Las técnicas quirúrgicas para tratar el colapso velofaríngeo de los pacientes con síndrome de apnea-hipopnea del sueño han evolucionado en los últimos años. Nuestro objetivo era conocer si estas nuevas técnicas proporcionan mejores resultados quirúrgicos.
Materiales y métodosEs un estudio retrospectivo de los pacientes con síndrome de apnea-hipopnea del sueño moderado-severo tratados quirúrgicamente del 2006 al 2018. Solo los pacientes adultos sin adherencia a la CPAP y en los que no se practicó cirugía multinivel simultánea fueron incluidos. Durante este período se practicaron 4 técnicas diferentes: resección parcial del paladar, faringoplastia lateral, faringoplastia de expansión y faringoplastia de reposición con sutura barbada. La tasa de éxito se calcula según los criterios de Sher, según el criterio de IAH<10/h y mediante la reducción relativa media del IAH (RRM).
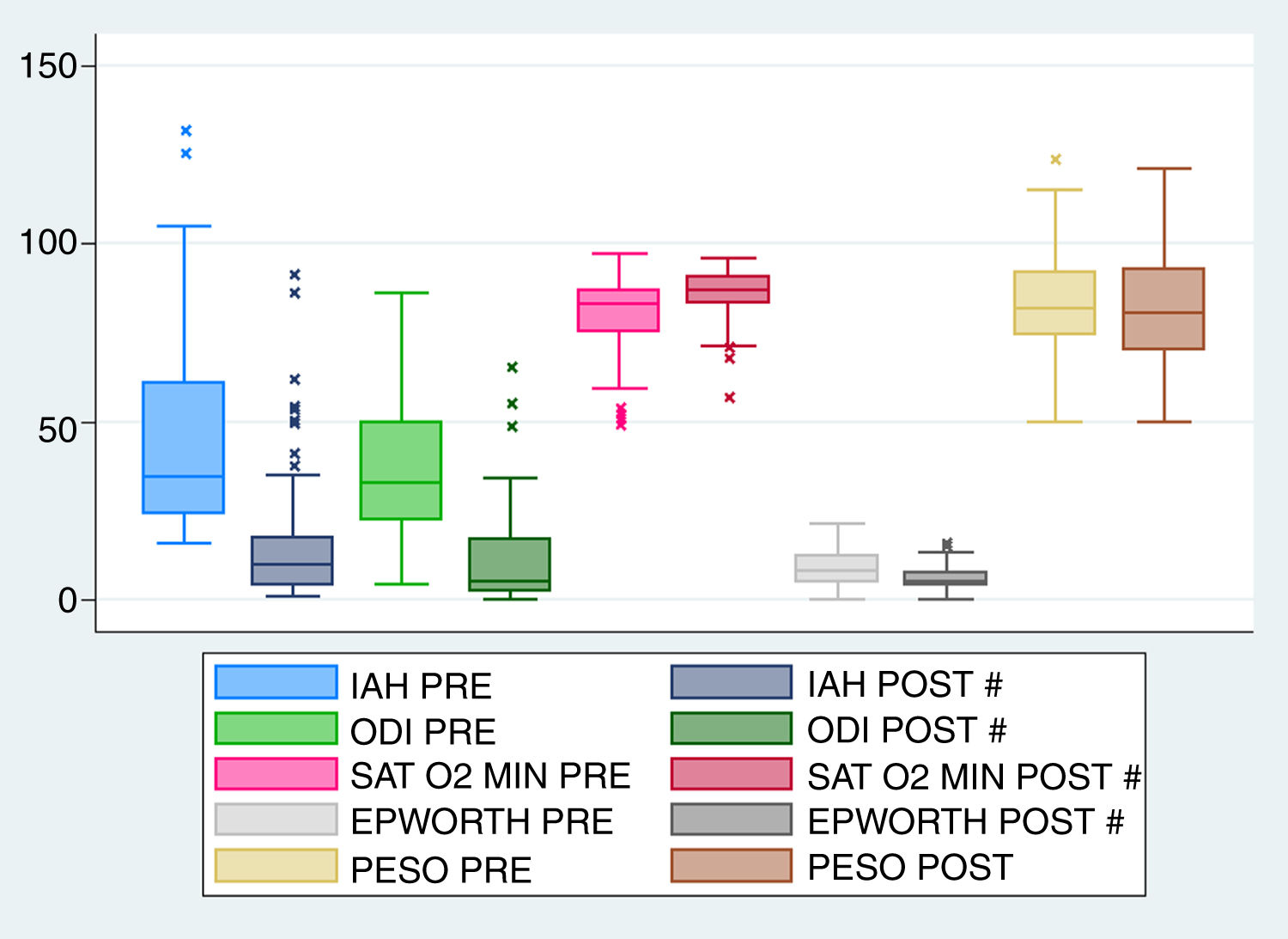
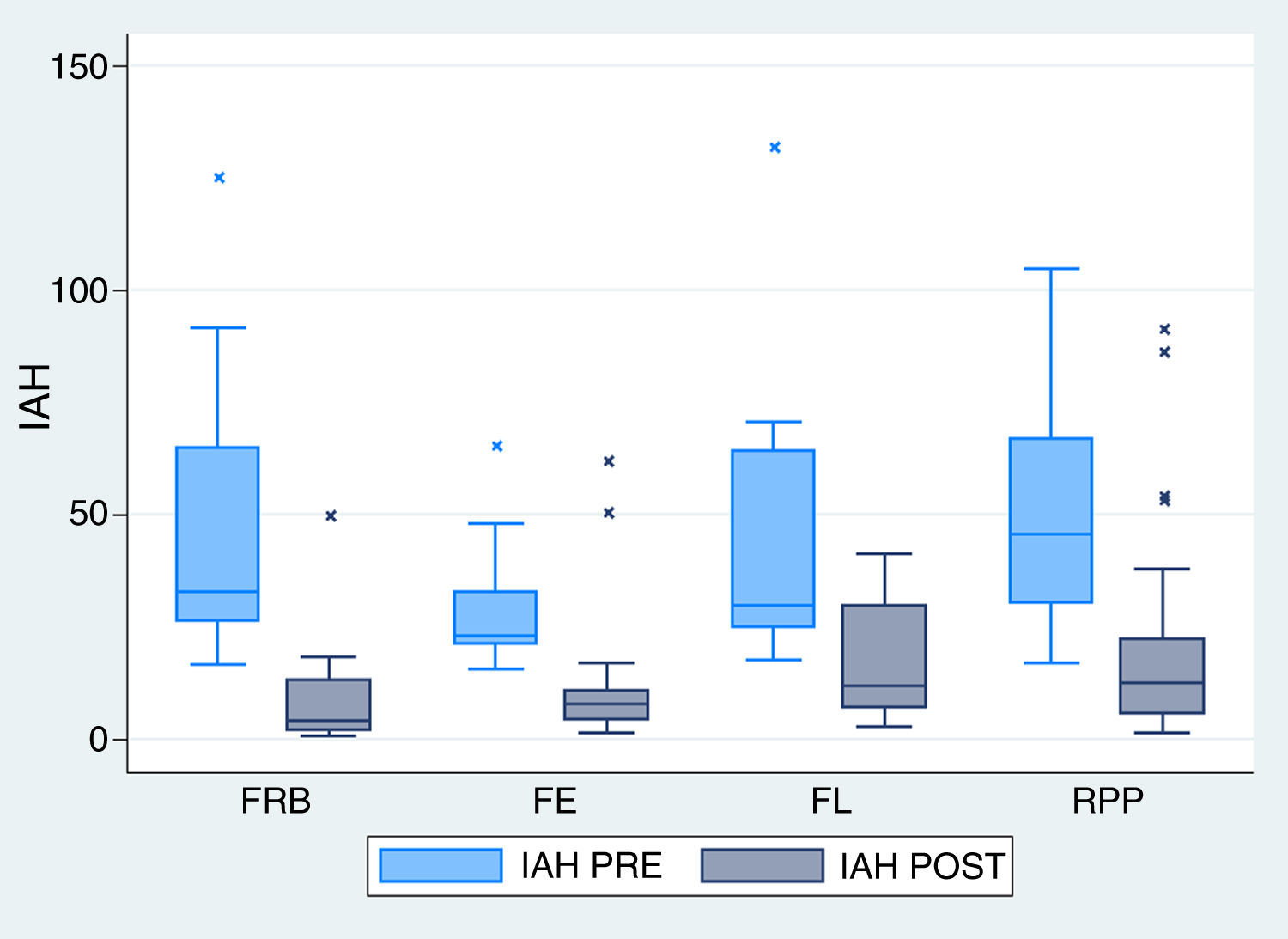
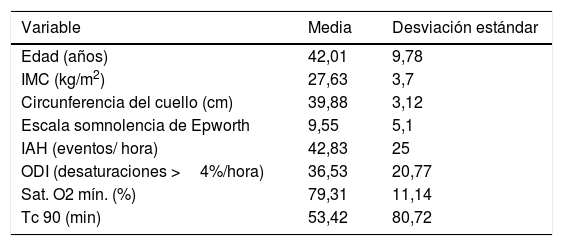
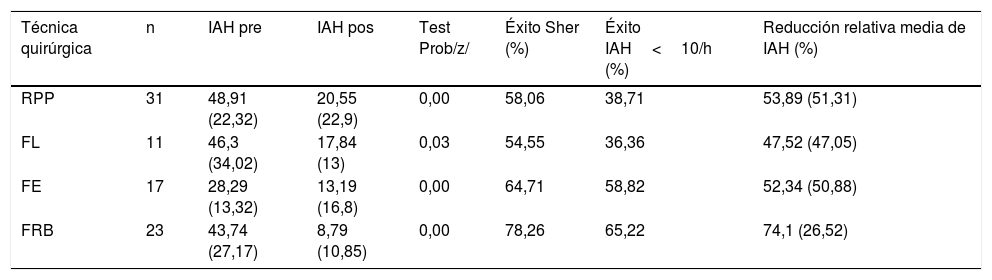
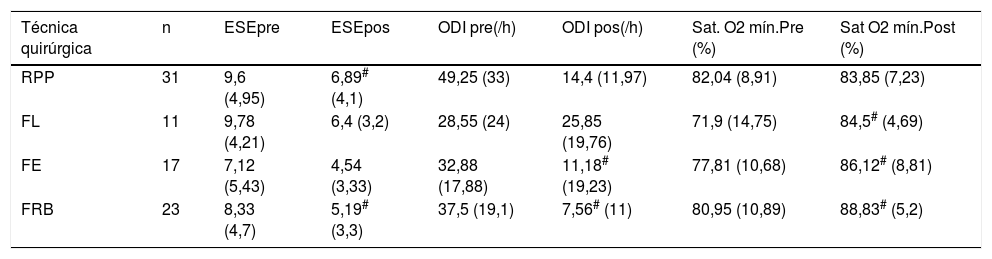
ResultadosOchenta y dos pacientes fueron incluidos. El IAH se redujo significativamente de 43,4±24/h a 15,6±18,6/h. No se observaron cambios significativos en el índice de masa corporal. Los valores de Tc 90, el índice de desaturación y la somnolencia según la escala de Epworth mejoraron tras la cirugía. La mayor tasa de éxito se obtuvo mediante la realización de la faringoplastia de reposición con sutura barbada (78,26% según criterios Sher, 65,22% para IAH<10/h y 74,1% en RRM). Las diferencias observadas fueron estadísticamente significativas.
ConclusionesLa faringoplastia de reposición con sutura barbada es una técnica de reciente introducción que mostró superioridad sobre el resto de faringoplastias en esta cohorte.
The surgical techniques used to treat velopharyngeal collapse in obstructive sleep apnoea patients have evolved over recent years. Our aim was to determine whether these new techniques have better surgical results.
Materials and methodsThis is a retrospective study of moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnoea patients surgically treated from 2006 to 2018. Only adult patients with no compliance to positive airway pressure and without simultaneous multilevel surgery were included. During this period, 4 different techniques were performed: uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, lateral pharyngoplasty, expansion pharyngoplasty and barbed reposition pharyngoplasty. Success rates as defined by Sher, as well as postoperative AHI<10/h and mean relative AHI reduction (MRR) were compared.
Results82 patients were included. AHI was significantly reduced from 43.4±24/h to 15.6±18.6/h. No significant changes in body mass index were observed. Hypoxaemia time, oxygen desaturation index, and Epworth sleepiness scale values improved after surgery. The best success rates were obtained performing barbed reposition pharyngoplasty (78.26% measured by Sher's criteria, 65.22% by AHI<10/h criteria and 74.1% by the MRR). The differences observed were statistically significant.
ConclusionsBarbed reposition pharyngoplasty is a recently introduced technique that showed superiority over the other palatal surgery techniques in this cohort.