Benign paroxysmal positioning vertigo is considered the most common disorder of the peripheral vestibular system. After successful physical manoeuvres for BPPV, a number of patients complain of non-positional sustained imbalance of variable duration called residual dizziness lasting for several days. The objective of this study was to compare the posturographic changes before and one week after successful repositioning manoeuvres in patients with idiopathic BPPV.
Materials and methodsThis study was a case–control study, where the first group was composed of 20 patients with confirmed BPPV diagnosis regardless of the affected canal or pathology. Twenty age and gender matched normal subjects constituted the control group. The sensory organization test was performed before and one week after a repositioning manoeuvre in BPPV patients.
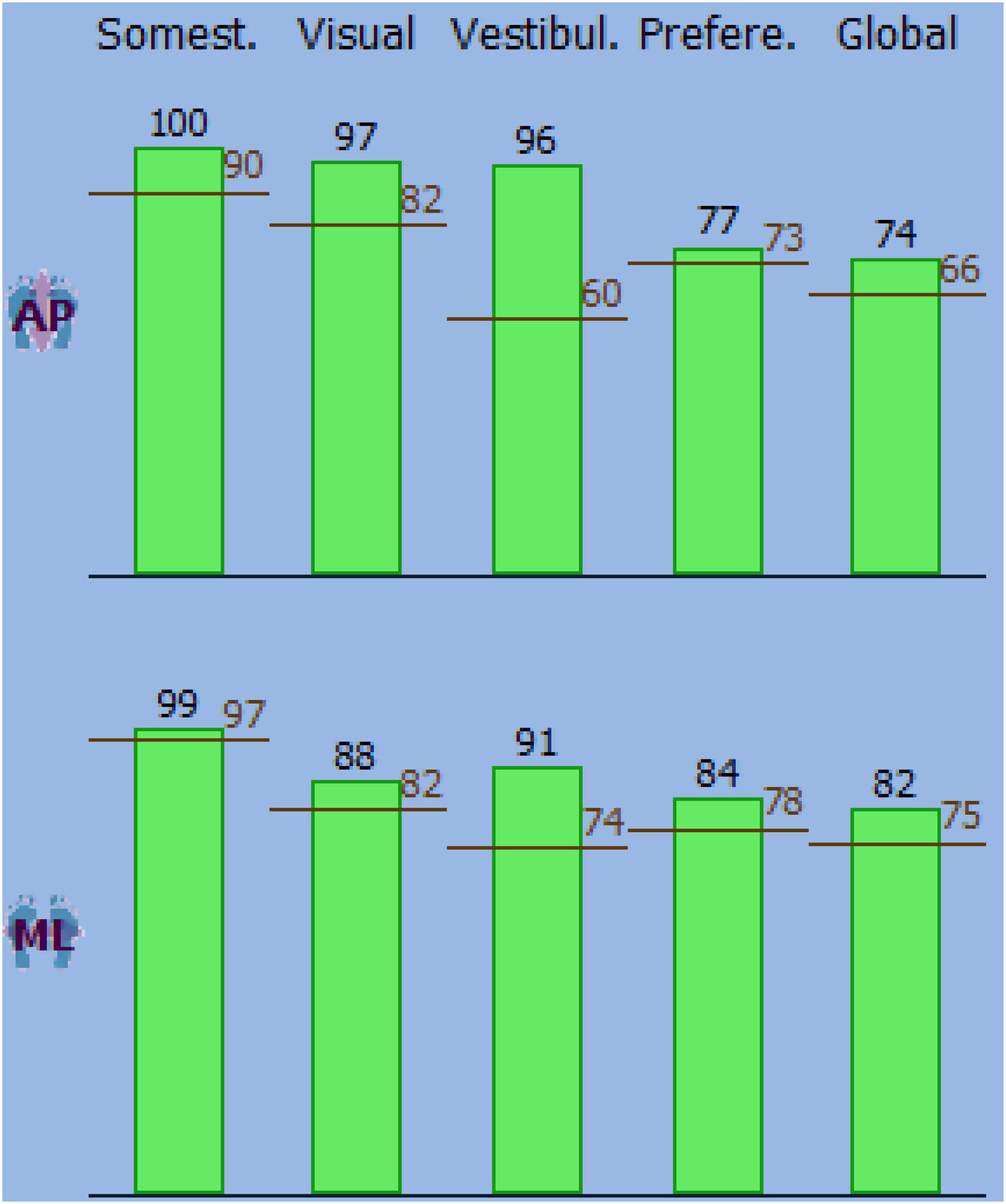
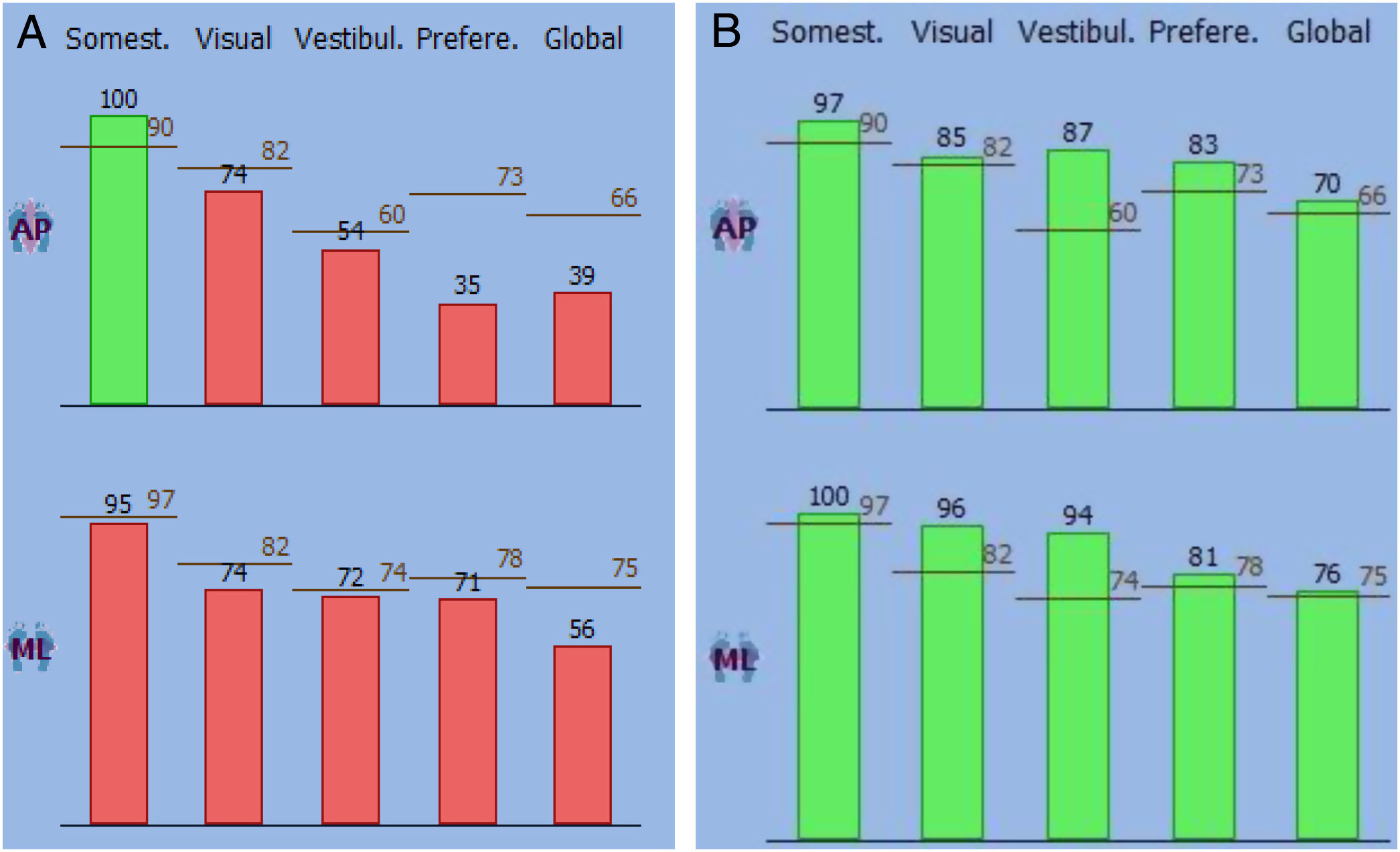
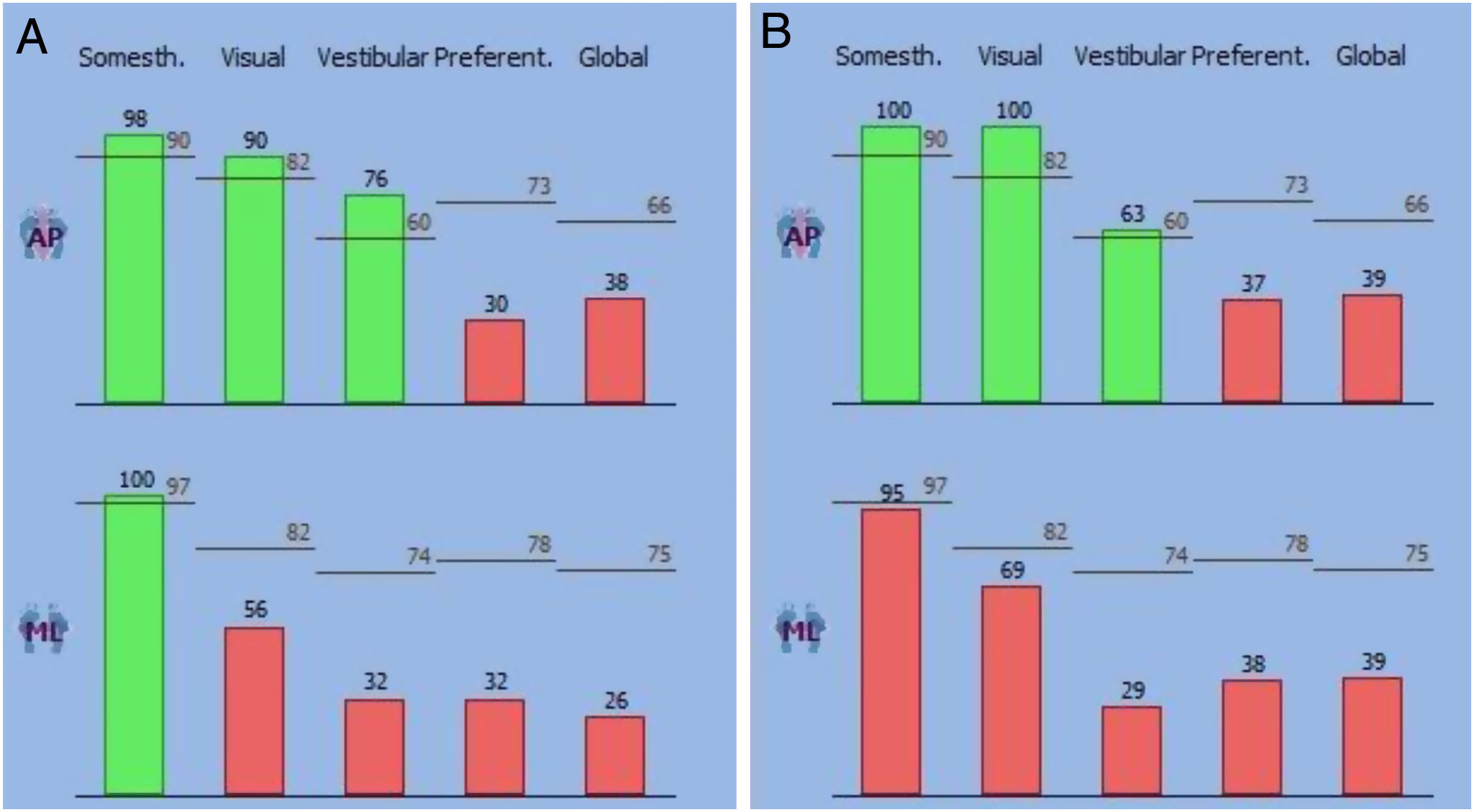
ResultsAll 20 BPPV patients, except 6 who had no significant improvement of symptoms even after disappearance of classic vertigo and nystagmus, had substantial improvement in sensory scores after CRPs in the antero-posterior visual and vestibular scores and the medio-lateral visual and global scores. All antero-posterior and medio-lateral scores before and after CRPs, except for the AP preferential score, were considerably poorer in BPPV patients than healthy subjects. The 6 patients, who showed no improvement after CRPs, presented with a history of non-specific symptoms i.e., light-headedness or sense of floating.
ConclusionsSensory organization test might have a role in the assessment of residual dizziness in patients with BPPV after CRPs.
El vértigo posicional paroxístico benigno (VPPB) se considera el trastorno más común del sistema vestibular periférico. Tras la realización exitosa de maniobras para VPPB, una serie de pacientes se quejan de desequilibrio sostenido no posicional de duración variable denominado mareo residual de varios días de duración. El objetivo de este estudio fue comparar los cambios posturográficos antes y una semana después de las maniobras de reposicionamiento exitosas en pacientes con VPPB idiopático.
Materiales y métodosEste estudio fue un estudio de casos y controles, donde el primer grupo estaba compuesto por 20 pacientes con diagnóstico confirmado de VPPB independientemente del conducto afectado o la patología. El grupo control lo integraban 20 sujetos normales pareados por edad y género. La prueba de organización sensorial se realizó antes y una semana después de una maniobra de reposicionamiento en pacientes con VPPB.
ResultadosLos 20 pacientes con VPPB, excepto 6 que no obtuvieron una mejoría significativa de los síntomas incluso después de la desaparición del vértigo clásico y el nistagmo, obtuvieron una sustancial mejora de las puntuaciones sensoriales tras CPR en las puntuaciones anteroposteriores visuales y las puntuaciones vestibulares y las puntuaciones mediolaterales visuales y globales. Todas las puntuaciones anteroposteriores y mediolaterales antes y después de las CPR, excepto la puntuación preferencial AP, fueron considerablemente peores en los pacientes con VPPB con respecto a los sujetos sanos. Los 6 pacientes, que no mostraron mejoría después de la CPR, presentaron antecedentes de síntomas inespecíficos, es decir, mareos o sensación de flotar.
ConclusionesLa prueba de organización sensorial podría desempeñar un papel en la evaluación del mareo residual en pacientes con VPPB tras la realización de CPR.