Special Issue: Lecciones aprendidas del COVID-19
More infoDiversos estudios han reportado alteraciones tromboembólicas en los pacientes con neumonía por SARS-CoV-2, sin embargo, no se cuentan con datos definitivos acerca de los factores de riesgo para la aparición de dichos eventos. El objetivo de este estudio fue analizar la relación existente entre los factores personales, clínicos y paraclínicos con el desarrollo de complicaciones tromboembólicas venosas en pacientes hospitalizados con COVID-19.
MétodosEstudio de seguimiento a una cohorte retrospectiva de pacientes con COVID-19 ingresados, de agosto del 2020 a febrero del 2021, en la Clínica Antioquia de Itagüí. Se incluyeron 525 historias clínicas de pacientes mayores de 18 años con diagnóstico confirmado para SARS-CoV-2.
ResultadosSe identificó la presencia de eventos tromboembólicos en el 3% de los pacientes hospitalizados. De los pacientes con COVID-19, el 25,1% ingresó a Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos (UCI), el 18,9% requirió ventilación mecánica invasiva. La mortalidad por COVID-19 en nuestro estudio fue de 18,1%.
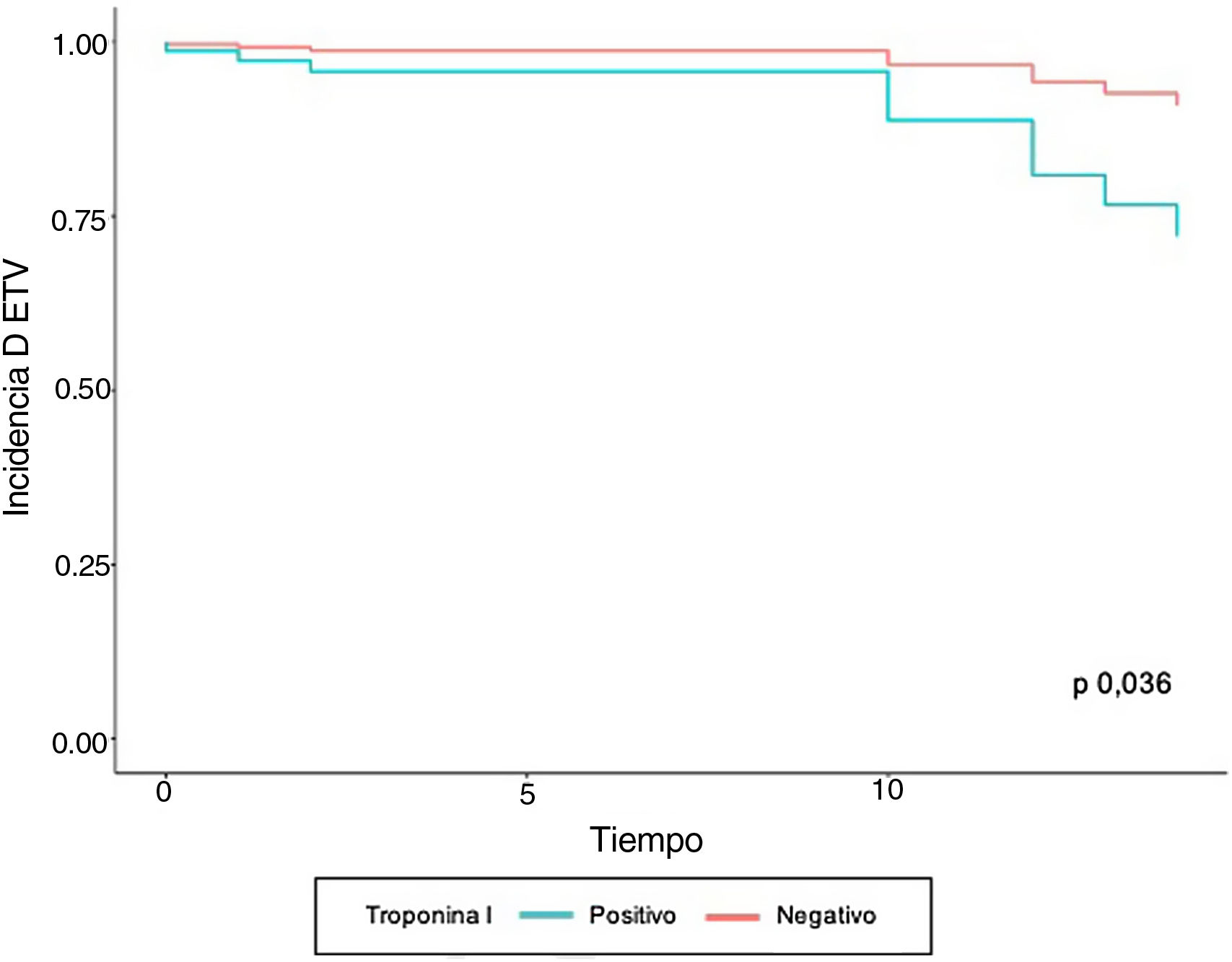
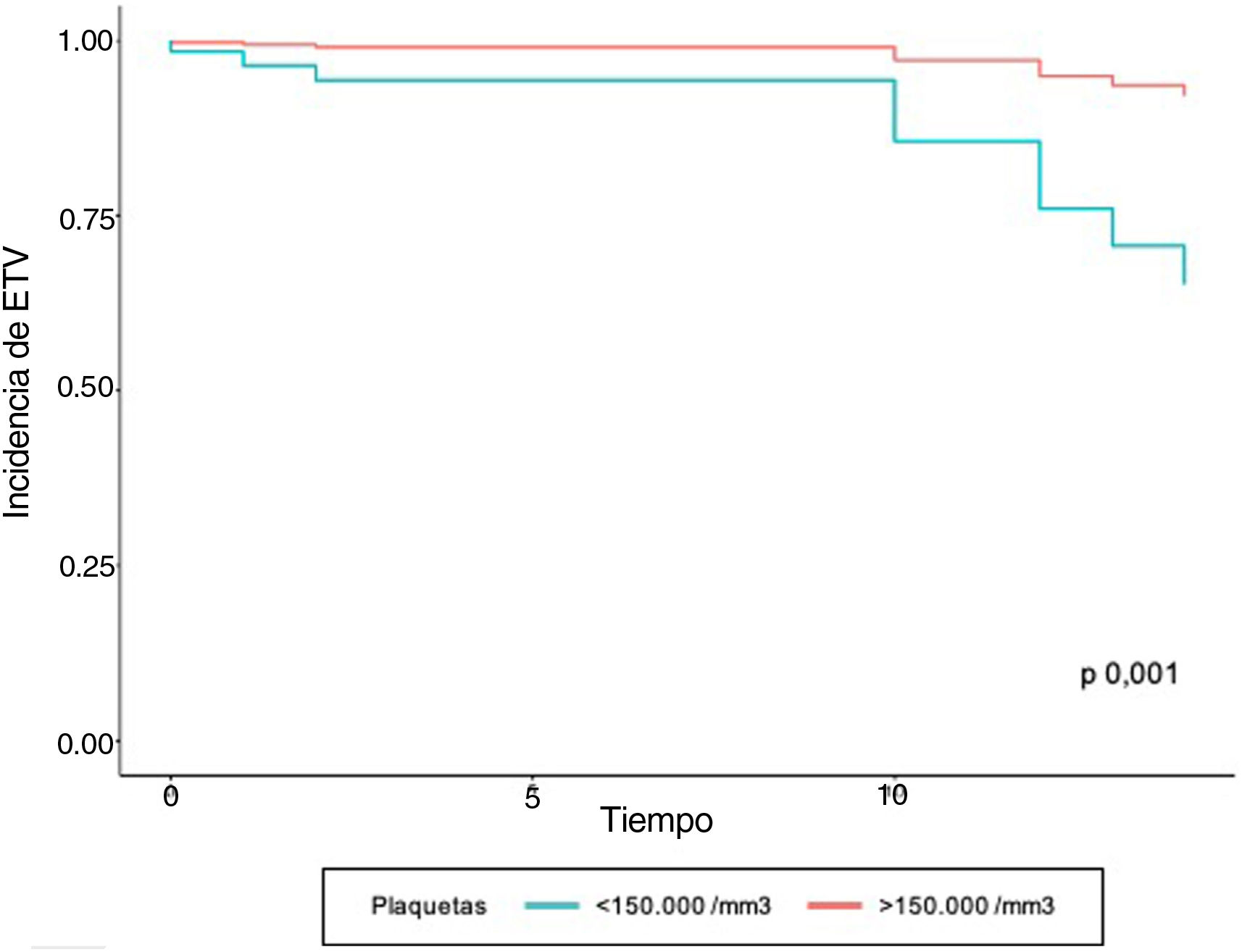
En los sujetos hospitalizados con SARS-CoV-2 se identificó asociación entre el desarrollo de eventos tromboembólicos con los niveles elevados de troponina I (HR 4,07; IC 95% 1,09-15,18), el antecedente de eventos tromboembólicos (HR 11,01; IC 95% 1,06-114,87) y trombocitopenia (HR 6,47; IC 95% 2,05-20,44).
ConclusionesSe encontró asociación entre las complicaciones tromboembólicas y el antecedente de ETV. Igualmente se concluyó que los valores de troponina ≧0,03 ngr/mL y niveles de plaquetas < 150.000/mm3 se asocian con ETV.
Several studies have reported on the thromboembolic alterations developed in patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, however, there are no definitive data on the risk factors for the appearance of these events. The aim of this study was to analyse the relationship between personal, clinical, and paraclinical factors and the development of venous thromboembolic complications in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
MethodsFollow-up study of a retrospective cohort of COVID-19 patients admitted, from August 2020 to February 2021, to the Clínica Antioquia de Itagüí. 525 medical records of patients older than 18 years with a confirmed diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 were included.
ResultsThe presence of VTE was identified in 3% of hospitalized patients. Of the patients with COVID-19, 25.1% were admitted to the intensive care unit, 18.9% required invasive mechanical ventilation. Mortality from COVID-19 in our study was 18.1%. In patients hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2, an increased risk of development of thromboembolic events was identified in those with elevated levels of troponin I (HR 4.07; 95% CI 1.09-15.18), a history of prior thromboembolic events (HR 11.01; 95% CI 1.06-114.87), and thrombocytopenia (HR 6.47; 95% CI 2.05-20.44).
ConclusionsAn association was found between thromboembolic complications and a history of VTE. Likewise, it was concluded that troponin values ≧ .03 ng/ml and platelet levels < 150,000/mm3 are associated with VTE.
Article
Socios de la Asociación de Medicina Crítica y Cuidado Intensivo
Para acceder a la revista
Es necesario que lo haga desde la zona privada de la web de la AMCI, clique aquí