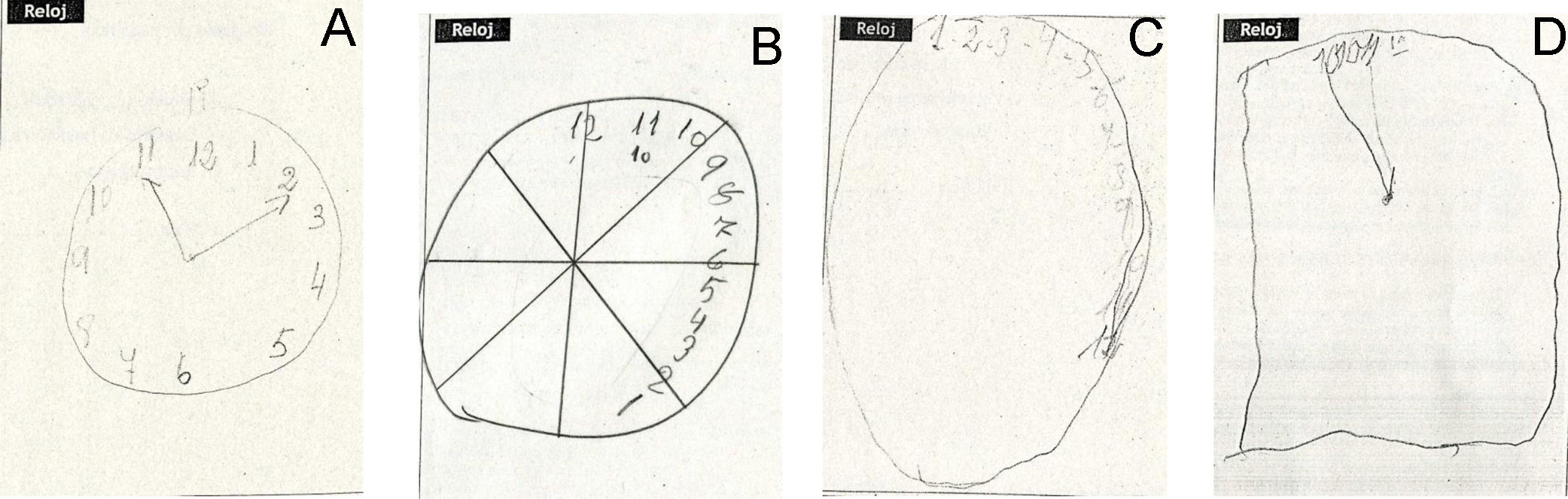
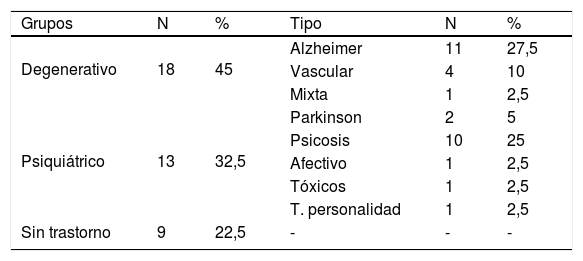
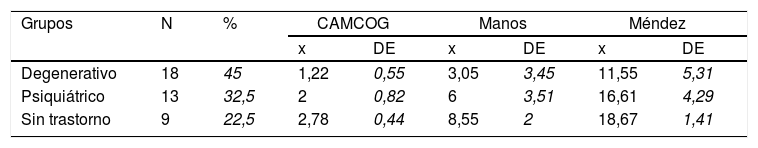
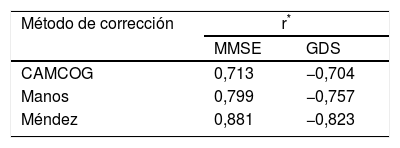
El test del reloj es una prueba de cribado neuropsicológico que se utiliza con frecuencia en la práctica clínica.
ObjetivoValorar la utilidad del test del reloj en el ámbito forense. Evaluar 3métodos de corrección, explorar la fiabilidad y validez, y valorar su utilidad en procesos judiciales de modificación de la capacidad de obrar.
Material y métodosSe analizaron 40 casos incursos en procedimientos judiciales. Se realizó una entrevista clínica estructurada, exploración neurológica y psicopatológica a través de la prueba CAMDEX-R. Se administró el Mini-Mental State Examination, la Global Deterioration Scale y el test del reloj a la orden corregido con los métodos de CAMCOG, Manos y Méndez. La muestra se dividió en 3grupos: degenerativo, psiquiátrico y sin trastorno.
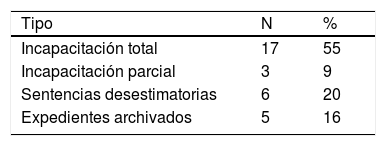
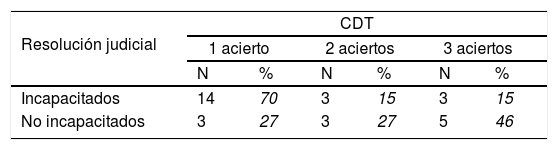
ResultadosEl grupo degenerativo es el que obtuvo peores resultados en el test del reloj en los 3métodos de corrección. La fiabilidad y validez de la prueba resultaron adecuadas. Los pacientes incapacitados judicialmente presentaron peor rendimiento en el test del reloj.
ConclusionesLos 3métodos de corrección del test del reloj se muestran eficaces. Valorando el coste-beneficio, se recomienda el método más breve. Los pacientes con una sentencia de modificación de la capacidad civil presentan peores resultados en el test del reloj.
The clock drawing test is a neuropsychological screening test that is frequently used in clinical practice.
AimTo evaluate the usefulness of the clock drawing test in the forensic environment. To evaluate 3methods of correction, and to determine its reliability and validity, and assess its usefulness in judicial processes of modification of legal capacity of a person.
Material and methodsA total of 40 cases were analysed in legal proceedings. A structured clinical interview, and a neurological and psychopathological examination were conducted using the CAMDEX-R test. The Mini-Mental State Examination, the Global Deterioration Scale, and the clock drawing test were administered to the order corrected using the CAMCOG, Manos and Méndez methods. The sample was divided into 3groups: degenerative, psychiatric, and without pathology.
ResultsThe degenerative group obtained the worst results in the clock drawing test in the 3correction methods. The reliability and validity of the test were adequate. Patients judged not to be legally capable had a worse performance in the clock drawing test.
ConclusionsThe 3methods of correction of the clock drawing test are shown to be effective. Evaluating the cost-benefit of the short method is recommended. Patients with a modification of legal capacity ruling showed worse results in the clock drawing test.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora