Mental, neurological, substance use, suicide, and related somatic disorders (MNSS, for the Spanish acronym) have a negative impact on the quality-of-life of people and the Mexican economy, but updated information is lacking. The objective of this work is to analyze the disability adjusted life years (DALYs) of the MNSS in Mexico by sex, age, state, and degree of marginalization between 1990 and 2019.
MethodsThe data and methodology of the «Global Burden of Disease Group» (GBD) are used. The GBD calculates DALYs as the sum of two components: years of life lost due to premature mortality (YLL) and years lived with disability (YLD). Likewise, the data on the degree of marginalization from the National Population Council in Mexico are used.
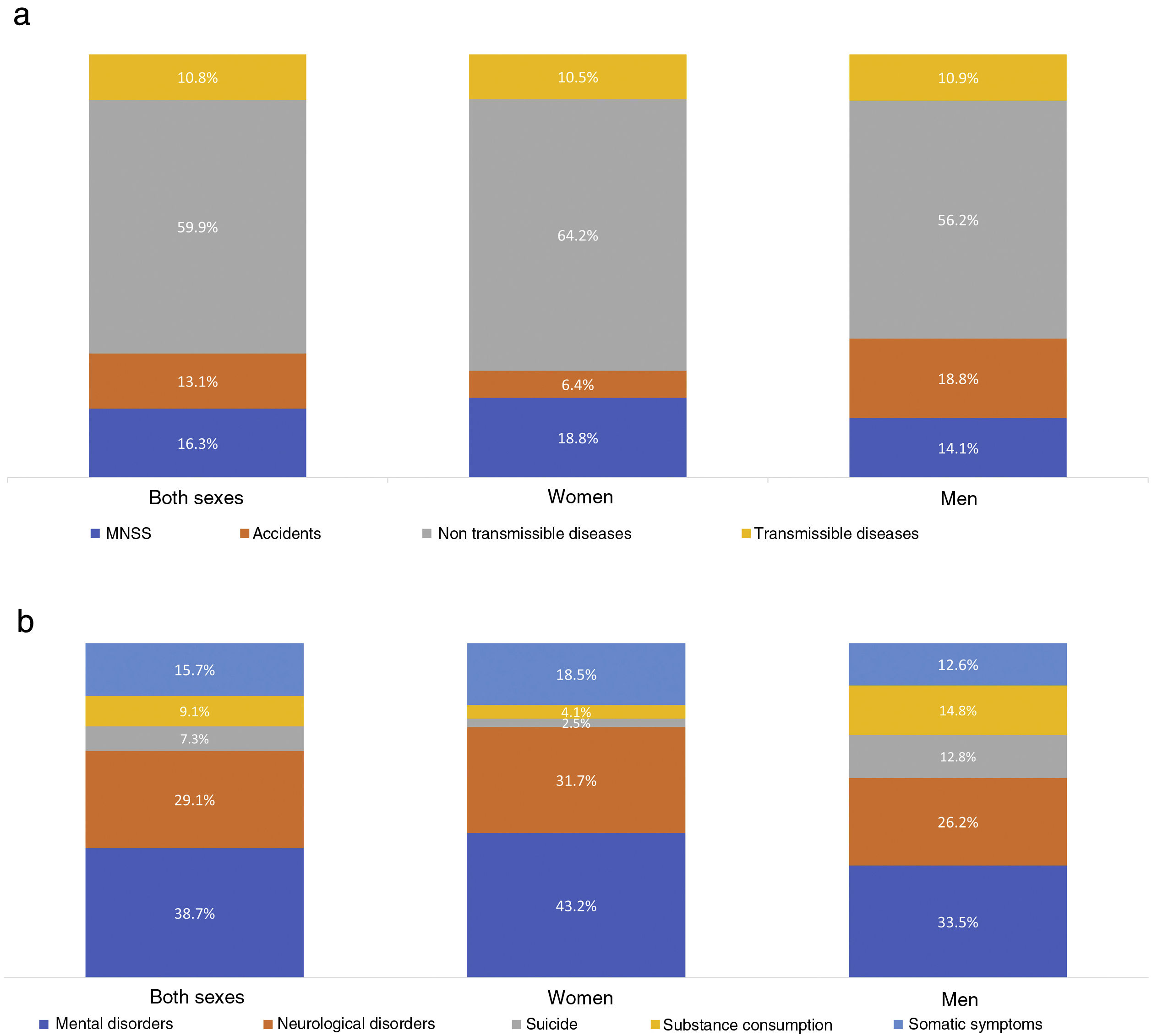
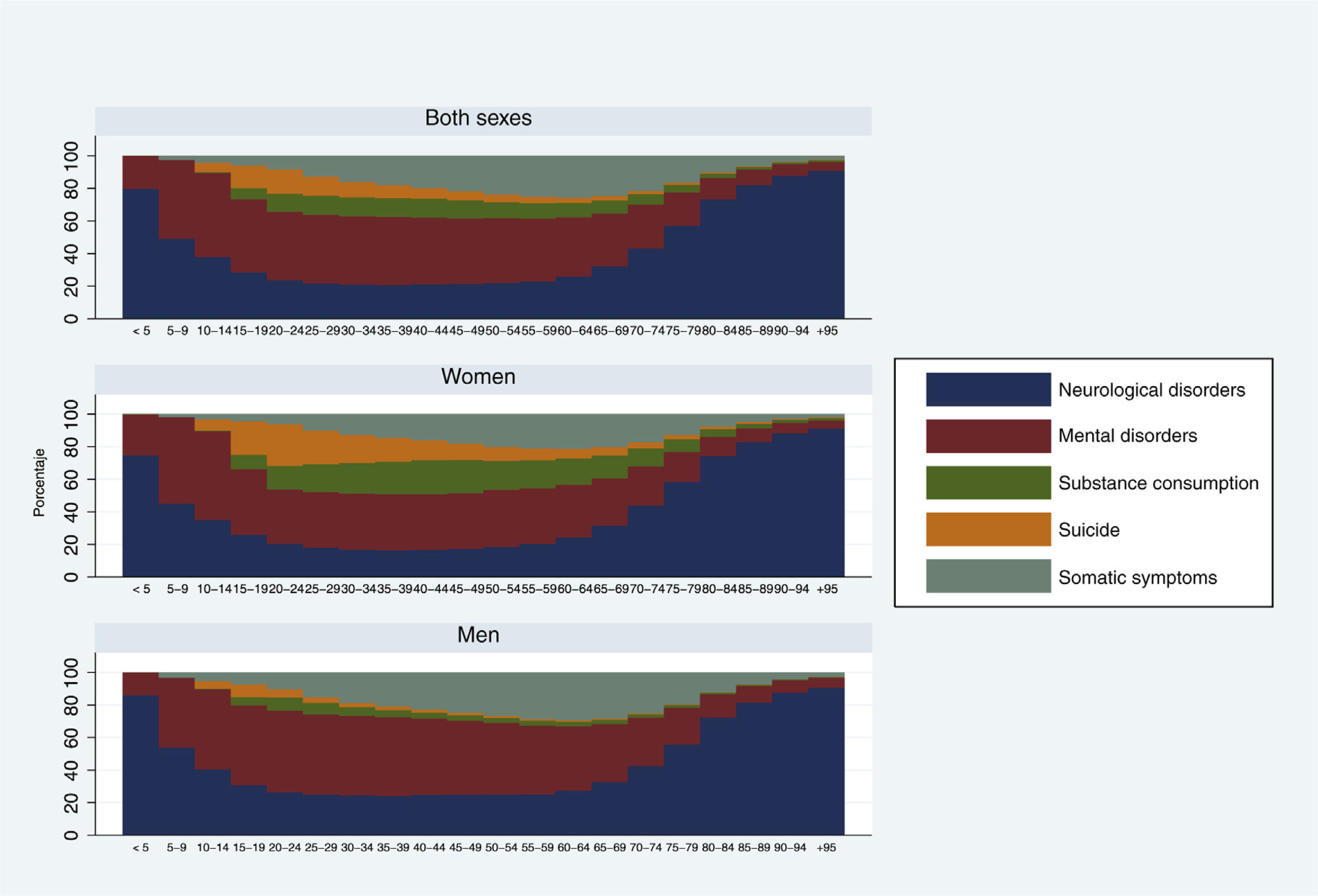
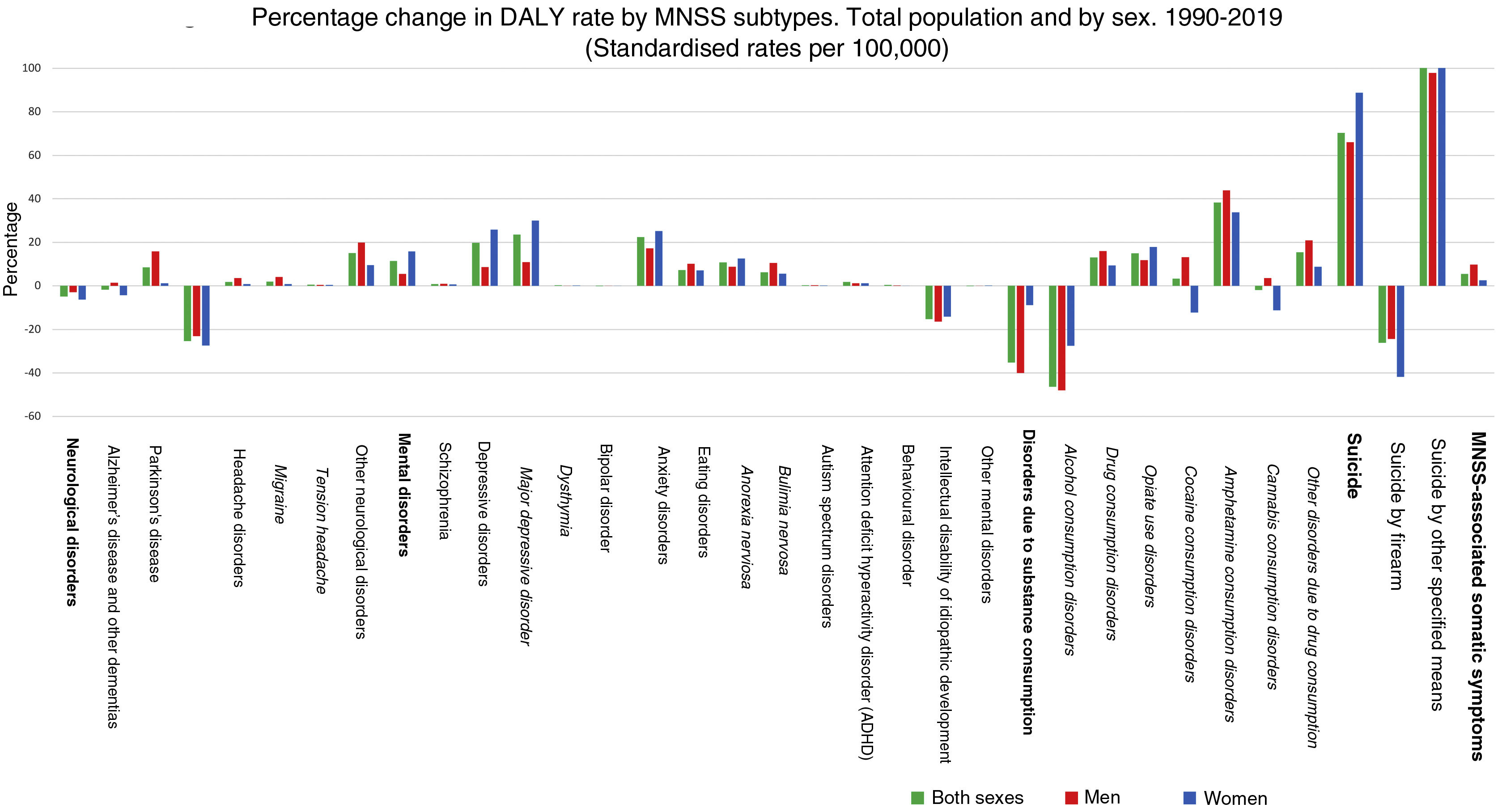
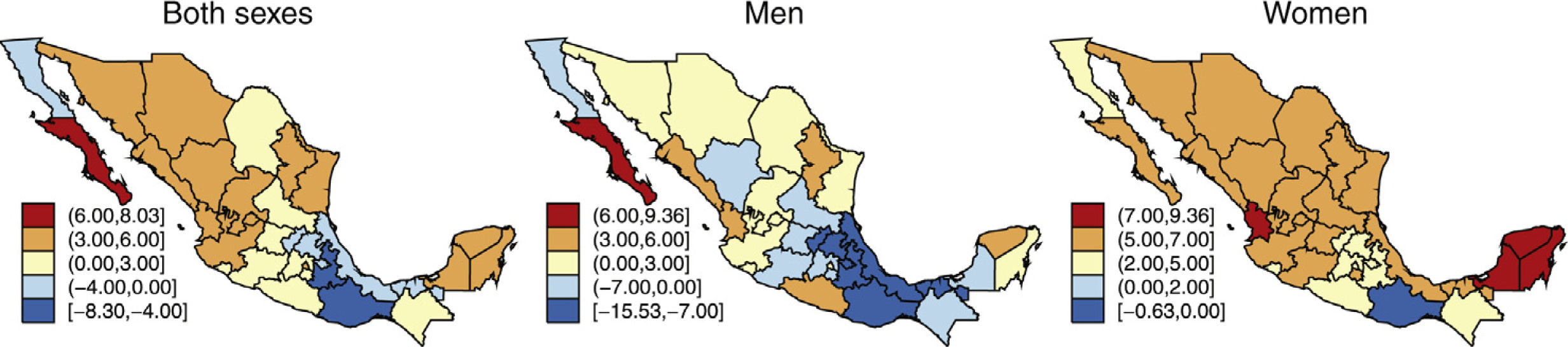
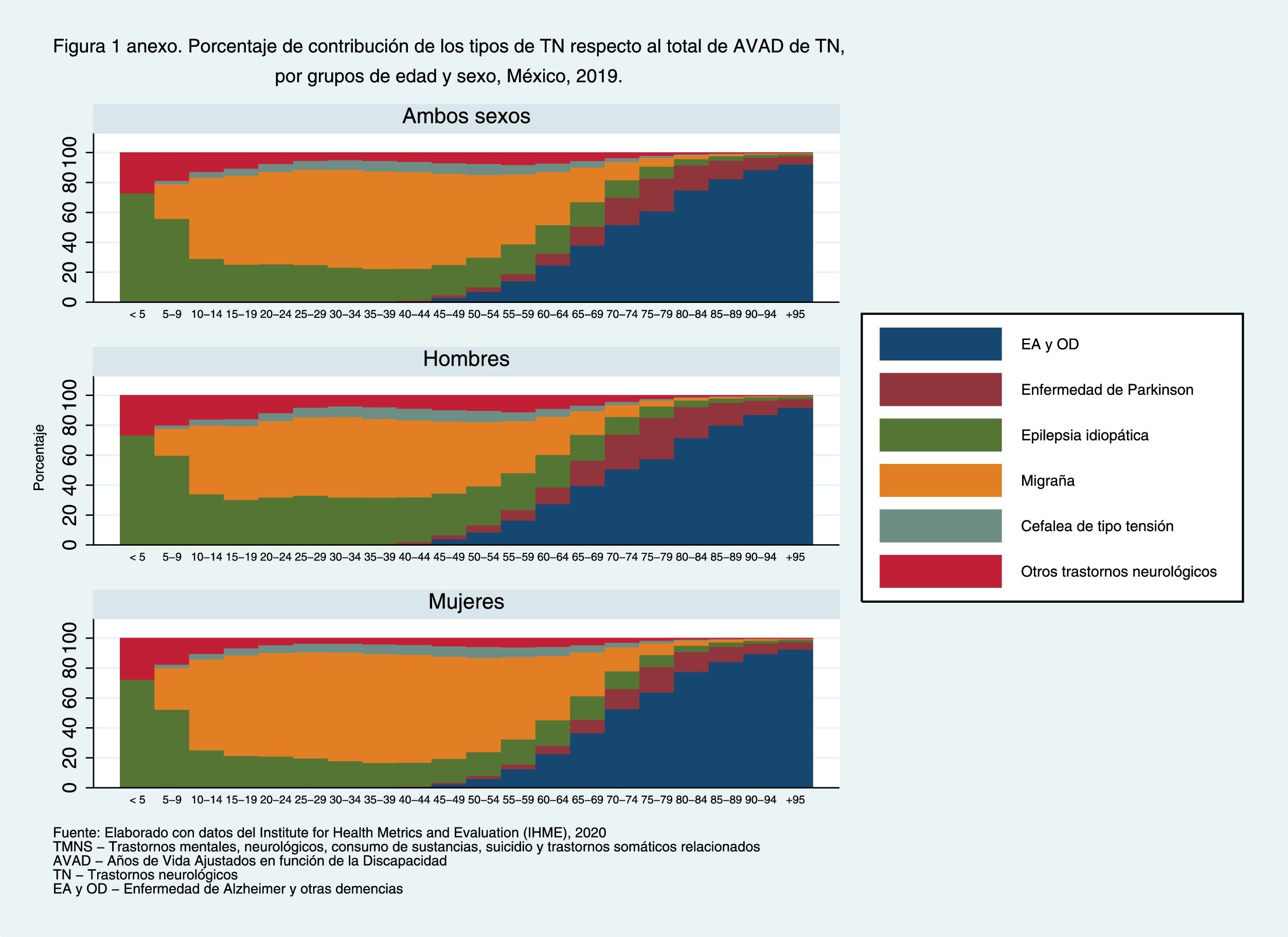
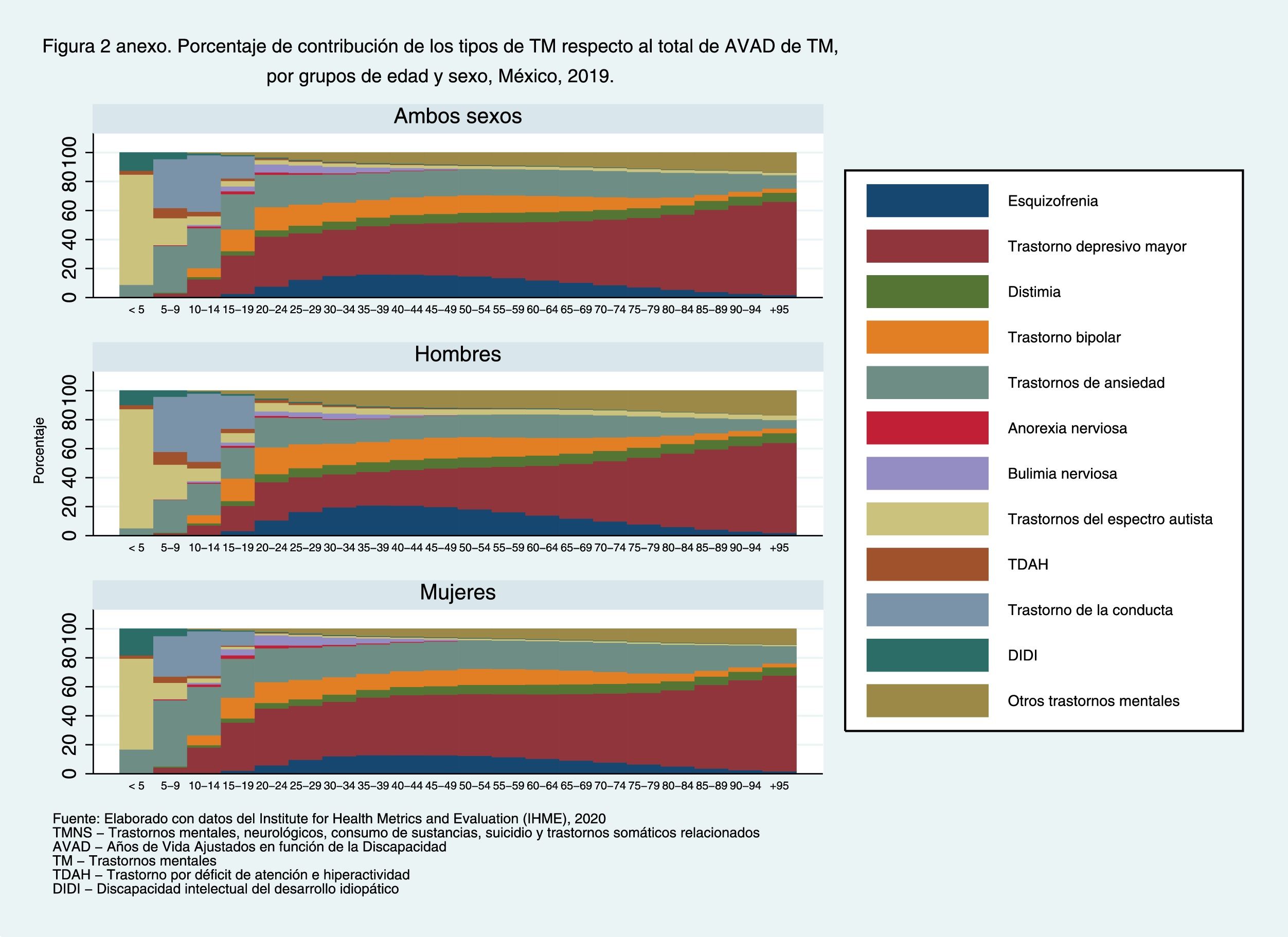
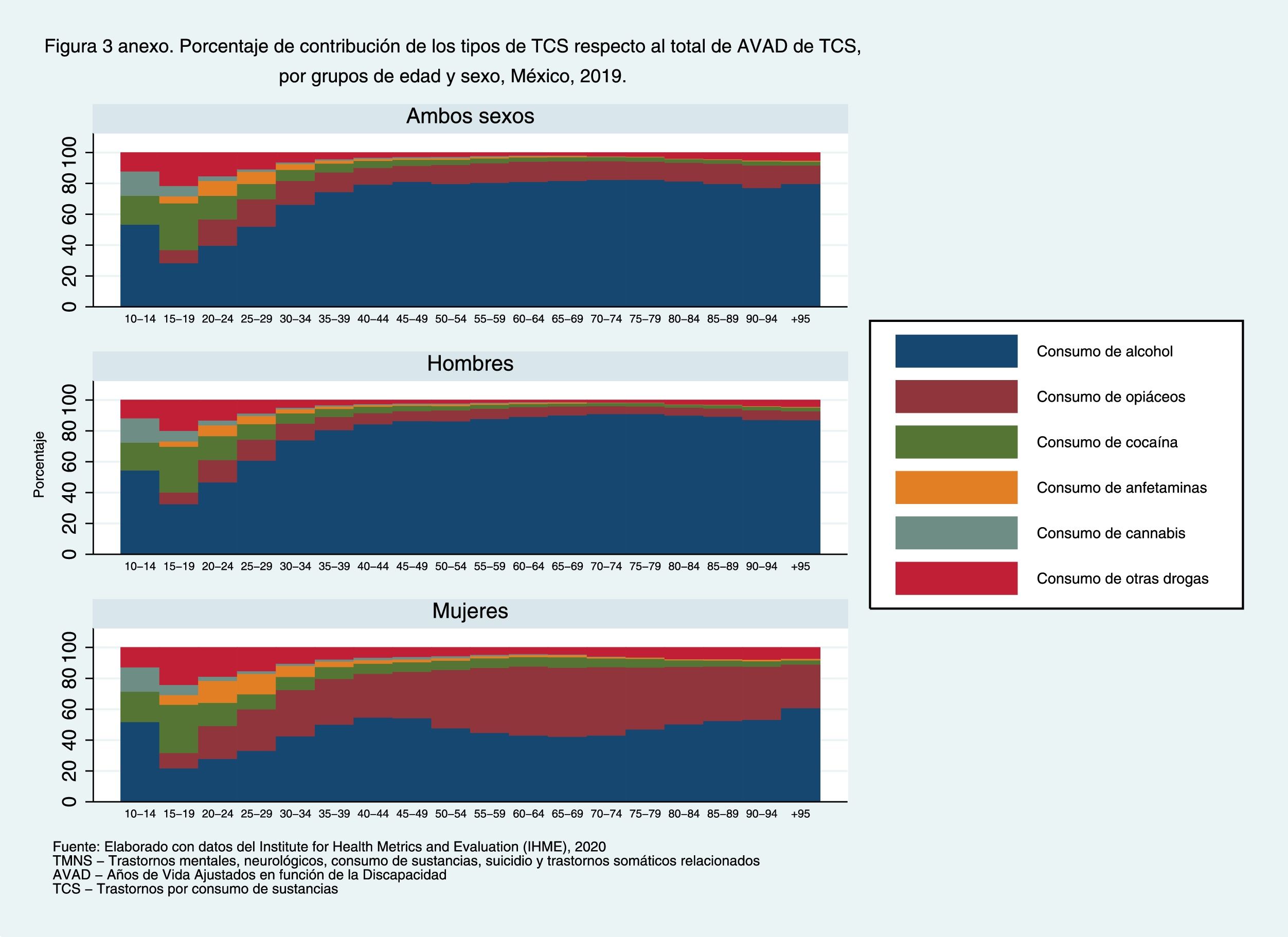
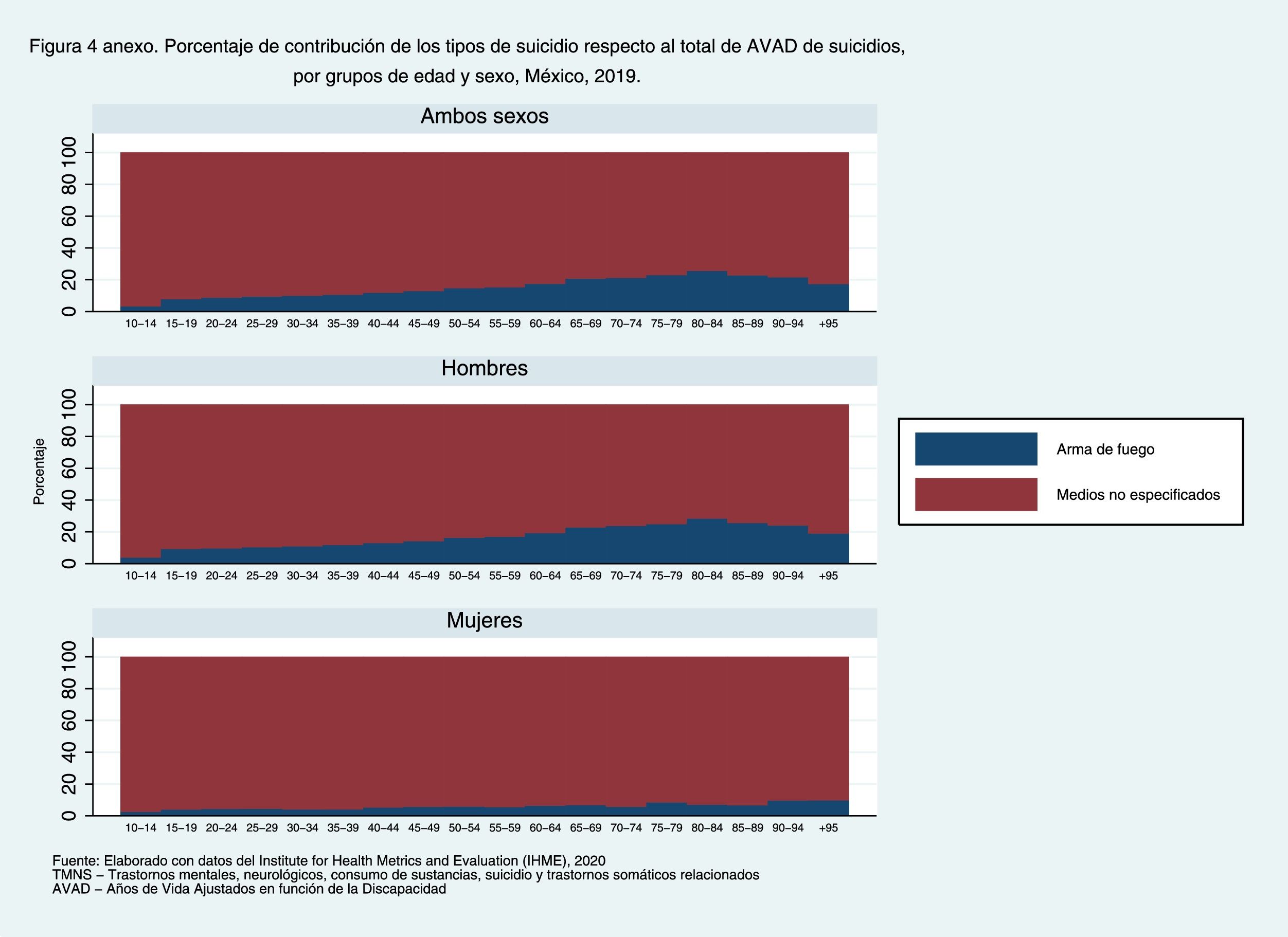
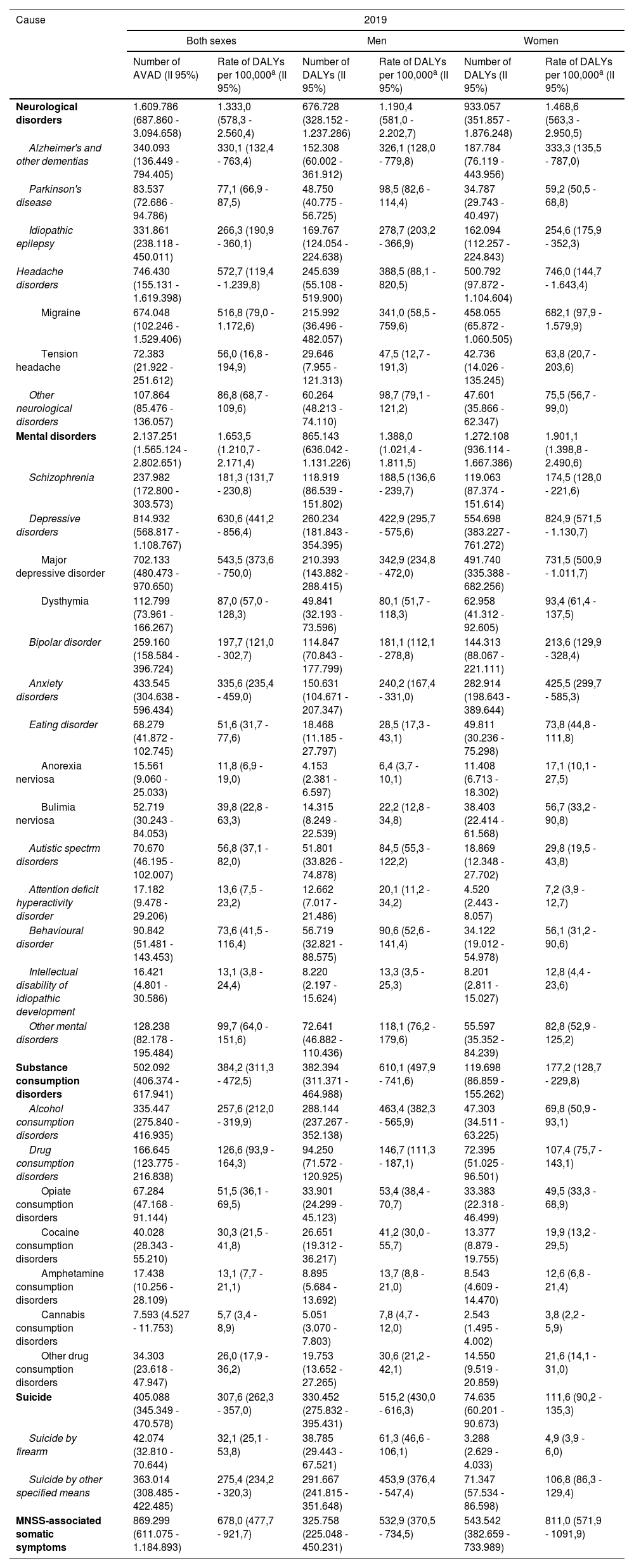
ResultsMNSS represented 16.3% of the disease burden in the Mexican population in 2019. The trend of the age-standardized rates of DALYs of the MNSS has increased little from 1990 to 2019. The highest increase has been for women. Mental (depression) and neurological (headache) disorders contribute the most to the disease burden among MNSS. In the interior of the country, Baja California Sur presented the highest increase in the period.
DiscussionThe results show a complex panorama of the MNSS and its subtypes by sex, age groups and territory. More resources are needed to improve mental health care.