Antipsychotics are an essential component in the treatment of schizophrenia. Long-acting injectable formulations (LAI) arose to improve adherence with the associated potential of reducing the risk of relapse. The objective of this article is to analyse the use of LAI antipsychotics in Spain, which is similar to other European countries but with a predominance of the use of second generation LAI, to discuss the possible causes of prescribing differences with respect to other countries (including organisational aspects, attitudes of psychiatrists, patients and family members, and clinical practice guidelines), and to discuss their use in acute psychiatric units, first episode, and in children and adolescents. In our view, while it is necessary to increase existing evidence regarding the advantages of LAI antipsychotics and the differentiation between LAI antipsychotics currently available, their use will likely continue to grow driven by clinical experience.
Los antipsicóticos son un componente esencial del tratamiento de la esquizofrenia. Las formulaciones inyectables de liberación prolongada (ILP) surgen para mejorar la adherencia con el potencial asociado de reducir el riesgo de recaídas. El objetivo de este artículo es analizar el uso de antipsicóticos ILP en España –que es similar al de otros países europeos pero con un predominio de la utilización de ILP de segunda generación–, discutir las posibles causas de las diferencias de prescripción respecto a otros países de nuestro entorno (entre otras, aspectos organizativos, actitudes de psiquiatras, pacientes y familiares, guías de práctica clínica), y discutir su utilización en unidades de agudos, primeros episodios, y en niños y adolescentes. A nuestro juicio, aunque es necesario aumentar las pruebas existentes respecto a las ventajas de los antipsicóticos ILP y la diferenciación entre aquellos disponibles actualmente, su utilización seguirá probablemente creciendo impulsada por la experiencia clínica.
Antipsychotic drugs are an essential component in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia, in both the acute phase to control the psychotic symptoms and the stable phase to reduce the risk of relapse, and to contribute to maximum functional capacity.1 However, some authors question their usefulness in long-term treatment,2 including their impact on functionality,3 mainly in patients with good prognosis after the first episode of psychosis.
One of the principal causes of relapse in the patient with schizophrenia is medication non-adherence,4 present in more than 40% of the patients.5 Better adherence has been linked to greater symptomatic and psychosocial remission, as well as integration into the community.6 The long-acting injectable (LAI) presentation, classically called depot, which originally arose to improve adherence, consists of an intramuscularly-administered formulation that is gradually released over several weeks; this keeps an effective dose present in the body longer than the oral formulations. Some studies indicate that using LAI antipsychotics instead of oral ones reduces the risk of relapse and hospitalisation.7–9 However, the results vary depending on whether observational studies or randomised clinical trials are analysed; such trials have greater thoroughness of methodology but are far from the clinical practice conditions.10–14 The indication for this dosage form is something that many clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) still do not cover. Consequently, psychiatrists currently prescribe LAIs using a shared-decision model in which the clinician helps patients to choose the best treatment according to patient preferences, values and clinical conditions.15
The objective of this review was to analyse the use of LAI antipsychotics in Spain, discuss possible reasons why their prescription here differs from other countries in our setting, and indicate certain aspects of their use in specific populations and clinical settings. A detailed review of the studies conducted in Spain with LAI antipsychotics is outside the scope of this article; however, interested readers can find a listing of such studies in the Appendix.
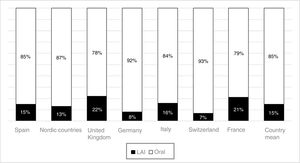
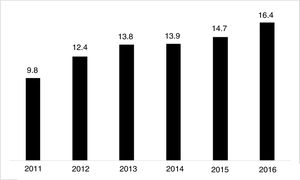
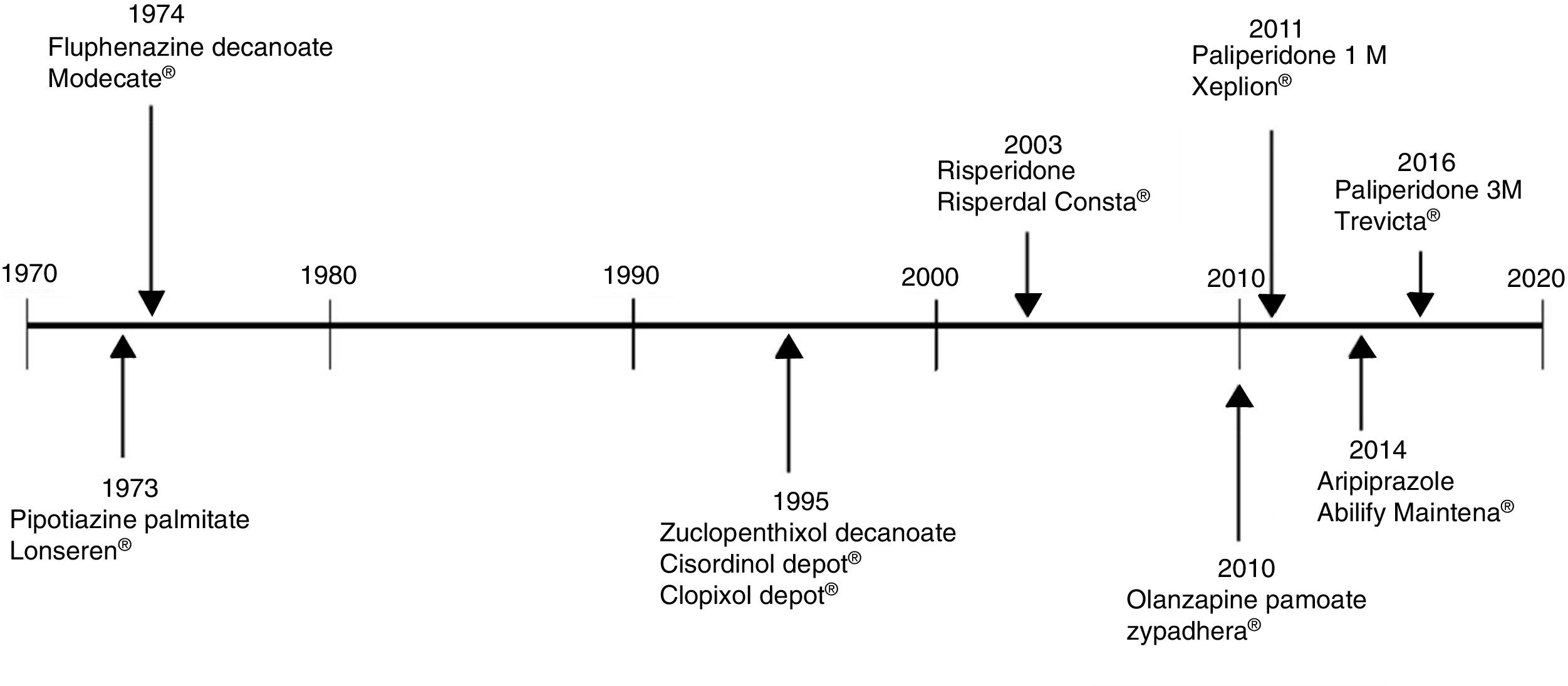
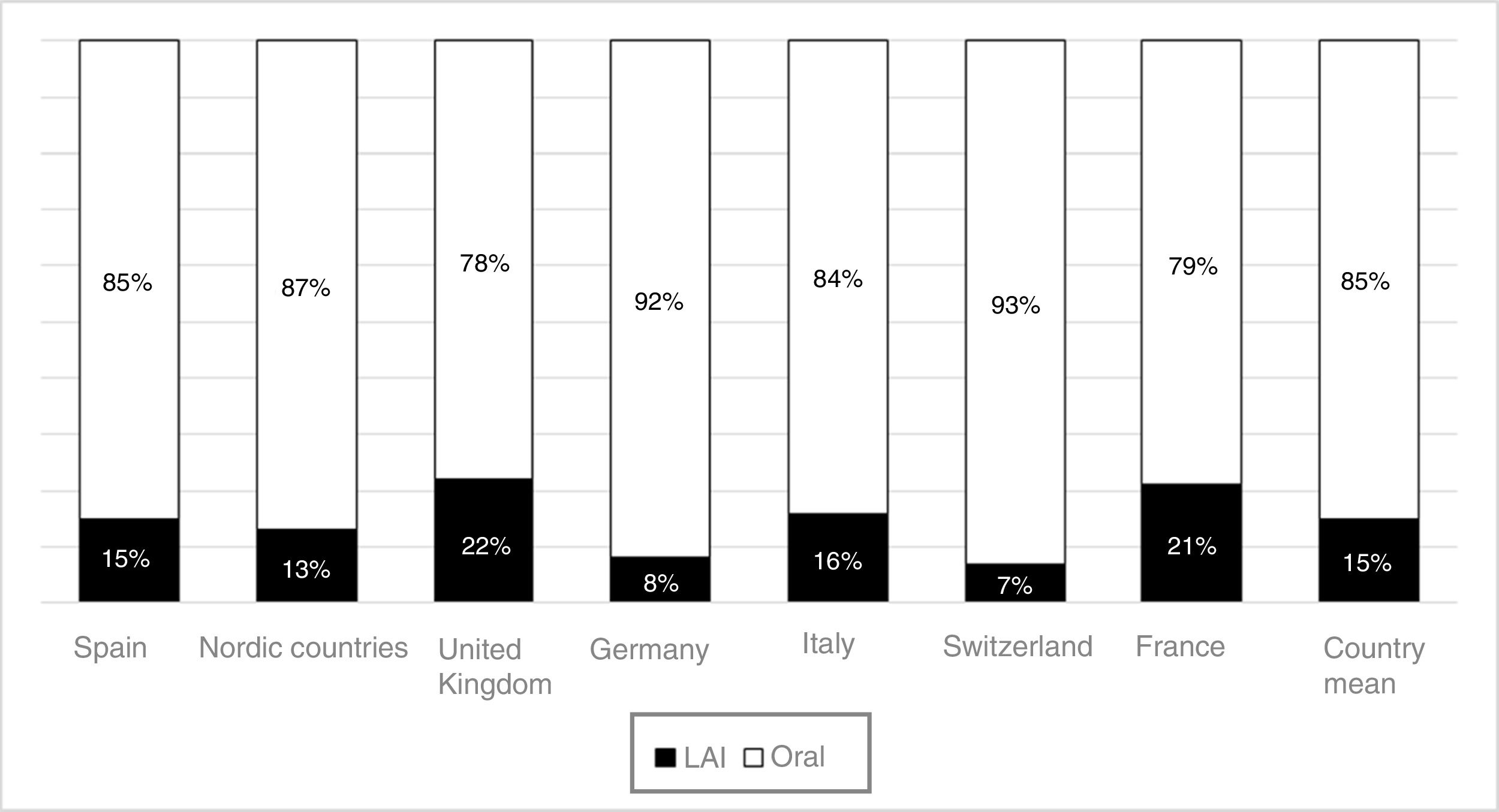
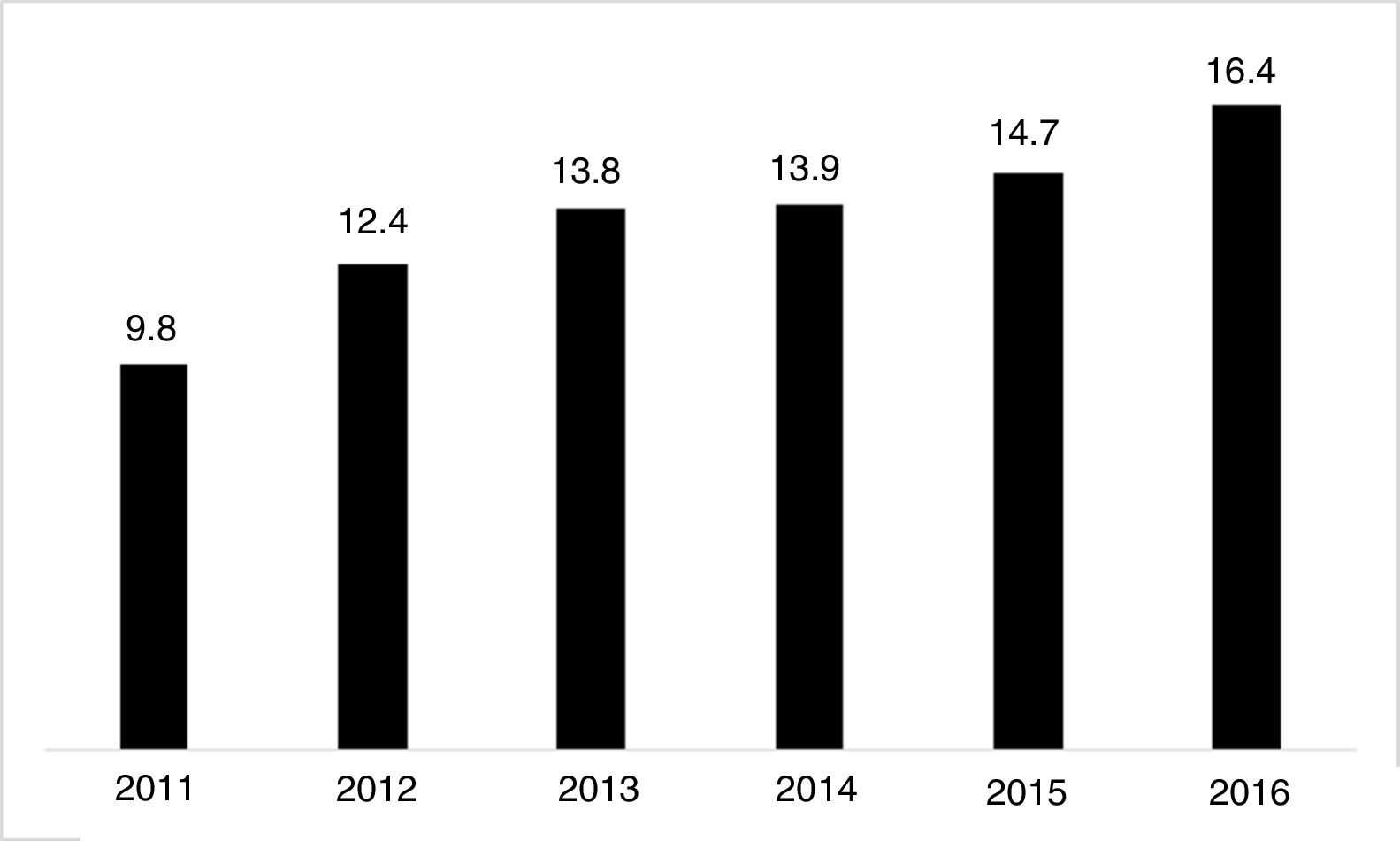
The use of long-acting injectable antipsychotics in Spain and other countriesThe first LAI antipsychotics appeared in the 1970s, pioneered by fluphenazine enanthate in 1966 and fluphenazine decanoate in 1968.16 A marketing timeline for various LAIs in Spain is shown in Fig. 1. Even though LAI antipsychotics have been available for several decades and have potential advantages, their use is much less frequent in the treatment of schizophrenia compared to the use of oral antipsychotics.14,17,18 It also varies considerably from one region to another and country to country. A study on world evolution of antipsychotic polypharmacy from 1970 to 2009 notes a considerably greater LAI use in Asia than in the USA (33.2 vs 13%, p=0.04), with no significant differences between Europe (24%) and Oceania (24.8%).19 In other areas, such as Japan, antipsychotic use is much lower (about 1%).20 Based on the 2011 IMS Institute for Health Care Informatics data (Fig. 2), in Spain the use of first- or second-generation LAI antipsychotics was 14.7% of the total antipsychotics, the same as the mean among the 7 European countries analysed and lower than the figures indicated for the United Kingdom and France (22% and 21%, respectively). Second-generation LAI antipsychotic use has grown in the last few years in Spain: the market share of second-generation LAI antipsychotic use against total second-generation antipsychotic consumption rose from 9.8% to 16.4% between 2011 and 2016 (Fig. 3). Focusing on the proportion of second-generation antipsychotics to total LAIs, the mean for the 7 countries analysed is 34%. Spain is in first place for the use of second-generation LAIs (74%), followed by Switzerland (59%) and the Nordic countries (47%), while the United Kingdom (14%) comes in last; countries near Spain, such as France and Italy, present figures close to the European mean. As a clinical data-based study analysing all patients diagnosed with schizophrenia treated at the mental health centres in Tarragona (Spain) between 2011 and 2013 (n=1646) revealed, 42% of the patients there initially received an LAI antipsychotic, and the second-generation LAI was the most frequently prescribed (66%).21
Commercialisation in Spain of long-lasting intramuscular antipsychotics.
Source: Data based on the information contained in the Online Medicine Information Centre of the Spanish Agency of Medicine and Healthcare Products [accessed on 24.10.17]. Available at: https://www.aemps.gob.es/cima/fichasTecnicas.do?metodo=detalleForm.
The situation in Europe differs from that of the USA, where the use of LAI antipsychotics is lower. However, it has been predicted that LAI use in the American market will double between 2014 and the end of this decade.22 In contrast to Europe, second-generation antipsychotics represent 99% of the LAI antipsychotic market in the USA.22
Consequently, it seems that Spain has a greater use of atypical LAIs than other countries, both within and outside of Europe.
Factors that influence the prescription of long-acting injectable antipsychoticsCultural aspectsAlthough we have not got hard data on Spain, it seems relevant that in the past 2 decades acceptance – not without controversies – has grown for biological treatments in mental disorders in general and schizophrenia in particular.23,24 Wider diffusion and deeper knowledge of the neurological bases of these disorders has contributed to this acceptance.
As has been mentioned earlier, the use of LAI antipsychotics in patients with schizophrenia varies considerably from one country to another, and their use is practically limited to very severe patients or those non-adherent to treatment. The fact that there are dissimilar attitudes towards LAI antipsychotics has been proposed as a factor that may lead to this variability, contrasting attitudes that stem from all parties involved – psychiatrists, patients and relatives/caregivers – as well as from healthcare/economic policies in different countries/continents.
The attitudes and beliefs of patients and psychiatristsAnalysing the attitudes that patients with schizophrenia have towards treatment with LAI is very complex because of the great number of confounding factors that have to be considered. Potential effects on these attitudes can stem from previous experiences with other injectable treatments (frequently applied coercively for acute disorders),25–27 the clinical development phase in which treatment is applied (chronic patients with greater number of relapses),26 the type of information that the patient is given, the way in which treatment decisions are made,26,28 and the attitudes of the various healthcare team members, among other factors.
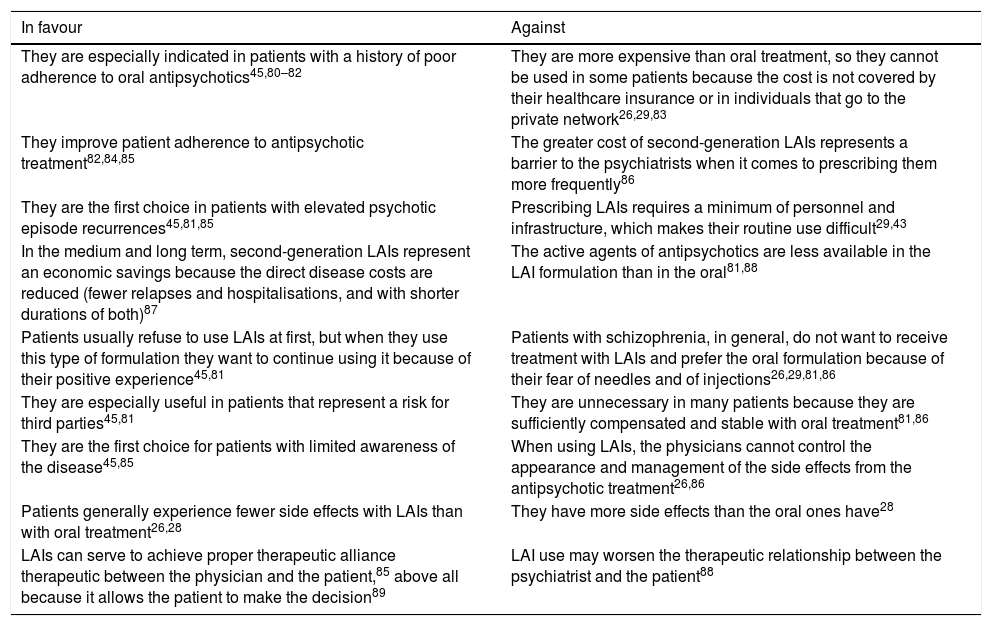
Although not results from studies carried out in Spain, data from international literature may explain such a negative attitude (on the part of both patients and psychiatrists) towards LAI antipsychotics. Patients generally have insufficient information on this treatment alternative27–29; in several studies, up to two thirds of the patients have not received information about LAIs.28 This situation may be due to the psychiatrist's erroneous concepts about the type, frequency and health consequences that administering LAI antipsychotics, in terms of efficacy as much as of tolerability. Some patients associate this medication form with coercion or loss of autonomy over the treatment29 and greater stigma.27 It should be noted that some physicians feel that administration of LAIs causes less stigma than using oral medication, which reminds patients of their illness every day.27,30Table 1 summarises, based on various published studies, favourable and unfavourable attitudes that psychiatrists have towards LAI antipsychotics.
Favourable and unfavourable attitudes of psychiatrists towards long-acting injectable antipsychotics.
| In favour | Against |
|---|---|
| They are especially indicated in patients with a history of poor adherence to oral antipsychotics45,80–82 | They are more expensive than oral treatment, so they cannot be used in some patients because the cost is not covered by their healthcare insurance or in individuals that go to the private network26,29,83 |
| They improve patient adherence to antipsychotic treatment82,84,85 | The greater cost of second-generation LAIs represents a barrier to the psychiatrists when it comes to prescribing them more frequently86 |
| They are the first choice in patients with elevated psychotic episode recurrences45,81,85 | Prescribing LAIs requires a minimum of personnel and infrastructure, which makes their routine use difficult29,43 |
| In the medium and long term, second-generation LAIs represent an economic savings because the direct disease costs are reduced (fewer relapses and hospitalisations, and with shorter durations of both)87 | The active agents of antipsychotics are less available in the LAI formulation than in the oral81,88 |
| Patients usually refuse to use LAIs at first, but when they use this type of formulation they want to continue using it because of their positive experience45,81 | Patients with schizophrenia, in general, do not want to receive treatment with LAIs and prefer the oral formulation because of their fear of needles and of injections26,29,81,86 |
| They are especially useful in patients that represent a risk for third parties45,81 | They are unnecessary in many patients because they are sufficiently compensated and stable with oral treatment81,86 |
| They are the first choice for patients with limited awareness of the disease45,85 | When using LAIs, the physicians cannot control the appearance and management of the side effects from the antipsychotic treatment26,86 |
| Patients generally experience fewer side effects with LAIs than with oral treatment26,28 | They have more side effects than the oral ones have28 |
| LAIs can serve to achieve proper therapeutic alliance therapeutic between the physician and the patient,85 above all because it allows the patient to make the decision89 | LAI use may worsen the therapeutic relationship between the psychiatrist and the patient88 |
Some of the difficulties mentioned are clearly conditioned by the existence or not of prior experience with LAI treatment, and by the type of antipsychotic involved in this experience (first- or second-generation). It is interesting that only 23% of the patients that have never been treated with LAI antipsychotics are in favour of their use, while 73% of individuals currently receiving them report a positive attitude towards using them.31 Patel et al. conclude that patients tend to favour treatment with the formulation that they are using at the time of the study,32 which would support the idea that direct knowledge influences treatment evaluation. As other studies have indicated, direct experience might even lead patients to recommend their treatment to other patients in a similar situation.27 Likewise, the more experience psychiatrists have with using LAI antipsychotics, the more favourable their attitude towards using them is (which means that the sample evaluated is not totally free from selection bias).25,33 For these reasons, patients’ and physicians’ unfavourable attitudes towards first-time LAI use seem to represent the main barrier to utilising them.
The attitudes and beliefs of relatives and caregiversThere are fewer studies on the attitudes of relatives than on the attitudes of physicians and patients, but such studies support the idea that involving relatives in the matter makes it easier for patients to accept LAI antipsychotics.26 In a study that compared the attitudes of physicians, patients and relatives, Jaeger and Rossler28 describe how relatives show a more open, positive attitude towards the benefits of LAI use than patients. Those researchers report that 50% of the relatives (belonging to an association of family members of the ill) feel that the patients are taking their medication improperly. In addition, the relatives frequently admit that many patients are not adhering to therapy correctly and that they are, consequently, in favour of using the LAI formulations that ensure that the patients regularly receive appropriate dosages. These study results support the idea that a considerable percentage of relatives have a positive attitude towards drug treatment of mental disorders.34 Strengthening relatives’ favourable impression of LAI medication using pertinent information and fluid communication is extremely important; the physician should understand this and use it, given that among the factors promoting treatment adherence is family and social support.35 Generally speaking, attempting to achieve a positive social and family atmosphere about the need to maintain good treatment adherence is essential for good evolution of patients with schizophrenia.
Organisational aspectsOne of the healthcare factors to be considered in explaining a possibly differential LAI antipsychotic use are the aspects related to healthcare organisation and the resources available. Kane36 points out that among the factors that may determine the low use of LAIs in the USA are organisational facets such as worry about the time and effort that psychiatrists require for prescribing LAIs (justification to private insurance companies), erroneous concepts about cost, and the lack of experience that there is in the medical staff and patients requiring their use.
In the past few years, Spain has seen the arrival of a series of organisational changes that are worth mentioning. They can be summarised as follows:
- 1.
Before the 1986 General Healthcare Law was approved,37 there was no unitary standard to regulate healthcare service for mental health problems in the Spanish public healthcare system. The development of such a law brought about a radical change in healthcare service, mostly stemming from imbalanced resource funding, resources that fell far behind those available in general healthcare service.38
- 2.
Gradual transfer of healthcare responsibilities to the Autonomous Communities (which was completed in December 2001) meant that the healthcare transformation mentioned was conducted with notable territorial differences. It also sometimes followed several lines or models that differed in both healthcare service organisation and coordination/implementation of alternate social services or support services for patients with mental disorders (continuance/disappearance of beds for medium-/long-term psychiatric stay; public or subcontracted resource management; prescription control using visas; development and degree of integration of alternate social resources; and so on).
- 3.
In 2007 the Spanish Ministry of Healthcare and Consumer Affairs published “Mental Health Strategy in the National Healthcare System.” In its justification, it pointed out the need to make a shared reflection between the State and the autonomous organisations to “achieve among all of us a more equitable and humanitarian National Healthcare System.”39
- 4.
The data available for recent years (2008–2013) on device use and resources in the European area40,41 show that in Spain there are 40 psychiatric beds per 100,000 inhabitants (the European mean is 72); mean psychiatric hospital discharge in Spain is just over 200 per 100,000 inhabitants (the European mean for admissions was 568 in 2013), and the number of psychiatrists here is 9 per 100,000 inhabitants (the mean for all of Europe is the same, but it is 12.9 in the EU-15 zone countries it is 12.9).41 In addition, in contrast to all the countries in our surrounding, Spain has no speciality of child and adolescent psychiatry.
- 5.
The data related to mean stay for patients diagnosed with schizophrenia, schizotypal personality disorder and delusional disorder are highly heterogeneous. Mean stay is 32 days in Spain, and it is interesting to note that variability in this factor may be related to very different healthcare organisations and traditions (for example, in the United Kingdom, the mean stay is 109 days, while in the USA, it falls short of 10 days).41
As an overall summary of the preceding, the hypothesis – not yet proven by any specific study – could be proposed that there are two factors promoting greater use of LAI formulations in the treatment of individuals with schizophrenia: the relatively recent development of a thorough renovation of the Spanish healthcare services model (a dynamic, ongoing process) and a purposeful (and sometimes “forced”) preference for outpatient care (the number of beds and the mean stays are comparatively lower than in the countries in our environment).
Clinical practice guidelines and therapeutic availabilityClinical practice guidelines (CPGs) represent a set of recommendations based on systematic evidence review and assessment of the risks and benefits of different alternatives. The objective of such guidelines is to optimise patient healthcare. Together with the consensuses of experts, CPGs have the potential to reduce variability in healthcare attention and to improve clinical practice. In Spain there are several guidelines and expert consensuses that cover the use of second-generation long-lasting antipsychotics from the initial phases of the disease. The Spanish clinical consensus on “Adherence to Treatment in Schizophrenia” published in 2007, in which 383 psychiatrists participated, includes the first-line recommendation of establishing second-generation LAI antipsychotics as a strategy to improve treatment adherence in outpatients with a recent diagnosis of psychosis (less than 2 years of evolution),42 without forgetting the need to intensify non-pharmacological treatment in this type of patient as well. These recommendations would reflect the preoccupation with adherence that Spanish psychiatrists share and second-generation LAI antipsychotics have been viewed for years as a good option for improving adherence and preventing deterioration from the initial disease phases. In addition, the clinician's level of involvement when it comes to presenting a treatment is a key factor in having the patient choose it. Along this line, the lack of LAI prescription in the early stages of the disease suggests that many clinicians in this country have not incorporated the recommendations of these clinical guidelines into their standard practice.43 Another important aspect in accepting this type of treatments is whether these drugs are immediately available once they have been presented to the patient as a therapeutic possibility; the Spanish public healthcare service generally offers this availability to commence injectable treatment at any moment throughout the course of the disease with few limitations.
Continuing with this line of recommendations, the work group for the clinical and therapeutic guidelines on first episodes of psychosis in childhood and adolescence of the Centre for the Network of Biomedical Research on Mental Health (Spanish acronym CIBERSAM) has emphasised that there is an elevated risk that children and adolescents with early-onset schizophrenia will interrupt treatment, regardless of the second-generation antipsychotics prescribed.44 It is suggested that second-generation LAI antipsychotics, if available, should be considered in these patients because of the advantages that they offer related to therapeutic adherence, the ability to ensure that the drug is taken at the prescribed dosage and the safety that LAIs represent (given that any lack of response would not be due to non-adherence, but to treatment resistance).
In agreement with these recommendations from expert professionals in the Spanish setting, the French Association of Biological Psychiatry and Neuropsychopharmacology has published (2013) a guideline on the use and management of long-lasting injectable antipsychotics in severe mental disorder; the first-line recommendation included by the experts is second-generation LAI antipsychotics as the best option in maintenance treatment after the first episode of psychosis and as the maintenance treatment for recent-onset schizophrenia.45 However, the guideline issued by the United Kingdom National Institute for Health and Care Excellence does not include the use of LAI antipsychotics among the indications for treatment of the first episodes of psychosis and indicates this option for only patients that ask for it.46 This mode of treatment is also ignored for recent-onset psychosis in the 2010 American Psychiatric Association's practical guideline for the treatment of patients with schizophrenia, which recommends it for patients with poor adherence or with recurrent flare-ups.47
This difference between the CPG recommendations from country to country accords with the frequency of prescribing LAI antipsychotics mentioned previously.
Using long-acting injectable antipsychotics in special populationsAcute unitsAlthough LAI antipsychotics are formulations designed for long-term maintenance treatment in stable patients, it is not rare to see this type of treatment initiated during hospitalisation in patients admitted for a psychotic decompensation. This practice is based on a series of factors: (a) many patients are admitted after abandoning their oral medication, which justifies attempting a different pharmacological strategy; (b) the hospital framework makes it easier for patients to begin an injectable treatment because more time is available to discuss the pros and cons of LAI use with patients and their families, and patients can accept the fact that the injectable may prevent the undesirable experience of a future hospitalisation like the one being experienced now; and (c) there is a presumption that treatment adherence will be better if patients do not have the opportunity to abandon the treatment immediately after hospital discharge. However, literature on the matter is limited. In the cohort study by Tiihonen et al.,8 in which 2588 patients with schizophrenia that had been admitted to hospital for the first time were followed up, 54.3% were no longer following any drug treatment by the end of 30 days following discharge. The patients that had begun treatment with LAI antipsychotics during hospitalisation had a risk 50–65% lower of being readmitted than those discharged on an oral medication regime, despite the fact that it is precisely the patients that supposedly will have worse treatment adherence are the ones that are more likely to receive LAI antipsychotics before hospital discharge.
First episodesApproximately 80% of the first episodes of psychosis (FEP) belong to what is called (DSM-5) “schizophrenia spectrum disorder”,48 although the epistemological diversity of this set of disorders as well as its more than controversial clinical entity must be remembered.49 Early detection and treatment are essential to improve the prognosis of a first episode of psychosis.50 Focusing on what is called the critical period of psychoses (the first 3–5 years), proper therapeutic fulfilment of the antipsychotic treatment is the single most relevant prognostic variable, modifiable from the clinical point of view, with respect to symptom remission, prevention of relapses and achievement of an optimal quality of life (and to a lesser degree, functional recovery) of the patients that undergo a FEP.51 A controversial subsidiary topic of a thorough research study is the proper duration of antipsychotic treatment after symptom remission or functional recovery, in the absence of biological or clinical markers to justify the decision.52 As we have mentioned before, in agreement with several clinical practice guidelines, the second-generation LAI formulations of antipsychotics are postulated as a first-line treatment for the FEP collective.45,53–55 Their prescription increases as professionals, patients and relatives become more familiar with these therapeutic formulations and their proper management.33 A Spanish study on 335 first episodes of psychosis reported that, when they were included in the study, .3% of the patients received LAIs as the only medication and 4.9% were given them combined with oral drugs.56
Children and adolescentsBased on published prescription studies, the use of antipsychotics in children and adolescents has significantly increased in the Western world over the last 15 years.57,58 There may be several reasons behind this growth: second-generation antipsychotics are perceived to offer greater safety, the duration of the treatment once introduced is longer, and the prescription of antipsychotics in non-psychotic disorders has risen. However, these studies on prescribing antipsychotics do not specify how often LAI antipsychotics are prescribed.
The information available about the efficacy and safety of LAI antipsychotics in children and adolescents is limited to case communications and one non-comparative study. Despite this, the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry recommends the use of these formulations in adolescents with schizophrenia, chronic psychotic symptoms and case histories indicating very reduced therapeutic adherence.59 Likewise, in Spain the therapeutic and clinical guidelines on first episodes of psychosis in childhood and adolescence (CIBERSAM45) suggest that the use of second generation LAI antipsychotics should be considered in children and adolescents with early-onset schizophrenia because of the advantages this type of antipsychotic offer, especially in terms of therapeutic adherence. Use of LAI antipsychotics for any indication in children and adolescents is off label prescribing in Spain.
The few studies there are on attitudes towards medication in children and adolescents show that a higher number of hospital admissions is a predictive factor of a positive attitude towards LAI antipsychotics in patients as well as relatives or caregivers.60 In addition, compliance and ease of use are factors in favour of using them, while fear of needles and of pain work against the use of these formulations in this population group.60
In the cases published, LAIs are used in schizophrenia spectrum disorders,61,62 but also in bipolar disorder with and without psychotic symptoms,61 autism,63 anorexia nervosa64 and behavioural alterations.62,65 It would be of significant value to increase the knowledge available about the true use of these drugs, and to study their efficacy and side effects in this population in randomised clinical trials.
DiscussionDrug treatment is an essential component in managing schizophrenia to achieve therapeutic objectives. Within the pharmacological options available, LAI antipsychotics have had a growing role in recent years, especially for improving therapeutic adherence and its influence on preventing relapses. Despite this, and in spite of the fact that LAI antipsychotics have been available since the end of the 1960s, many authors feel that this therapeutic option is underutilised.17,18,66 The reason for this is that patients, relatives or caregivers, and physicians as well, have barriers against them; additional obstacles are others of an organisational or administrative nature. The prescription of LAI antipsychotics in Spain falls around the European mean, although the prescription of second-generation LAI antipsychotics has risen in the past few years and is more than in other countries around us. This increase will probably continue in the coming years, but it should be accompanied by further studies that provide more data on the efficacy and effectiveness of these treatments in normal clinical practice. We have reviewed and presented these aspects and will now briefly discuss some of them.
In Spain, in concordance with other European countries, 15% of the antipsychotics prescribed are LAI formulations. This figure could be considered low, given how extensive the problem of treatment adherence is in these disorders and the benefits that have been shown to appear with the use of LAI antipsychotics. In contrast to the situation in some European countries, second-generation LAI antipsychotics constitute the majority of these prescriptions in Spain. It is possible that a contributing factor in this consists of CPG and consensus recommendations in our environment that began incorporating LAI antipsychotics several years ago as a first-line option in some clinical situations, such as that of recently-diagnosed patients. Other factors that may have spurred Spanish LAI growth are the accessibility of these drugs in most Spanish Autonomous Communities (although not in all of them), as well as the new evidence on the use of these formulations in first episodes and in earlier phases of the disease67,68 and even in acute patients.69,70 This evidence has been obtained using LAI second-generation LAI antipsychotics, which may be encouraging their use beyond patients with problems of long-term adherence and repeated relapses. In addition, it is important not to forget the possible influence of commercial promotion activities linked to the introduction of second-generation LAI antipsychotics. This situation is not limited to Spain: in France, where more LAI antipsychotics are prescribed than in Spain (21% of total prescriptions), the prescription of these formulations has also grown slightly in recent years, and it has done so at the expense of second-generation LAI antipsychotics.71
Both the first- and second-generation LAI antipsychotics have proven their efficacy in the treatment of schizophrenia in placebo-controlled comparative clinical trials.72 These LAI formulations seem to have, especially based on observational studies, advantages over oral antipsychotics in improving adherence and preventing relapses.14 In addition, although the number of studies is limited (as we have just mentioned), second-generation LAI antipsychotic results in patients with a first episode or in early disease stages are promising, so much so that some authors believe that they should be a first-line treatment in first episodes.18 However, randomised clinical trials – pragmatic if possible – are needed to compare these LAI formulations with the oral formulations of the same active agent in order to better define their advantages; studies such as the European Long-acting Antipsychotics in Schizophrenia Trial73 (currently ongoing and in which Spanish centres are participating) fulfil these objective. A recent meta-analysis using indirect comparisons has also contributed to better knowledge of the possible differences between LAIs and their corresponding oral formulations; the results indicate some slight differences in tolerability (compared to oral forms, LAIs are linked with more akinesia, changes in LDL-cholesterol and anxiety, and with less hyperprolactinemia).74 There are few direct comparisons between first- and second-generation LAI antipsychotics in randomised clinical trials,75,76 and there are only 3 randomised clinical trials that have compared different second-generation LAI antipsychotics with each other.77–79 These comparisons have shown important differences in tolerability and impact on quality of life, without any apparent differences in relapses. Apart from that, despite the usefulness of second-generation LAI antipsychotics in first episodes of psychosis, no comparative studies of these drugs in children and adolescents have been published,61 studies that would make it possible to confirm their potential advantages in this population. Lastly, and applicable to both oral and LAI formulations of the antipsychotics, we do not know the proper duration of treatment and the best dosage of these drugs should be in long-term preventative treatment for patients with an acute psychotic episode.3
There is a clear need to expand the existing evidence on the advantages of LAI antipsychotics and the differentiation between the different current pharmacological options. Nevertheless, the use of these formulations has grown and is likely to continue increasing, driven by clinical experience. This is not a new phenomenon in psychopharmacology; an example is how the dosage of antipsychotics (including that of LAI formulations) based on results of registered clinical trials has been gradually modified with the experience and knowledge acquired in clinical practice.18 However, overcoming the current barriers to the prescription of LAI antipsychotics (and a consequent increase in the use of this therapeutic option) will be determined by – besides better understanding of these formulations on the part of patients, caregivers and relatives – the results of research in the areas that have been mentioned.
Conflict of interestsDr Arango has received fees for participating in advisory councils and giving conferences or has received funding for research projects in the last 5 years from: CIBERSAM, Fundación Alicia Koplowitz, Forum, Gedeon Richter, Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Janssen Cilag, Lundbeck, Merck, the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation, the Spanish Ministry of Healthcare, Social Services and Consumer Affairs, the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness, Mutua Madrileña, Otsuka, Pfizer, Roche, Servier, Shire, Schering Plough, Sumitomo-Dainippon, Sunovion and Takeda. Dr Baeza has received fees as a speaker for Janssen and Otsuka-Lundbeck; has received research grants from the Instituto de Salud Carlos III and the Fundación Alicia Koplowitz; and has received travel grants from Janssen and Otsuka-Lundbeck. Dr Bernardo has received fees for consultation or advice or research grants from ABBiotics, Adamed, Almirall, Eli Lilly, Ferrer, Forum Pharmaceuticals, Janssen-Cilag, Lundbeck and Otsuka; has received research grants from the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, the Spanish Ministry of Science and Education, Culture and Sport, the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness, the Centre for the Network of Biomedical Research on Mental Health (Spanish acronym CIBERSAM), the Government in Catalonia, Secretaria d’Universitats i Recerca del Departament d’Economia i Coneixement (2014SGR441), the European Group for Research in Schizophrenia (EGRIS) and the 7th European Union Framework Program. Dr Cañas is a member of advisory committees for Lundbeck, Janssen Cilag, Otsuka and Servier; and has received fees as a speaker for Lundbeck, Janssen Cilag, Otsuka and Servier. Dr de Dios a member of the Lundbeck advisory committee; has received research grants from Fondo Investigaciones Sanitarias and Fondos FEDER; and has received fees as a speaker for Janssen-Cilag, Lundbeck and Pfizer. Dr García-Portilla has been a consultant or has received fees or grants from Alianza Otsuka-Lundbeck, CIBERSAM, the European Commission, Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Janssen-Cilag, Lilly, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Pfizer, Servier, Roche and Rovi. Dr Gutiérrez-Rojas has been a speaker and a member of advisory committees for Janssen-Cilag, Astra-Zeneca, Rovi, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Exeltis and Pfizer. Dr Olivares has been a member of advisory committees or a consultant for Astra-Zeneca, Eli Lilly, Janssen-Cilag, Lundbeck, Otsuka y Sanofi-Aventis; and has received fees as a researcher or speaker for Janssen-Cilag, Lundbeck, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Sanofi-Aventis and Pfizer. Dr Rico-Villademoros has received fees for consulting, giving training sessions or providing medical writing services for AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Janssen-Cilag, Lundbeck, Otsuka and Pfizer; and has participated in the editing of this manuscript with Alianza Otsuka-Lundbeck funding. Dr Rodríguez-Jiménez has been a consultant for, a speaker in activities for, or has received grants from: Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria (FIS), the Centre for the Network of Biomedical Research on Mental Health (CIBERSAM), the Community of Madrid (S2010/BMD-2422 AGES), Janssen-Cilag, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Pfizer, Ferrer and Juste. Dr Sánchez-Morla has received research grants from Instituto de Salud Carlos III and the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness; and has received travel grants from Janssen-Cilag and Otsuka. Dr Segarra has received funding for research projects and/or fees as a consultant or speaker from the following companies and organisations: Astra Zeneca, Bristol Myers-Squibb, Eli Lilly, Glaxo-Smith-Kline, Janssen Cilag, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Pfizer, Sanofi-Aventis, Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Basque Government, CIBERSAM and MINECO. Dr Crespo-Facorro has received fees as a speaker for Otsuka and Lundbeck.
To coordinate this article, Alianza Otsuka–Lundbeck has provided non-financial support (literature search, market data, etc.). No pharmaceutical company has revised this article or made any type of petition about its content.
| First author and year | Title | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Studies on the use of medications and pharmacoeconomics | ||
| Gaviria 2017 | Noninterventional, naturalistic, retrospective study to describe prescription patterns of long-acting injectable antipsychotics and the impact of introducing a new atypical antipsychotic in the Spanish province of Tarragona catchment area | Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2017;19(2). https://doi.org/10.4088/PCC.16m02044 |
| Berrouiguet 2016 | Development of a web-based clinical decision support system for drug prescription: Non-interventional naturalistic description of the antipsychotic prescription patterns in 4345 outpatients and future applications | PLoS One. 2016;11(10):e0163796 |
| Vázquez-Mourelle 2016 | [Efficiency of a pharmaceutical care program for long-acting parenteral antipsychotics in the health area of Santiago de Compostela] | Gac Sanit. 2016;30(1):73–6 |
| Quintero 2016 | Cost-minimisation analysis of paliperidone palmitate long-acting treatment versus risperidone long-acting treatment for schizophrenia in Spain | Clin Drug Investig. 2016;36(6):479–90 |
| Gaviria 2015 | A non-interventional naturalistic study of the prescription patterns of antipsychotics in patients with schizophrenia from the Spanish province of Tarragona | PLoS One. 2015;10:e0139403 |
| Bernardo 2012 | Antipsychotic polypharmacy in a regional health service: a population-based study | BMC Psychiatry. 2012;12:42 |
| Alda Díez 2010 | Differences in the diagnosis and treatment of immigrant and local psychiatric inpatients admitted to a general hospital in Spain: a controlled study | Actas Esp Psiquiatr. 2010;38(5):262–9 |
| Arilla 2010 | [Antipsychotic polypharmacy in a general hospital in-patient psychiatric unit] | Rev Psiquiatr Salud Ment. 2010;3(3):90–6 |
| Lerma-Carrillo 2008 | Antipsychotic polypharmacy in patients with schizophrenia in a brief hospitalization unit | Clin Neuropharmacol. 2008;31(6):319–32 |
| Olivares 2008 | Cost-effectiveness analysis of switching antipsychotic medication to long-acting injectable risperidone in patients with schizophrenia: a 12- and 24-month follow-up from the e-STAR database in Spain | Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2008;6(1):41–53 |
| Haro 2003 | The European Schizophrenia Outpatient Health Outcomes Study: baseline findings across country and treatment | Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 2003;(416):7–15 |
| Kiivet 1995 | Patterns of drug treatment of schizophrenic patients in Estonia, Spain and Sweden | Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1995 Nov;40(5):467–76 |
| Studies on effectiveness and other related results in adults (general) | ||
| Fernández-Miranda 2015 | Effectiveness, good tolerability, and high compliance of doses of risperidone long-acting injectable higher than 75mg in people with severe schizophrenia: a 3-year follow-up | J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015;35(6):630–4 |
| Acosta 2014 | Influence of antipsychotic treatment type and regimen on the functionality of patients with schizophrenia | Nord J Psychiatry. 2014;68(3):180–8 |
| Acosta 2014b | Should full adherence be a necessary goal in schizophrenia? Full versus non-full adherence to antipsychotic treatment | Compr Psychiatry. 2014;55(1):33–9 |
| Palmarola-Ginesta 2014 | [Medication adherence and use of health services in patients with psychosis in the region of Osona (Catalonia, Spain)] | Rev Enferm. 2014;37(4):50–7 |
| San 2013 | Socio-demographic, clinical and treatment characteristics of relapsing schizophrenic patients | Nord J Psychiatry. 2013;67(1):22–9 |
| Ciudad 2012 | Relapse and therapeutic interventions in a 1-year observational cohort study of nonadherent outpatients with schizophrenia | Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2012;36(2):245–50 |
| Bravo-Ortiz 2011 | Influence of type of treatment on the well-being of Spanish patients with schizophrenia and their caregivers | Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract. 2011;15(4):286–95 |
| Gutiérrez-Casares 2010 | Adherence to treatment and therapeutic strategies in schizophrenic patients: the ADHERE study | CNS Spectr. 2010;15(5):327–37 |
| Olivares 2009 | Long-term outcomes in patients with schizophrenia treated with risperidone long-acting injection or oral antipsychotics in Spain: results from the electronic Schizophrenia Treatment Adherence Registry (e-STAR) | Eur Psychiatry. 2009;24(5):287–96 |
| Arango 2008 | Randomised clinical trial comparing oral versus depot formulations of zuclopenthixol in patients with schizophrenia and previous violence | Eur Psychiatry. 2006;21(1):34–40 |
| Studies on acute units | ||
| Parellada 2017 | An open-treatment six-week study of the clinical effectiveness of Paliperidone Palmitate in schizophrenia: data from acute units in Spain (SHADOW study) | Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract. 2017:1–9 |
| De la Gándara 2009 | Experience with injectable long-acting risperidone in long-term therapy after an acute episode of schizophrenia: the SPHERE Study | Expert Rev Neurother. 2009;9(10):1463–74 |
| Studies on first episodes of psychosis or recent-onset psychosis | ||
| Bioque 2016 | A Pharmacovigilance study in first episode of psychosis: psychopharmacological interventions and safety profiles in the peps project | Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016;19(4) pii: pyv121. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyv121 |
| Barrio 2013 | Effectiveness of long-acting injectable risperidone versus oral antipsychotics in the treatment of recent-onset schizophrenia: a case-control study | Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2013;28(4):164–70 |
| Studies on children and adolescents | ||
| Fortea 2018 | Long-acting injectable atypical antipsychotic use in adolescents: An observational study | J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1089/cap.2017.0096 |
| Fàbrega 2015 | Two cases of long-acting paliperidone in adolescence | Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2015;5(5):304–6 |
| Studies on safety/tolerability and communication of adverse reactions | ||
| Sanchez-Martinez 2017 | Metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk in people treated with long-acting injectable antipsychotics | Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2017. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871530317666171120151201 |
| Martín Arias 2017 | Risk excess of mortality and use of antipsychotics: a case-noncase study | Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2017;32(1):1–5 |
| Duran-Sindreu 2013 | [Olanzapine long-acting post-injection syndrome: a case report and brief review] | Actas Esp Psiquiatr. 2013;41(1):60–2 |
| Montalvo 2013 | Changes in prolactin levels and sexual function in young psychotic patients after switching from long-acting injectable risperidone to paliperidone palmitate | Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2013;28(1):46–9 |
| Montejo 2010 | Frequency of sexual dysfunction in patients with a psychotic disorder receiving antipsychotics | J Sex Med. 2010;7(10):3404–13 |
| Ramos-Ríos 2010 | QTc interval in a sample of long-term schizophrenia inpatients | Schizophr Res. 2010;116(1):35–43 |
| Garcia-Unzueta 2003 | Alterations of liver function test in patients treated with antipsychotics | J Clin Lab Anal. 2003;17(6):216–8 |
| Herrán 2000 | Higher levels of serum copper in schizophrenic patients treated with depot neuroleptics | Psychiatry Res. 2000;94(1):51–8 |
| de Leon 1990 | Neuroleptic-induced catatonia: neuroleptic malignant syndrome? | Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1990;14(1):129–36 |
| Other studies | ||
| Palomares 2015 | Effectiveness of long-acting paliperidone palmitate in borderline personality disorder | Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015;30(6):338–41 |
| González-Rodríguez 2014 | Effectiveness of long-acting injectable antipsychotics in delusional disorders with nonprominent hallucinations and without hallucinations | Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2014;29(3):177–80 |
| Martinez-Gras 2009 | The relationship between prepulse inhibition and general psychopathology in patients with schizophrenia treated with long-acting risperidone | Schizophr Res. 2009;115(2–3):215–21 |
| Díaz-Marsá 2008 | [Long-acting injectable risperidone in treatment resistant borderline personality disorder. A small series report] | Actas Esp Psiquiatr. 2008;36(2):70–4 |
| Vieta 2008 | A long-term prospective study on the outcome of bipolar patients treated with long-acting injectable risperidone | World J Biol Psychiatry. 2008;9(3):219–24 |
The search was conducted in PubMed up to 3 March 2018 using the terms “long acting”, “depot” or “injectable” in title or abstract, crossing with the terms “antipsychotic” or “neuroleptic” in title or abstract and with the terms “spain” or “spanish” in title or abstract, or “spain” in affiliation. With these criteria, 82 registers were found, excluding from this list any registers that were not clinical studies or that did not present data specific to Spain.
Please cite this article as: Arango C, Baeza I, Bernardo M, Cañas F, de Dios C, Díaz-Marsá M, et al. Antipsicóticos inyectables de liberación prolongada para el tratamiento de la esquizofrenia en España. Rev Psiquiatr Salud Ment (Barc). 2019;12:92–105.






![Commercialisation in Spain of long-lasting intramuscular antipsychotics. Source: Data based on the information contained in the Online Medicine Information Centre of the Spanish Agency of Medicine and Healthcare Products [accessed on 24.10.17]. Available at: https://www.aemps.gob.es/cima/fichasTecnicas.do?metodo=detalleForm. Commercialisation in Spain of long-lasting intramuscular antipsychotics. Source: Data based on the information contained in the Online Medicine Information Centre of the Spanish Agency of Medicine and Healthcare Products [accessed on 24.10.17]. Available at: https://www.aemps.gob.es/cima/fichasTecnicas.do?metodo=detalleForm.](https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/21735050/0000001200000002/v1_201907130752/S2173505019300160/v1_201907130752/en/main.assets/thumbnail/gr1.jpeg?xkr=ue/ImdikoIMrsJoerZ+w96p5LBcBpyJTqfwgorxm+Ow=)