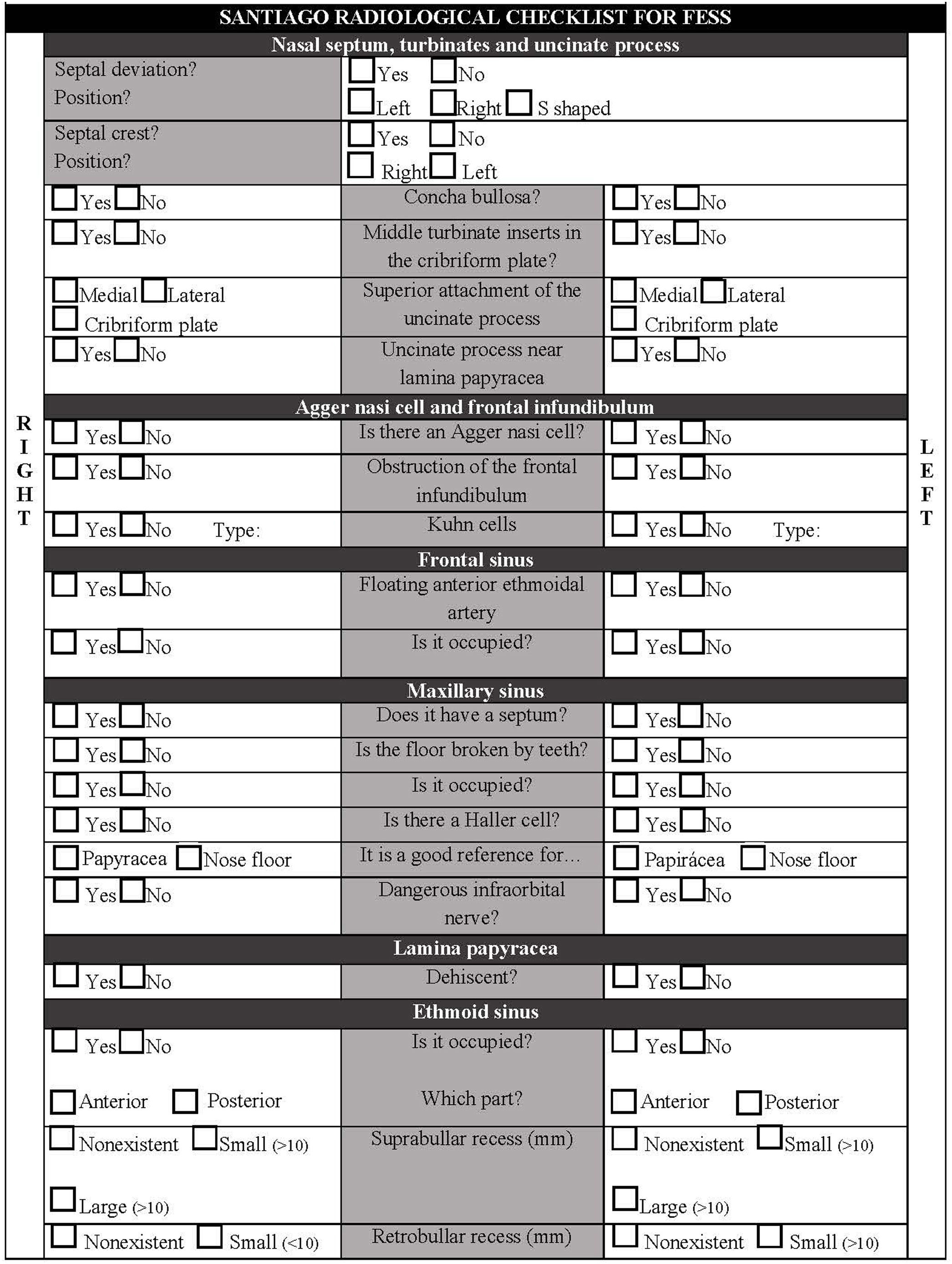
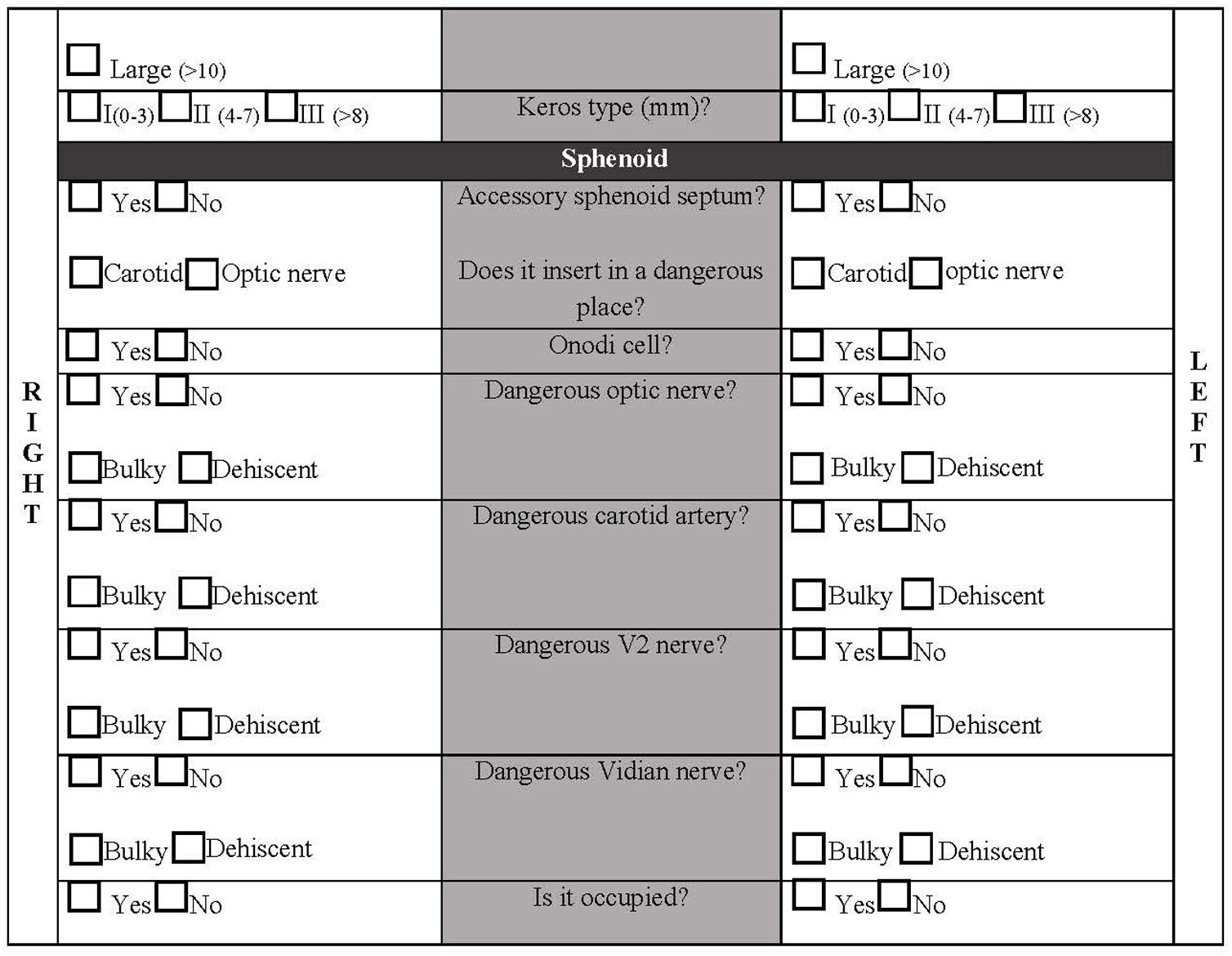
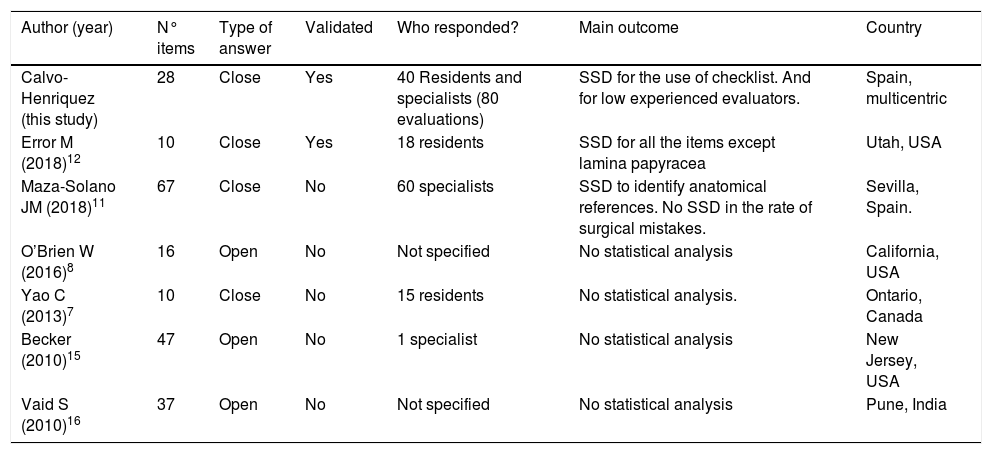
Functional endoscopic sinus surgery might lead to dangerous complications. Studying and analysing preoperative CT scans provides surgeons with a precise knowledge of their patient's anatomy, thus reducing the risk of potential complications. Checklists highlighting key anatomical areas have been published and proven useful. However, none of these are widely accepted or systematically used in daily practice.
ObjectiveIn this paper, the rhinology group of the Young-Otolaryngologists of the International Federations of Otorhinolaryngological Societies (YO-IFOS) aim to create and validate a new checklist designed to be fast and user friendly for daily practice.
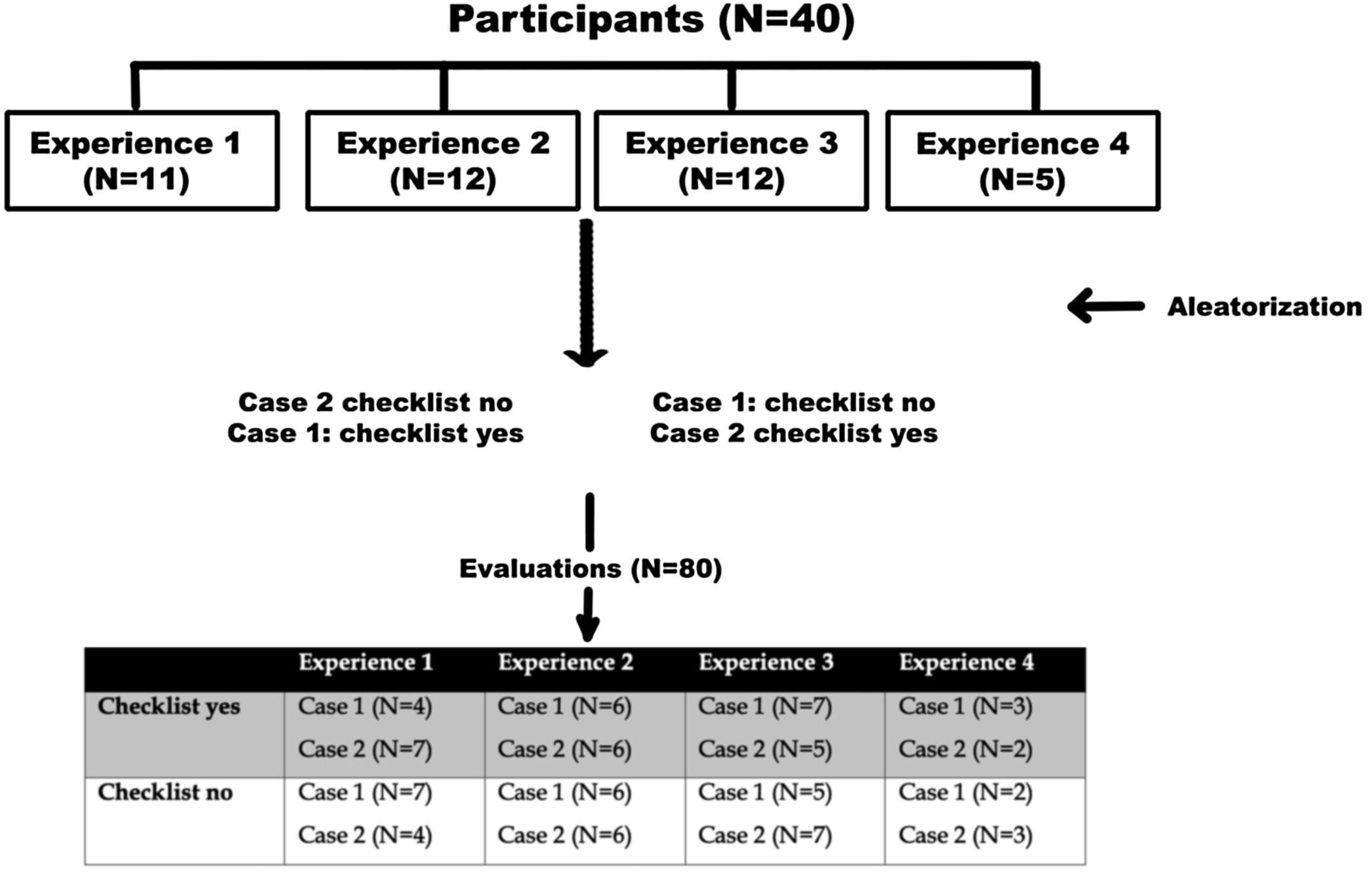
MethodsTwo CT sinonasal scans were selected as test cases. Forty otolaryngologists were selected from five tertiary referral hospitals. It was a cross-sectional study; each participant was their own control. All participants completed a questionnaire after the analysis of both CT scans to prevent learning bias. The evaluation included ten items critical in endoscopic sinus surgery according to previous publications.
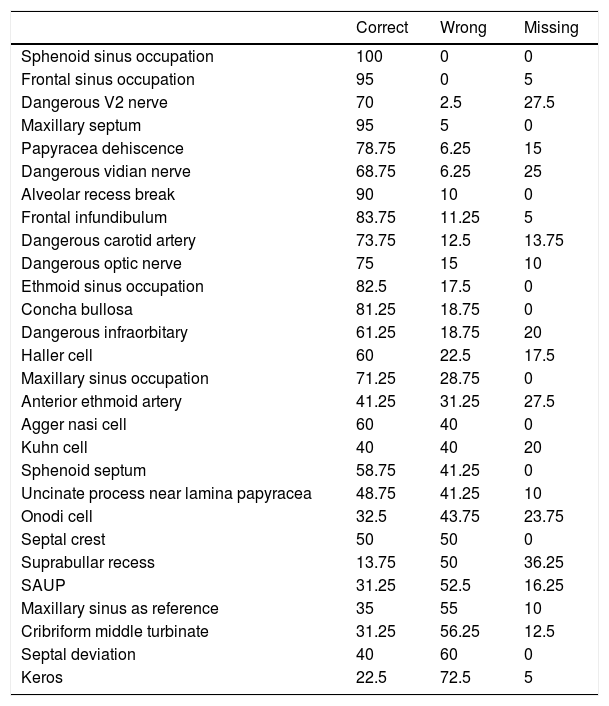
ResultsThere were 80 evaluations. There was a significant increase in the number of correctly identified critical structures with the use of the checklist (p=.009). There was a statistically significant difference in low- experience evaluators, while it was not statistically significant for experienced surgeons. The most unanswered structures were suprabullar recess, dangerous v2 nerve, anterior ethmoid artery, dangerous vidian nerve and Onodi cell. The most wrongly identified structures were Keros type, septal deviation and cribiform middle turbinate.
ConclusionThe YO-IFOS radiological checklist has proven a useful tool for correctly studying sinonasal anatomical variations. There is a clear learning component in the use of the checklist although it does not in any way exempt specialists from thorough study of sinonasal anatomy. Given the risk-benefit ratio, we strongly suggest the routine use of the checklist to systematically assess CT-scans prior to endoscopic sinonasal surgery.
La cirugía endoscópica nasosinusal (CENS) tiene complicaciones peligrosas. El estudio peroperatorio de la tomografía nasosinusal otorga un conocimiento preciso de la anatomía del paciente, reduciendo así el riesgo de complicaciones. Se han publicado listas de comprobación para cirugía nasosinusal, y estas han demostrado su utilidad. En este trabajo, desde el grupo de rinología de Young-Otolaryngologists of the International Federations of Oto-rhino-laryngological Societies (YO-IFOS), se diseñó y validó una lista de comprobación con el objetivo de ser amplia, cómoda y práctica para uso en la práctica clínica diaria.
MétodosSe seleccionaron 2 tomografías nasosinusales como caso problema. Cuarenta otorrinolaringólogos fueron reclutados de 5 centros de tercer nivel. Se diseñó un estudio cruzado, por lo que cada participante fue su propio control. Todos los participantes completaron una evaluación tras el análisis de ambos casos con el objetivo de evitar sesgo de aprendizaje.
ResultadosSe completó un total de 80 evaluaciones. El uso del checklist supuso una mejoría en el número de variantes peligrosas identificadas (p=0,009). La diferencia fue estadísticamente significativa para evaluadores poco experimentados, pero no para los experimentados. Las variantes con mayor número de respuestas en blanco fueron el receso suprabullar, el nervio V2, la arteria etmoidal anterior, el nervio vidiano y la celda de Onodi. Las estructuras con mayor número de error fueron Keros, desvío septal e inserción del cornete medio en lámina cribosa.
ConclusiónEl checklist radiológico nasosinusal de YO-IFOS ha demostrado ser una herramienta válida para el estudio peroperatorio de la tomografía nasosinusal. Dado la relación riesgo-beneficio recomendamos el uso rutinario del checklist radiológico para el estudio de la tomografía nasosinusal de manera sistemática previo a la CENS.