The aim of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of anterior and posterior dacryorhinocystostomy (En-Dcr) by assessing the surgical outcome with a new objective technique, nose sinus manometry.
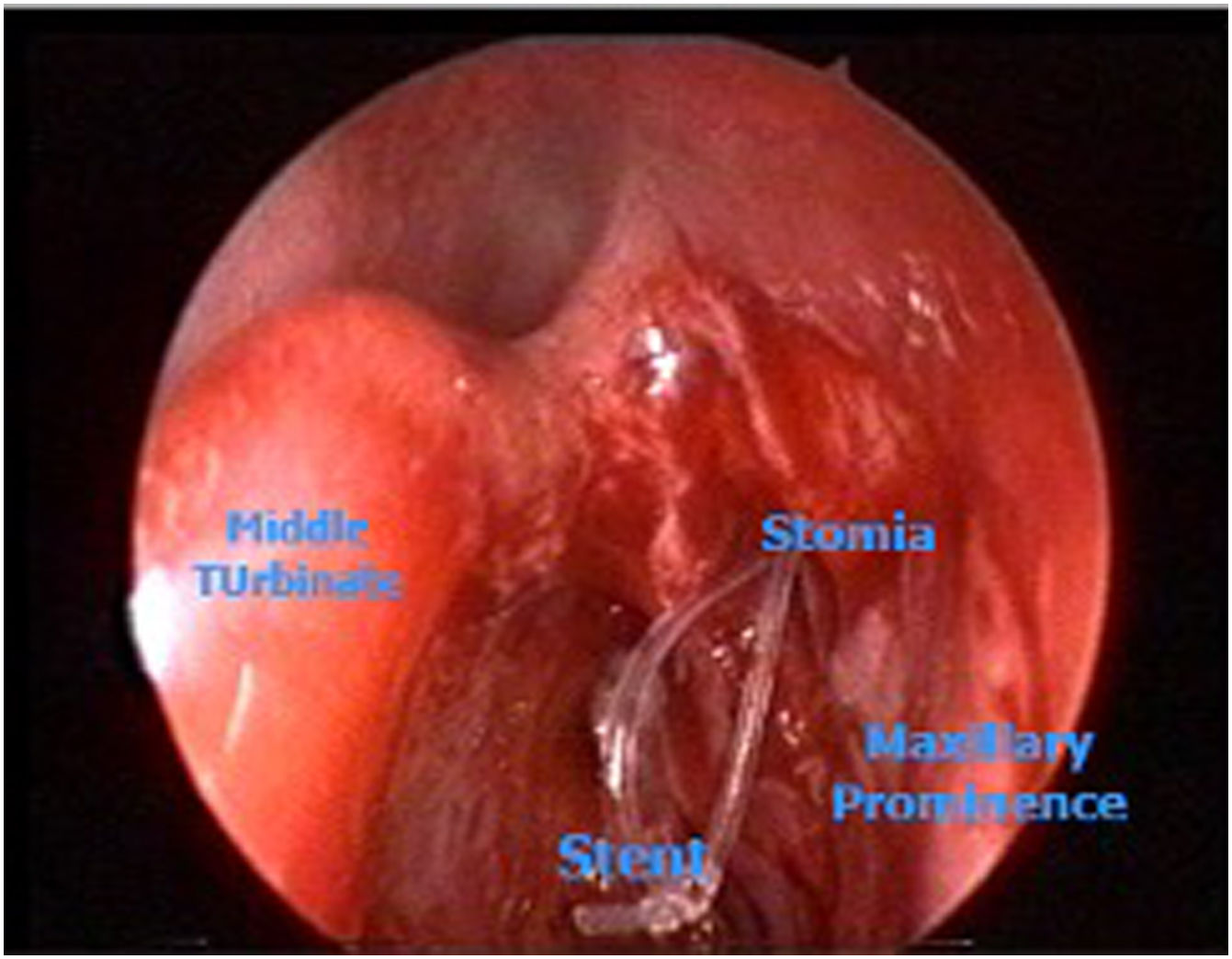
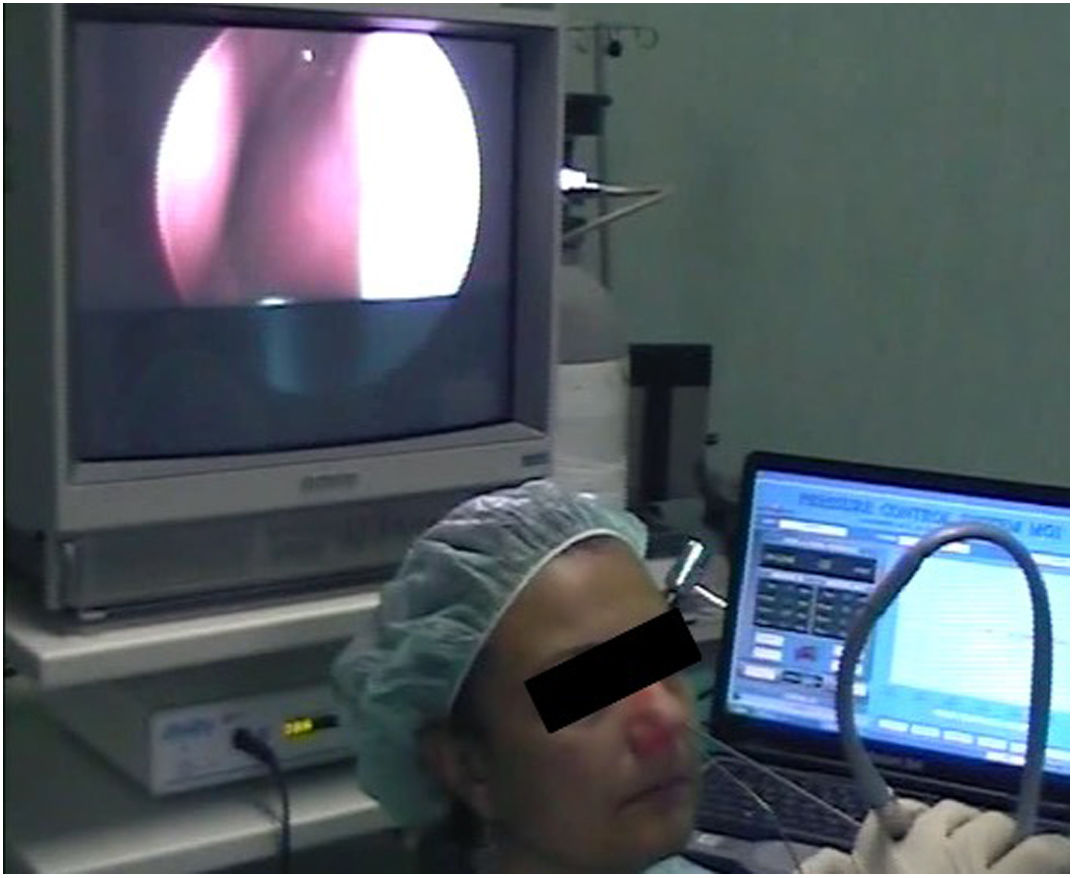
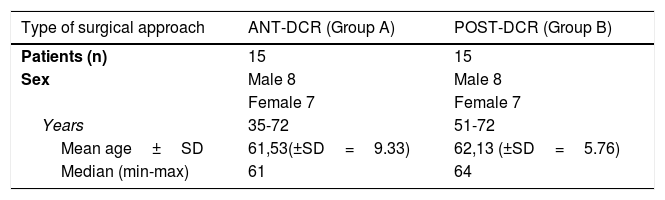
Materials and methodsThirty adult patients presenting nasolacrimal duct obstruction were enrolled in this study and randomly divided in two groups. In group A patients underwent anterior endonasal dacryorhinocystostomy, group B underwent the posterior approach. All patients were evaluated through Nose Sinus Manometry, endoscopic dye disappearance functional test (EDFT) and subjective assessment three months post-op. Pearson test and T-student Test were used for evaluations.
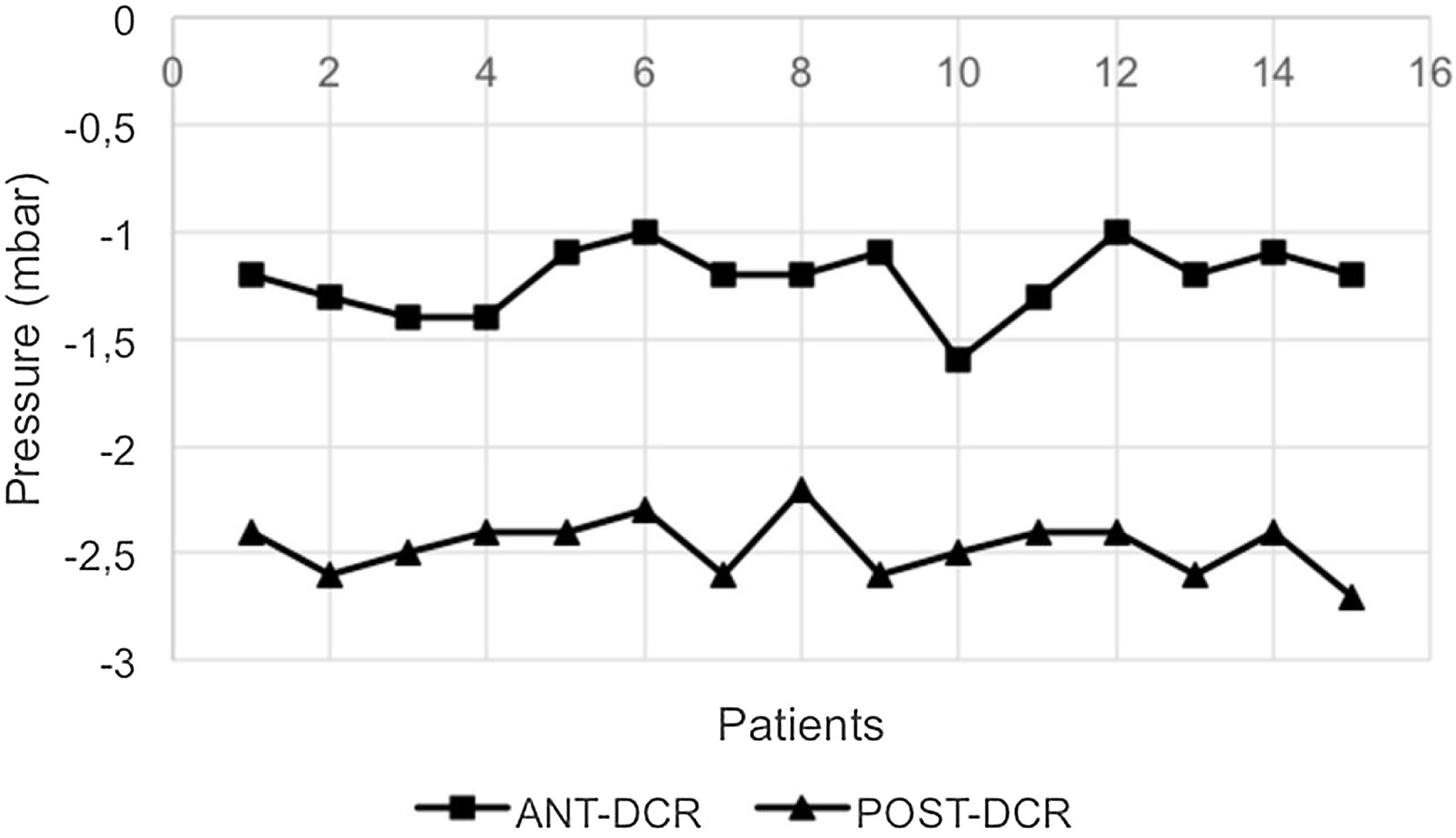
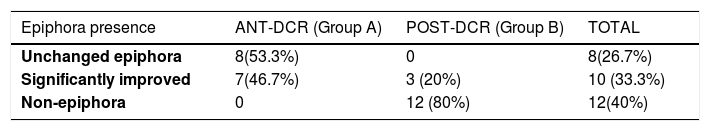
ResultsThe mean differences in the pressure values were significantly different in the two groups of treatment, therefore, the patients of group B had strong improvement in pressure values compared with patients of group A.
ConclusionThis study confirms a relevant physical distinction between posterior En-Dcr outcomes compared to anterior En-Dcr and reveals a significant success rate difference between the two groups of patients. The posterior surgical technique shows better results than the anterior one, by providing an almost physiological post- operative endonasal outcome. These results also showed the effectiveness of Nose Sinus Manometry in assessing the post- operative outcomes after En-Dcr.
El objetivo de este estudio es evaluar la efectividad de la dacriocistorrinostomía anterior y posterior (En-Dcr) mediante la evaluación del resultado quirúrgico con una nueva técnica objetiva, la manometría del seno nasal.
Materiales y métodosTreinta pacientes adultos que presentaban obstrucción del conducto nasolagrimal se inscribieron en este estudio y se dividieron al azar en dos grupos. En el grupo A, los pacientes se sometieron a dacriocistorrinostomía endonasal anterior, en el grupo B se sometió al abordaje posterior. Todos los pacientes fueron evaluados mediante manometría de seno nasal, prueba EDFT y evaluación subjetiva tres meses después de la operación. Análisis estadístico utilizado: la prueba de Pearson y la prueba t Student se utilizaron para las evaluaciones.
ResultadosLas diferencias medias en los valores de presión fueron significativamente diferentes en los dos grupos de tratamiento, por lo tanto, los pacientes del grupo B tienen una fuerte mejora en los valores de presión en comparación con los pacientes del grupo A.
ConclusionesEste estudio confirma una distinción física relevante entre los resultados posteriores de En-Dcr, en comparación con los anteriores En-Dcr, y revela una diferencia significativa en la tasa de éxito entre los dos grupos de pacientes. La técnica quirúrgica posterior muestra mejores resultados que la anterior, al proporcionar un resultado endonasal postoperatorio casi fisiológico. Estos resultados también mostraron la efectividad de la manometría de seno nasal para evaluar los resultados postoperatorios después de En-Dcr.