To determine the rate and risk factors for additional tympanostomy tube (TT) placement after first set of TT extrusion in children.
Materials and methodsSingle-centre cohort study. Clinical records of children undergoing TT placement from January 2015 to December 2017 were reviewed and factors related to the need for subsequent TT were evaluated.
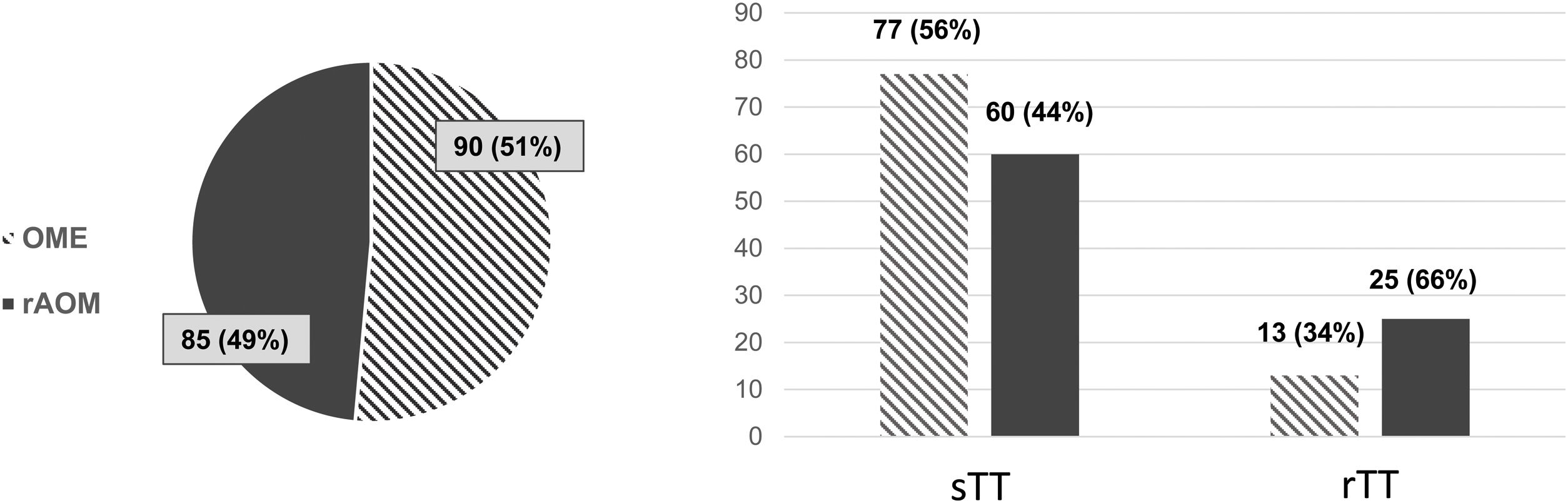
ResultsA total of 183 children were included, with a mean age of 5.45±2.672 years old. All surgeries were performed simultaneously with adenoidectomy and 64.3% with tonsillectomy. The mean TT retention time was 12.13±6.033 months and the rate of second TT insertion was 21.9%. The TT retention time was significantly lower in children who needed a second TT (8.97±3.962 vs 13.05±6.229, p<.001). Other factors significantly associated with the need for a second TT in the univariate analysis were the presence of otorrhoea and snoring after TT placement (p=.042 and p=.02), RAOM (p=.016), passive smoking (p=.038) and rhinorrhoea (p=.008). However, on multivariate analysis only TT retention time (OR=.831, 95% CI: .727–.950) and RAOM as an indication for surgery (OR: 5.767; 95% CI: 1.696–19.603) were predictors of a second TT. Gender, age, asthma, prematurity, and low birth weight were not significantly associated with a second TT.
ConclusionsRAOM and a short TT retention time were significantly associated with additional TT placement, enhancing the need for and importance of follow up of these children after TT extrusion.
Determinar la tasa y los factores de riesgo para la colocación de tubos de timpanostomía (TT) adicional después de la extrusión de los primeros TT en niños.
Materiales y métodosEstudio retrospectivo de los registros médicos de los niños sometidos a la colocación de TT desde enero del 2015 hasta diciembre del 2017; se evaluaron los factores relacionados con la necesidad de TT posterior.
ResultadosSe incluyó a 183 niños, con una edad media de 5,45±2,672 años. Todas las cirugías se realizaron simultáneamente con adenoidectomía y el 64,3% con amigdalectomía. El tiempo medio de retención del TT fue de 12,13±6,033 meses y la tasa de segunda inserción del TT fue del 21,9%. El tiempo de retención del TT fue significativamente menor en los niños que necesitaron un segundo TT (8,97±3,962 vs. 13,05±6,229, p<0,001). Otros factores asociados significativamente a la necesidad de un segundo TT en el análisis univariable fueron la presencia de otorrea y ronquidos tras la colocación del TT (p=0,042 y p=0,02, respectivamente), la otitis media aguda de repetición (OMAr) (p=0,016), el tabaquismo pasivo (p=0,038) y la rinorrea (p=0,008). Sin embargo, en el análisis multivariado solo el tiempo de retención del TT (OR=0,831, IC del 95%: 0,727-0,950) y la OMAr como indicación de cirugía (OR: 5,767; IC del 95%: 1,696-19,603) fueron predictores de un segundo TT. El sexo, la edad, el asma, la prematuridad y el bajo peso al nacer no se asociaron significativamente con un segundo TT.
ConclusionesLa OMAr y un corto tiempo de retención del TT se asociaron significativamente con la colocación de un segundo TT, lo que refuerza la necesidad e importancia del seguimiento de estos niños tras la extrusión del TT.