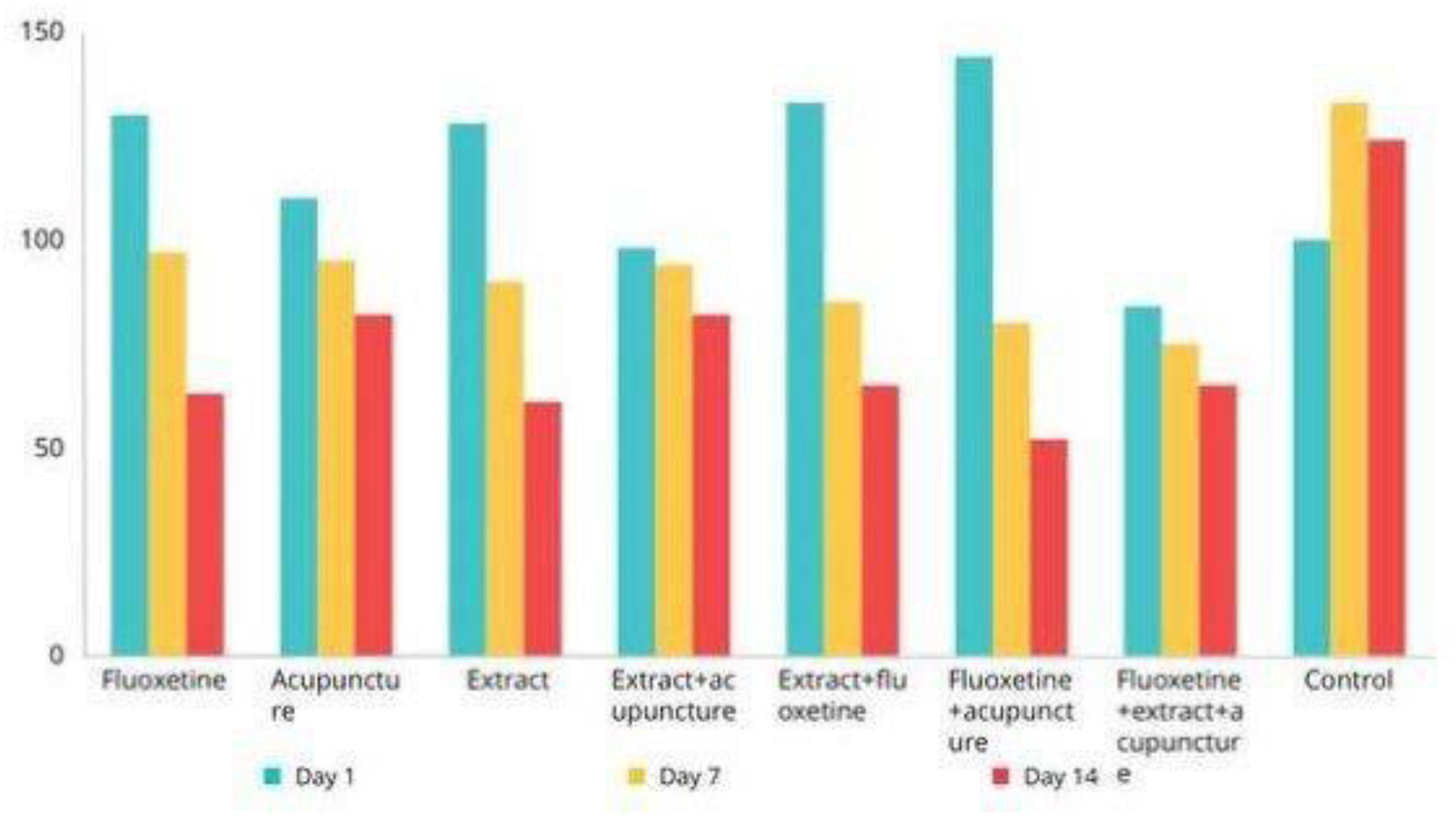
ResultFig. 4 displays the results of the OFT conducted to evaluate the antidepressant effects of a hydro alcoholic extract of Aloe Vera plant and the acupuncture medicine. The control group and a group treated with fluoxetine were also included for comparison.
The results of the OFT indicated that the Aloe Vera extract, particularly at a dose of 150 mg/kg, exhibited greater antidepressant effects compared to other groups on the 1st day. However, the highest antidepressant effects were observed in the Aloe Vera-treated groups with a dose of 150 mg/kg on the 7th and 14th day. Nevertheless, no significant differences were observed between the groups at different time points.
Furthermore, the FST was performed to assess the antidepressant effects of the hydro alcoholic extract of Aloe Vera at a dosage of 150 mg/kg. The results revealed a higher antidepressant effect in groups 6 and 7, which received a combination of the Aloe Vera extract and fluoxetine in addition of acupuncture therapy This combination yielded superior results compared to other groups.
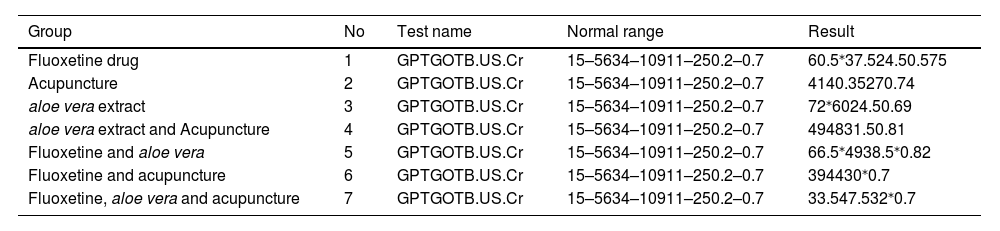
The measured values of both liver and kidney biomarkers are listed in Table 2.
Liver and kidney biomarkers in the experimental groups.
| Group | No | Test name | Normal range | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluoxetine drug | 1 | GPTGOTB.US.Cr | 15–5634–10911–250.2–0.7 | 60.5⁎37.524.50.575 |
| Acupuncture | 2 | GPTGOTB.US.Cr | 15–5634–10911–250.2–0.7 | 4140.35270.74 |
| aloe vera extract | 3 | GPTGOTB.US.Cr | 15–5634–10911–250.2–0.7 | 72⁎6024.50.69 |
| aloe vera extract and Acupuncture | 4 | GPTGOTB.US.Cr | 15–5634–10911–250.2–0.7 | 494831.50.81 |
| Fluoxetine and aloe vera | 5 | GPTGOTB.US.Cr | 15–5634–10911–250.2–0.7 | 66.5⁎4938.5⁎0.82 |
| Fluoxetine and acupuncture | 6 | GPTGOTB.US.Cr | 15–5634–10911–250.2–0.7 | 394430⁎0.7 |
| Fluoxetine, aloe vera and acupuncture | 7 | GPTGOTB.US.Cr | 15–5634–10911–250.2–0.7 | 33.547.532⁎0.7 |
Between the groups, * p value for the measured biomarkers is significant (<0.005) the test used is student T test.
Fluoxetine is a hypothesis based on the monoaminergic theory for depression (Fig. 5) and is linked to the malfunction of neurotransmitters such as noradrenaline and serotonin. Reduced levels of serotonin have been observed in the cerebrospinal fluid of individuals diagnosed with depression.11 Fluoxetine undergoes extensive transformation by various CYP450 enzymes, resulting in only 2.5% of the administered dose being excreted unchanged in urine. The demethylation of fluoxetine produces norfluoxetine, an active metabolite that exhibits potent selective serotonin reuptake inhibition (SSRI) activity which has the antidepressant activity.12
Fluoxetine mechanism of action.12
The ongoing findings indicate that the hydroalcoholic extract of the Aloe vera plant has produced an antidepressant effect, which is amplified with an increase in the duration of treatment. Our results align with other studies examining the impact of Aloe vera and fluoxetine on rat behavior and effectiveness as antidepressants, although there are some differences. These variations could be attributed to variances in the method of preparing the hydroalcoholic extract of Aloe vera or the addition of acupuncture in our experiment.
The antidepressant effect of the hydroalcoholic extract of Aloe vera plant is thought to be due to its various active components. Aloe vera contains several bioactive compounds such as polysaccharides, flavonoids, and anthraquinones, which have been found to possess potential antidepressant properties. These compounds may act on different neurotransmitter systems in the brain, such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, which are known to be involved in regulating mood and emotions. By modulating these neurotransmitters, the extract of Aloe vera may help to alleviate symptoms of depression and improve overall mood.13
Additionally, Aloe vera extract has been found to possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Depression is often associated with increased oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Aloe vera may help reduce these processes and protect against neuronal damage, which could contribute to its antidepressant effects.14
Acupuncture is believed to stimulate the central nervous system and release chemicals that enhance the body's natural healing abilities. While its exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, there are several theories explaining the acupuncture potential antidepressant effects. One theory suggests that acupuncture may regulate neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which play a crucial role in mood regulation.15 Another explanation is that acupuncture stimulates the release of endorphins, natural substances that promote feelings of well-being and reduce stress and anxiety. Additionally, acupuncture may modulate specific brain regions and neural networks involved in mood regulation, as shown by studies using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Lastly, acupuncture's ability to reduce stress levels by regulating the release of stress hormones like cortisol may also contribute to its antidepressant effects.16
Biochemical tests assessing kidney and liver function revealed a recent increase in GPT enzyme activity, which has been associated with potential liver damage caused by Aloe vera products as some components of Aloe vera products, such as anthraquinones, have been reported to have potential toxic properties. Anthraquinones are natural compounds found in the latex of Aloe vera, and they have been associated with laxative effects.17,18 However, prolonged or excessive use of anthraquinone-containing products can lead to adverse effects, including diarrhea, electrolyte imbalances, and even liver damage.19
Lastly, the mechanism through which fluoxetine leads to elevated liver enzymes (Table 2) and liver injury remains unknown, but there are several theories and observations. One possibility is that fluoxetine may cause liver injury through an idiosyncratic reaction, meaning that it affects certain individuals in a unique and unpredictable way. Another theory is that the liver injury could be immune-mediated, involving the immune system's response to the medication.20 Additionally, fluoxetine is metabolized in the liver by specific enzymes, and it is possible that the metabolism process may result in the production of reactive metabolites that can damage liver cells. However, more research is needed to fully understand these mechanisms. It's important to note that while fluoxetine has been associated with liver injury in rare cases, the overall risk is relatively low.21
ConclusionIn conclusion, the study conducted on the effects of Aloe Vera extract on depression has shown promising results. Aloe Vera extract, especially at a dose of 150 mg/kg, demonstrated significant antidepressant effects. Additionally, when combined with fluoxetine and acupuncture therapy, the antidepressant effects were further enhanced. The study also found that Aloe Vera extract had negative effects on kidney and liver function. However, further research is necessary to determine the optimal dosage and fully understand the underlying mechanisms behind these effects.in addition, It's important to note that acupuncture should not be considered a standalone treatment for depression but rather as a complementary therapy alongside conventional treatments. Consulting with a qualified acupuncturist or healthcare provider is recommended for personalized advice and treatment options.
Declaration of Competing InterestNo conflict of interest.