La rehabilitación respiratoria (RR) está indicada en todas las enfermedades respiratorias crónicas con síntomas permanentes y limitación de la capacidad física a pesar de un adecuado tratamiento médico. No obstante, la implantación de unidades de RR es escasa en España. El objetivo de este estudio es conocer el grado de implantación de los programas de rehabilitación respiratoria en España, sus características y distribución.
Material y métodosSe diseñó una encuesta para valorar el número de centros que realizaban RR en España y sus características. Las preguntas de la encuesta son cerradas y se clasifican en diferentes áreas: datos de identificación y localización, recursos materiales y humanos existentes en las unidades de rehabilitación respiratoria, planteamiento de los programas de rehabilitación respiratoria en atención primaria.
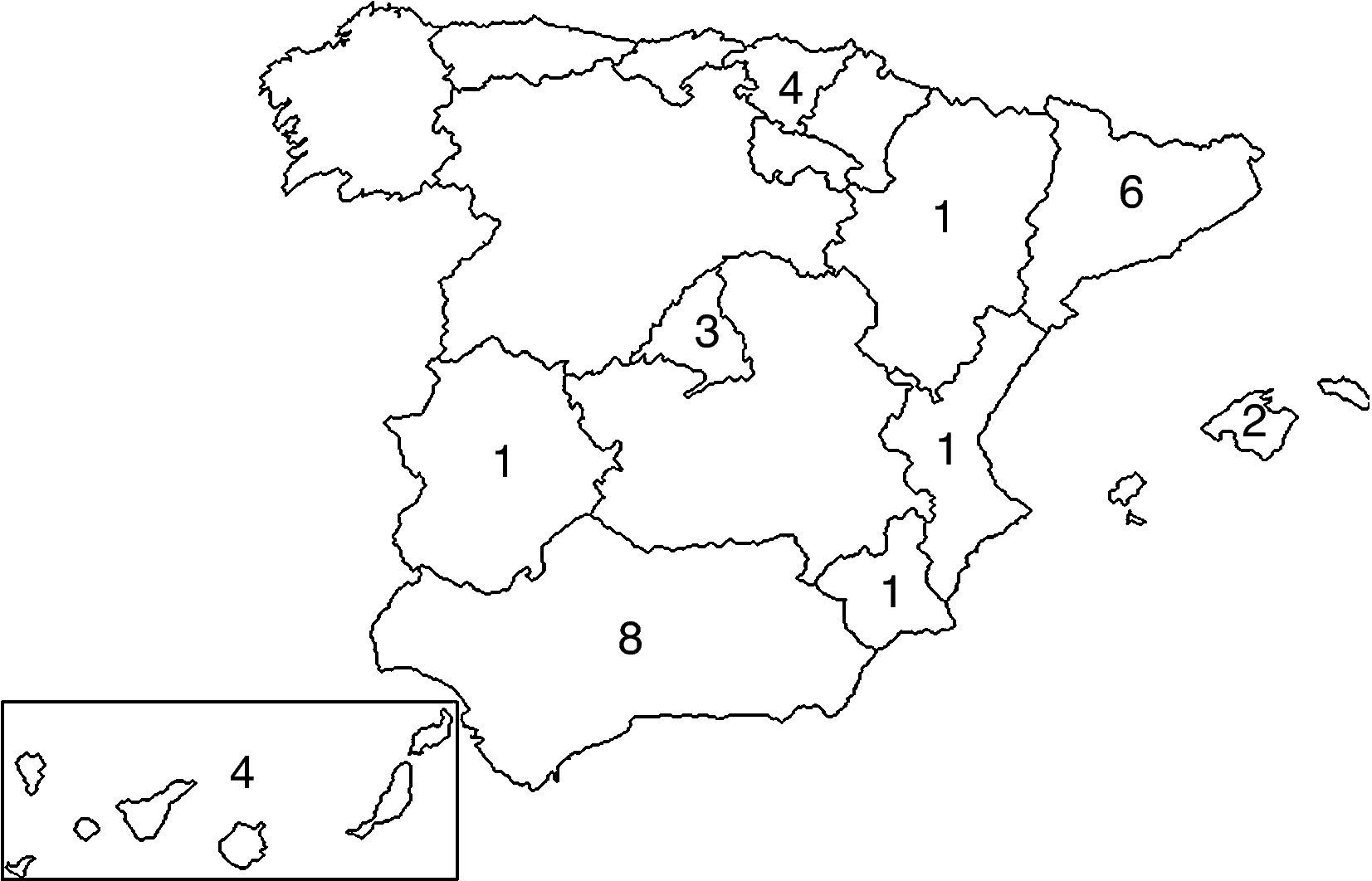
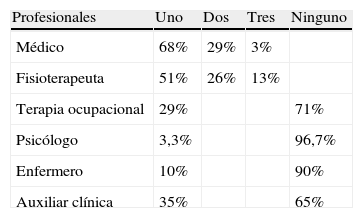
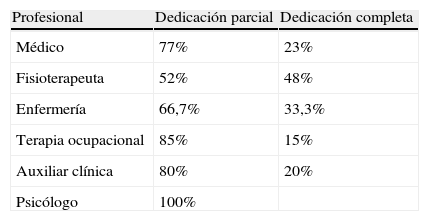
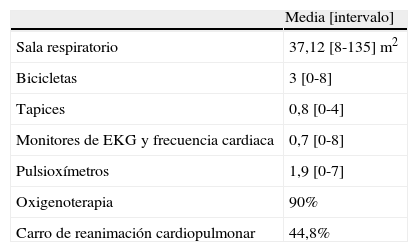
ResultadosRecibimos 66 encuestas, que representan a un total de 15 comunidades autónomas. Existen 31 centros con unidades de RR. De estos, la mayoría se desarrolla en hospitales de tercer nivel (74,2%), le siguen los de segundo (19,4%) y primer nivel (6,5%). La coordinación de estas unidades la realiza el médico rehabilitador en el 93,5%, el rehabilitador y un neumólogo en el 6,5% y el neumólogo en el 3,2%. El número medio de pacientes/unidad tratados al año es 647 (intervalo, 40-2.600), contabilizándose tanto los pacientes tratados de forma ambulatoria como los ingresados. Se desconoce el número de pacientes tratados de forma ambulatoria en programas de RR.
ConclusionesTeniendo en cuenta que la RR es la intervención que más aumenta la calidad de vida, junto al cese del tabaquismo y la optimización del tratamiento médico en la EPOC, creemos que el abordaje de la RR que se hace en España es insuficiente.
Respiratory rehabilitation (RR) is indicated in all chronic respiratory diseases with permanent symptoms and limitation of physical capacity in spite of adequate medical treatment. However, the introduction of RR units is scarce in Spain. The purpose of this study is to known the grade of introduction of respiratory rehabilitation programs in Spain, their characteristics and distribution.
Material and methodsA survey was designed to evaluate the number of centers who perform RR in Spain and their characteristics. The survey questions were closed and were classified into the following areas: data on identification and localization, existing material and human resources in the respiratory rehabilitation units, approach to respiratory rehabilitation in primary care.
ResultsWe received 66 surveys, which accounted for 15 regional communities. There are 31 RR units. Of these, most are within third level hospitals (74.2%), second level (19.4%), and the rest first level (6.5%). The coordination of these Units is carried out by the rehabilitation physician in 93.5%, rehabilitator + pneumologist in 6.5% and by the pneumologist in 3.2%. The mean number of patients/units treated per year is 647 (range, 40-2600), this counting both treated outpatient and inpatients. The number of patients treated as outpatients in the RR program is unknown.
ConclusionsConsidering that the RR is the intervention that increases quality of life most together with smoking cessation and the optimization of medication treatment in COPD, we believe that the RR approach made in Spain is not sufficient.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora