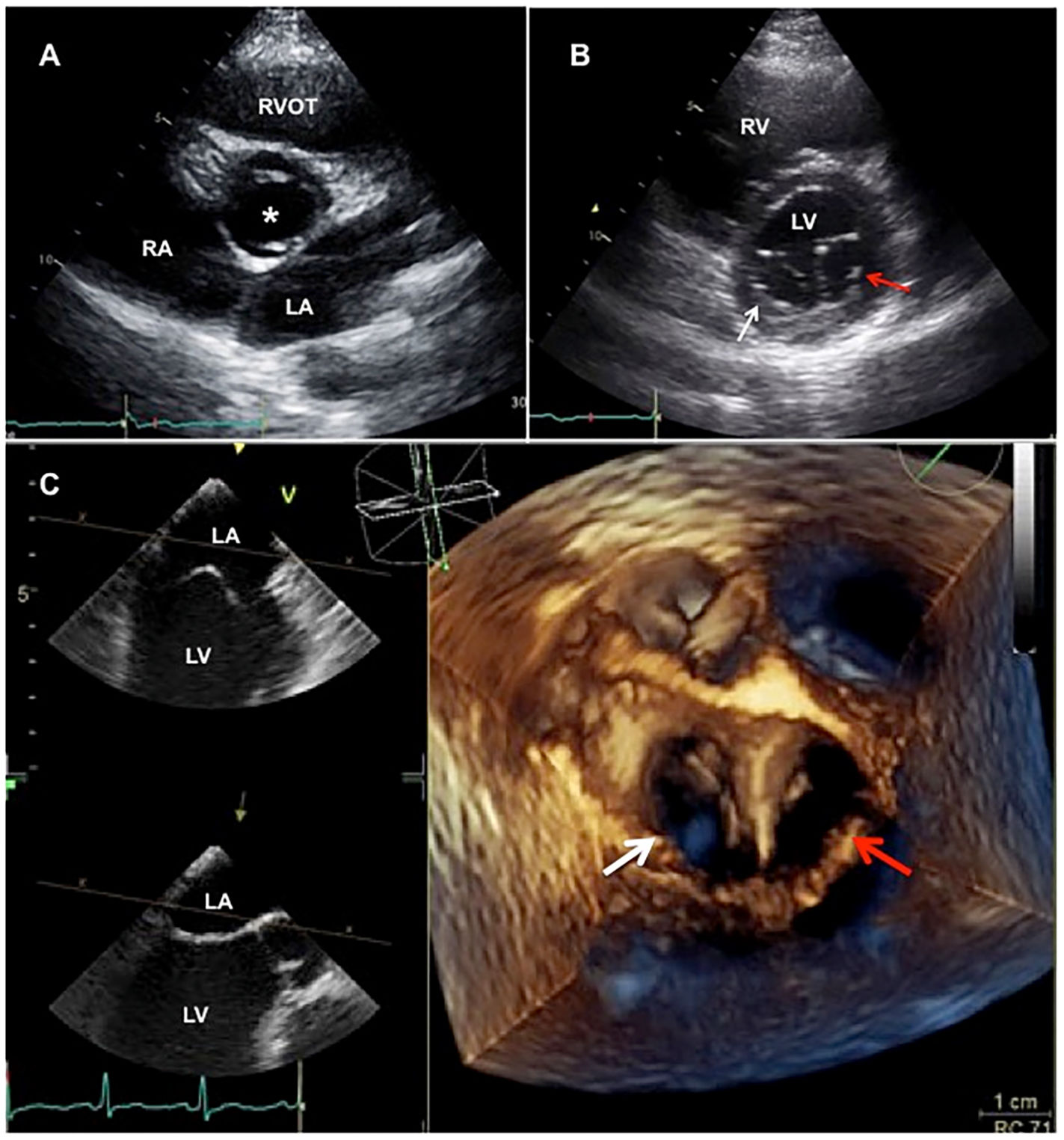
An 18-year-old patient was referred to the adult congenital heart disease unit, with previous history of bicuspid aortic valve (BAV). Her physical examination was unremarkable. Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) revealed a BAV with fusion of the right and left coronary cusps (Fig. 1A). On parasternal short-axis view, 2 separate mitral valve orifices were visualized (Fig. 1B). A three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiogram (3D TEE) was performed showing a complete double orifice mitral valve (DOMV): the mitral subvalvular apparatus was located between the anterior and posterior leaflets, and the mitral orifice was divided in 2 components by a fibrous bridge, with the 2 orifices of equal size (Fig. 1C and Video 1).
Transthoracic echocardiogram. A. Paraesternal short axis view at the great vessels in diastole. Bicuspid aortic valve with fusion of the right and left coronary cusps (white asterisk). B. Paraesternal short axis mitral view. Two separate mitral valve orifices were visualized; right (white arrow) and left orifice (red arrow). C. 3D transesophageal echocardiogram (multiplanar reconstruction); right (white arrow) and left orifice (red arrow). Two mitral orifices of equal size are shown. LA: left atrium, LV: left ventricle, RA: right atrium, RV: right ventricle, RVOT: right ventricular outflow tract. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
DOMV is an extremely rare pathology, with an incidence of 0.05%, characterized by a 2-channel atrioventricular valve in the left ventricle that is typically asymptomatic. The most common associated lesions reported are BAV and coarctation of the aorta. It can present as mitral regurgitation or, less frequently, stenosis. Management is related to the type and severity of mitral valve dysfunction.
The following are the supplementary data related to this article.
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcpsp.2024.100467.
Consent for publicationThe patient or a legally authorized representative provided written informed consent for patient information and images to be published.
FundingNo funding.
Authors' contributionsEGC and DMS: Original idea, image acquisition, analysis and writing the original draft, review and editing. JMTM: Writing the original draft. COS: Image acquisition.