A coronary angiography and percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty in anterior descending artery was performed on a 77-year-old man with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction secondary to dilated cardiomyopathy in the context of new onset heart failure. After the procedure the patient presented with hemodynamic instability due to pericardial tamponade, requiring two additional coronary angiographies to rule out a possible leak from coronary arteries. The three procedures entailed an accumulative dose area product estimated of 1400 Gy.cm2.
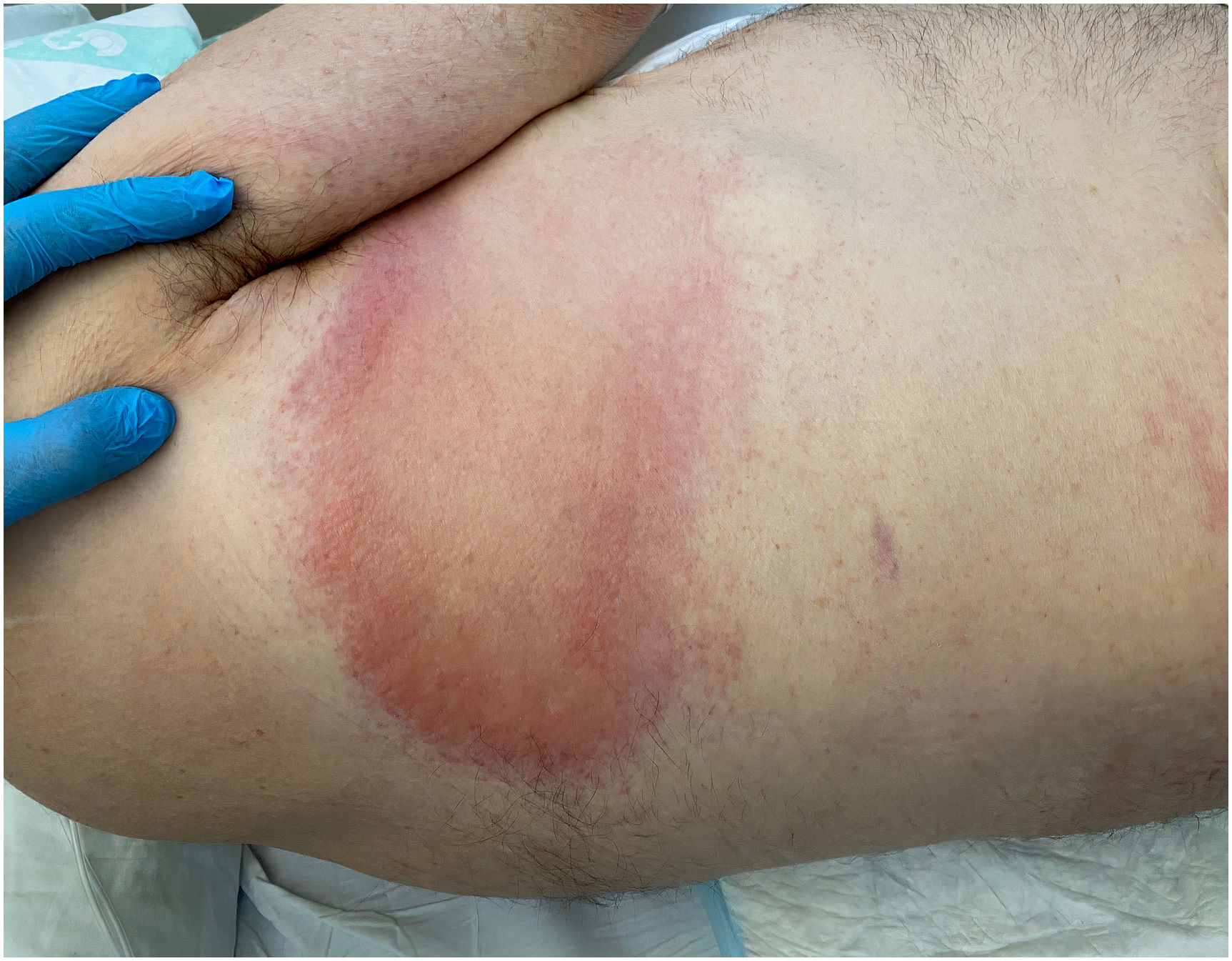
A couple of days after the last procedure the patient presented an asymptomathic erythematous and edematous plaque on the back, close to the right shoulder, with clear edges, vanishing after brief pressure, non scaly and non blistering, with alopecia on the affected area. (Fig. 1).
Clinical diagnosis of acute radiodermatitis was performed and topical corticosteroid once a day was prescribed during ten days with complete resolution of the lesion.
Acute radiodermatitis is nowadays an uncommon finding due to established protocols to avoid iatrogeny. However, prolonged or multiple procedures on account of emergency or cardiovascular complications are a possibility. Therefore cardiologists, radiologists and dermatologists should be aware of this entity to correctly diagnose, treat and follow-up these patients.