Our aim was to study the radiological anatomy of the ethmoidal arteries.
MethodsA descriptive study was performed including CT images of 20 cadaver heads. The specimens were perfused with a radiopaque material and various anatomical parameters were analysed.
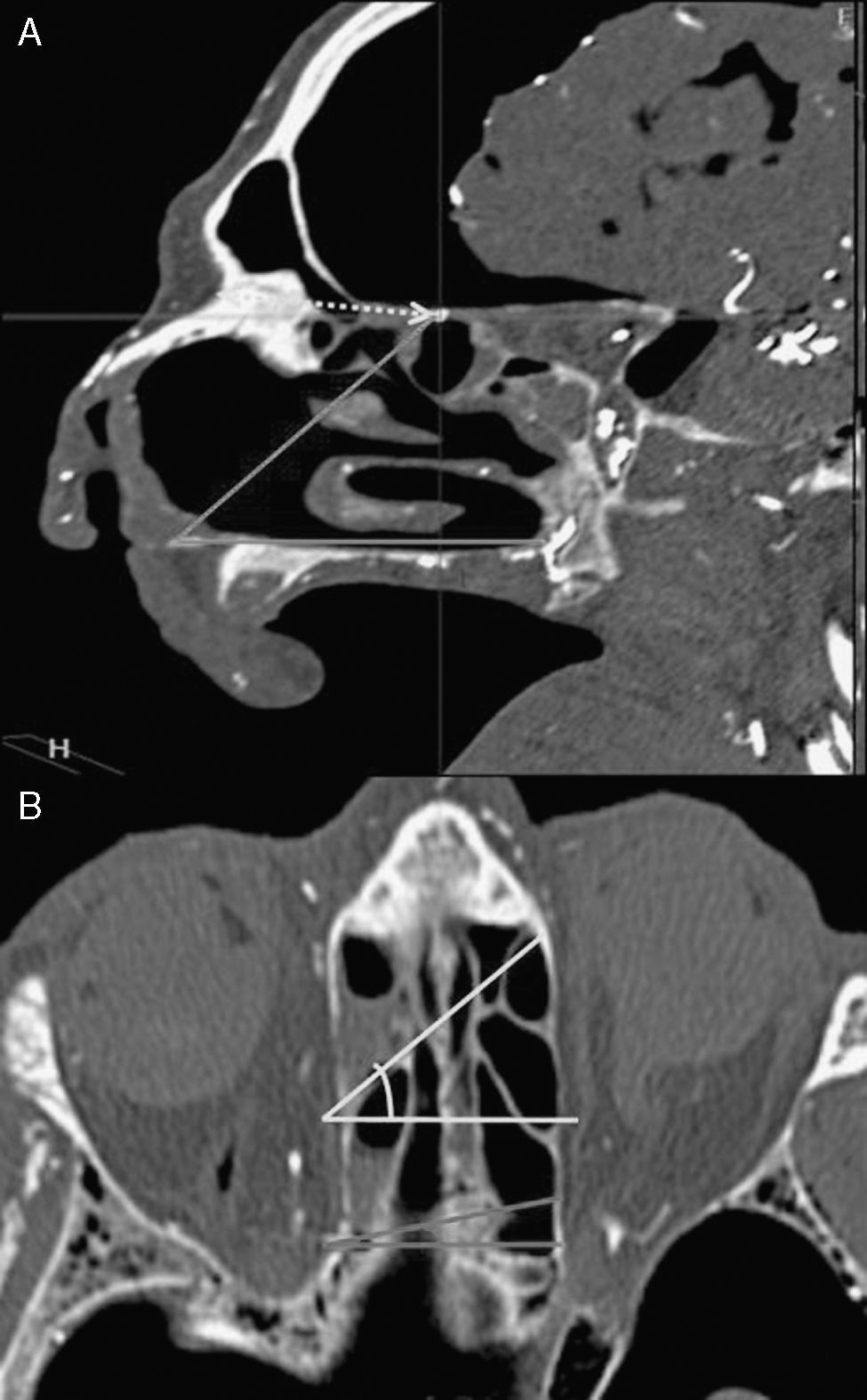
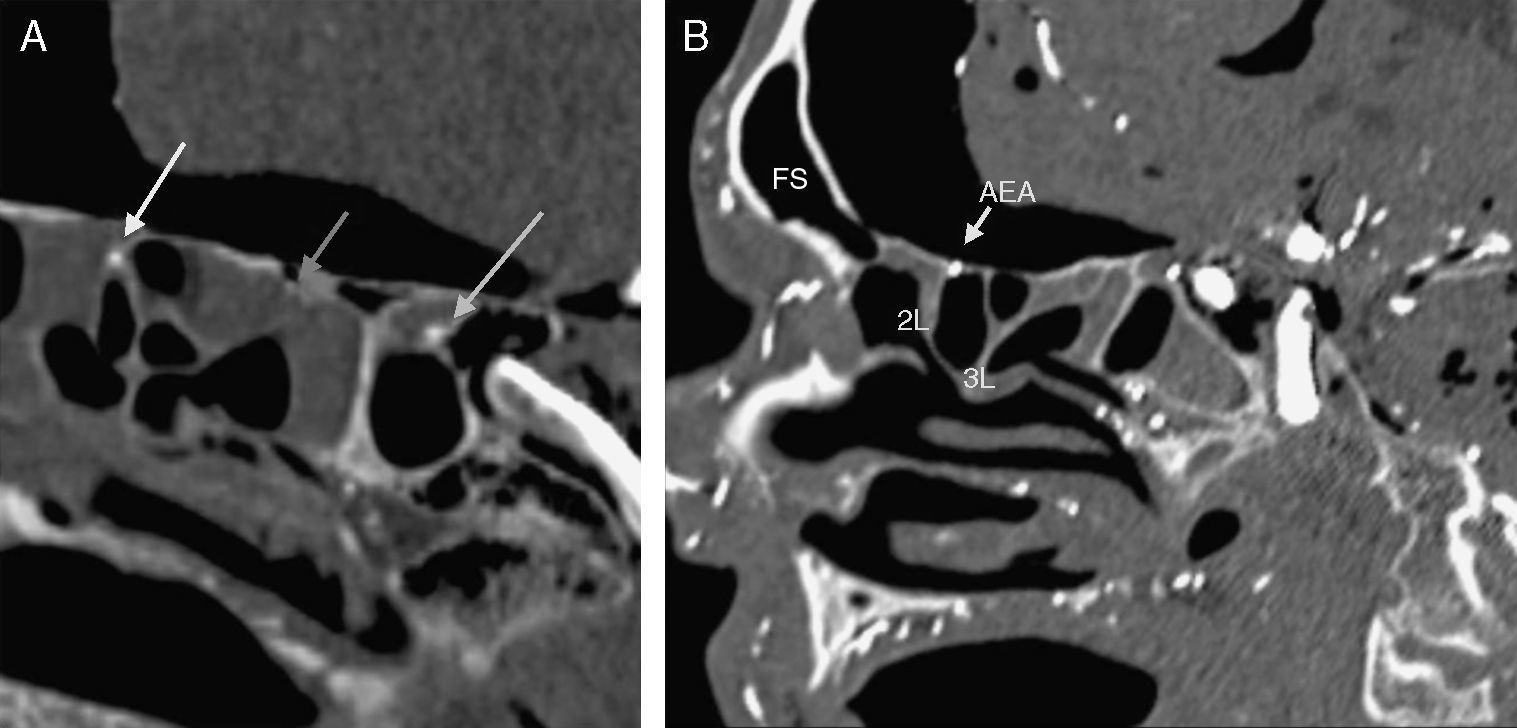
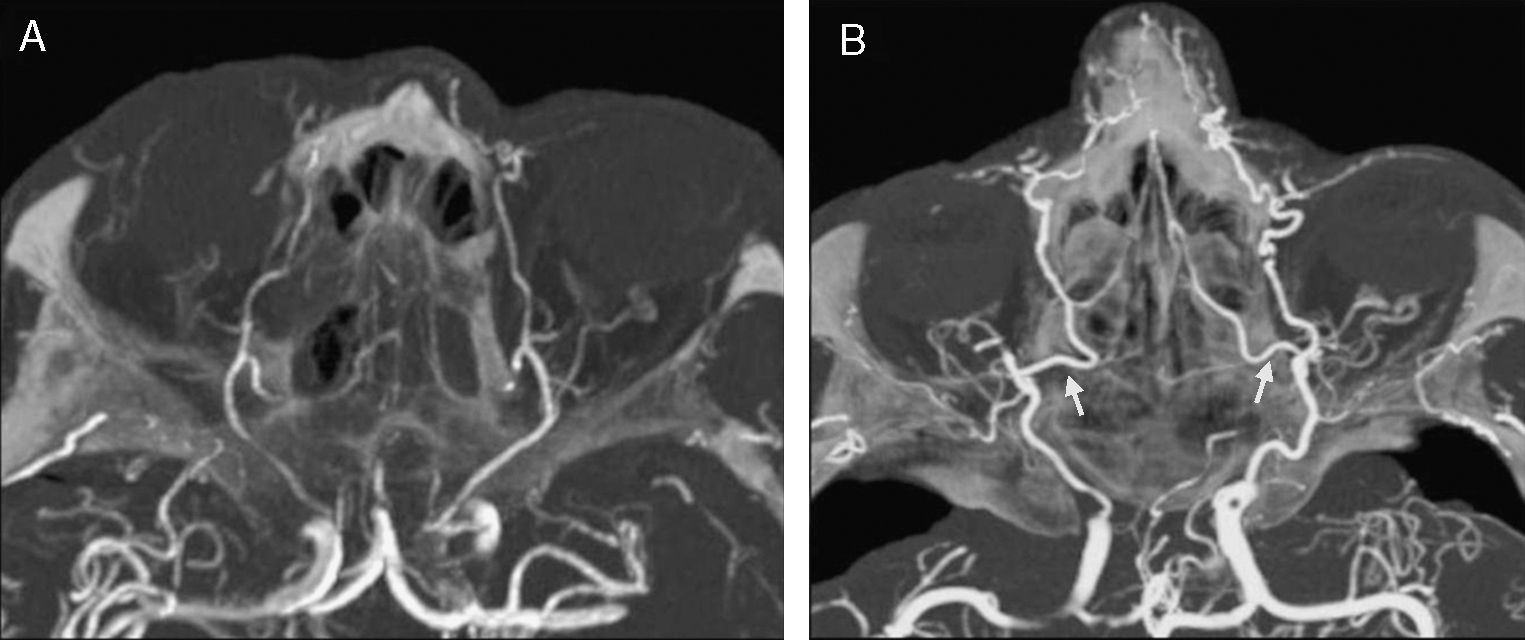
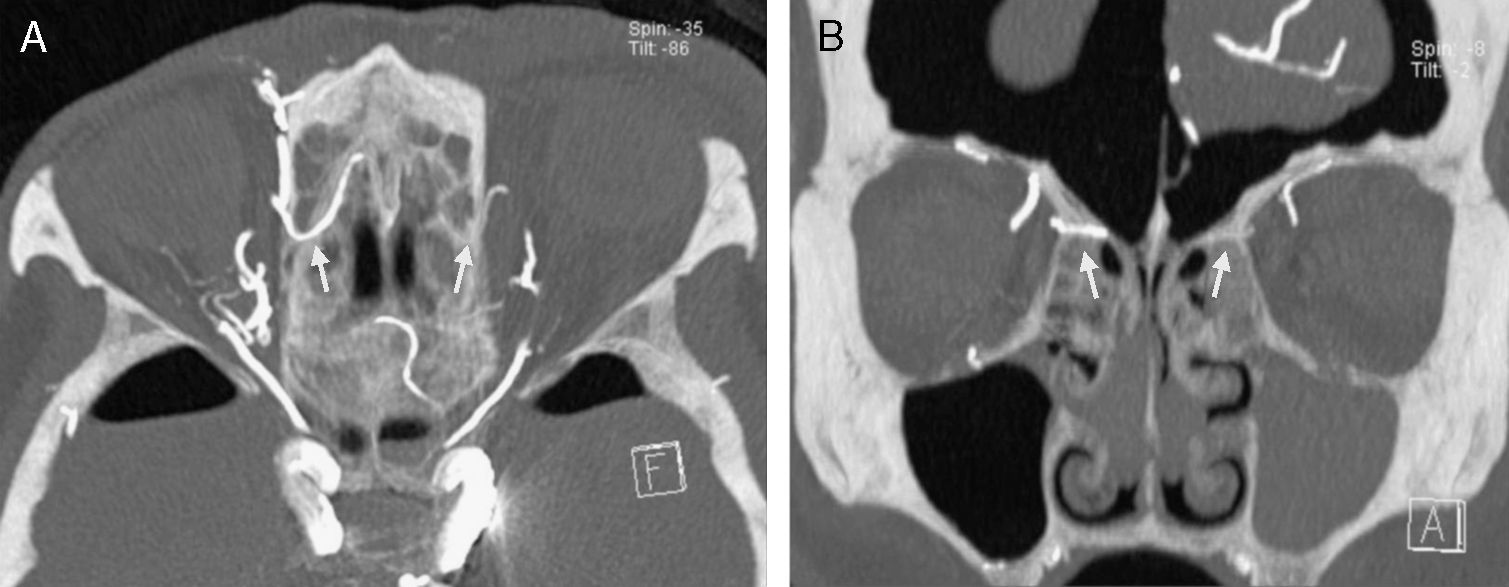
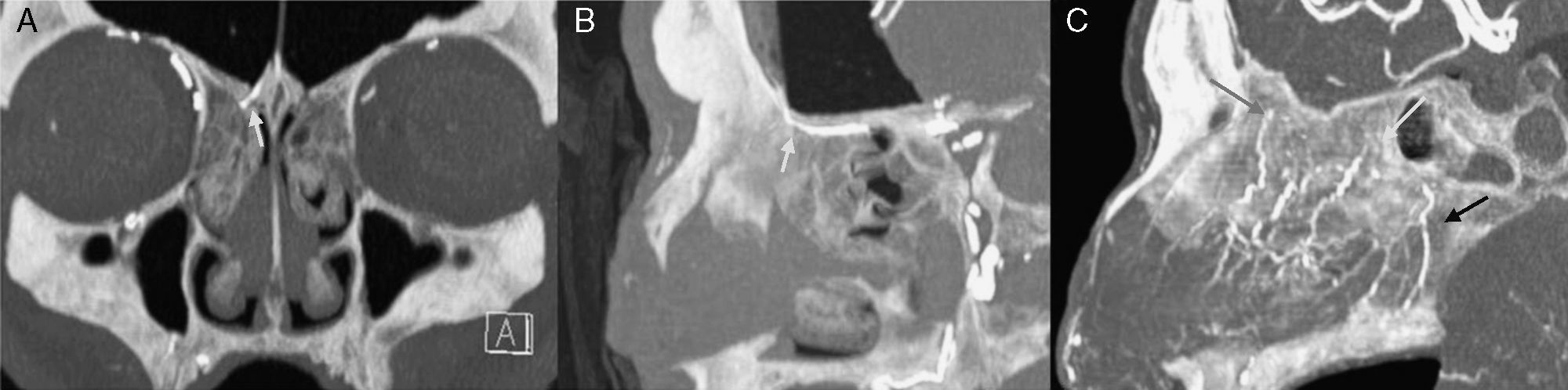
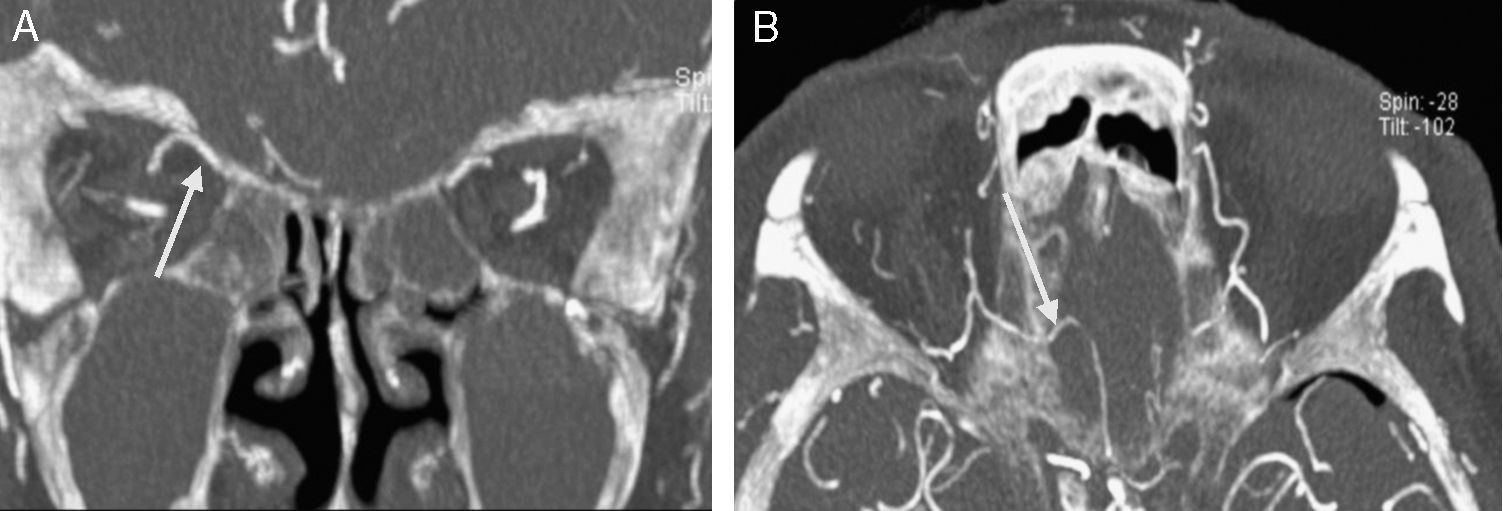
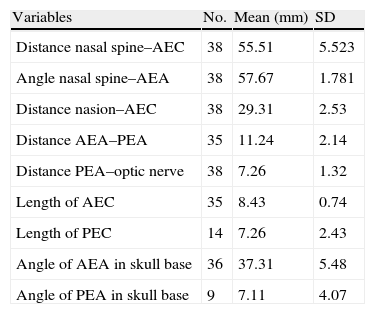
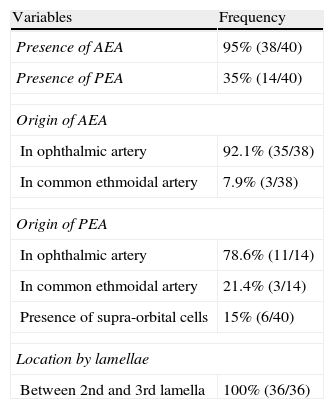
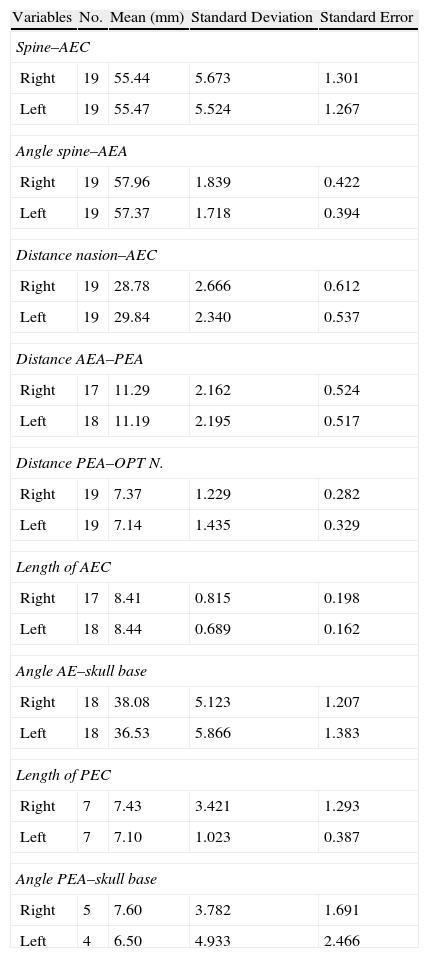
ResultsThe anterior ethmoidal artery was found in 95% (38/40) of cases. It originated from the ophthalmic artery in 87.5% (34/40) of nasal cavities. In 6 cases, normal variants were found. The mean length of the anterior ethmoidal canal was 8.43±0.74mm. The angle performed into the skull base was 37.3±5.48°. In 90% of cases (36/40), it was located between the second and third lamella. The posterior ethmoidal artery was localised only in 14/40 cases, with 28.5% (4/14) of them showing normal variants. The mean length of the posterior ethmoidal canal was 7.1±1.02mm. The angle performed into the skull base was 7.11±4.07°. The distance from sill to the anterior ethmoid artery was 55.51±5.52mm. The angle between the nasal spine and the anterior ethmoidal canal was 57.67±1.68°. The distance between the nasion and the anterior ethmoidal canal was 29.31±2.53mm, the distance was 11.24±2.14mm from the anterior ethmoid artery to the posterior ethmoid artery and from the posterior ethmoid artery to the optic nerve, 7.26±1.33mm. Supraorbital cells were observed in 15% (6/40) of the cases.
ConclusionsA complete vascular study of the ethmoidal arteries was possible by using this technique.
El objetivo del trabajo es realizar un estudio de la anatomía radiológica de las arterias etmoidales.
MétodosSe realizó un estudio descriptivo con imágenes de tomografía computarizada correspondientes a 20 cabezas de cadáver perfundidas con material radiopaco. Se analizaron diferentes parámetros anatómicos.
ResultadosLa arteria etmoidal anterior se localizó en el 95% (38/40) de los casos. En el 87,55% (35/40) de las fosas se originó de la arteria oftálmica, encontrando en seis casos variantes de la normalidad. La longitud media del canal etmoidal anterior fue de 8,43±0,74mm con un ángulo de entrada en la base de cráneo de 37,3±5,48°. En el 90% de los casos (36/40), se localizó entre la segunda y la tercera lamela. La arteria etmoidal posterior sólo pudo localizarse en (14/40) fosas nasales. El 28,5% (4/14) presentaron variantes en su origen. La longitud media del canal etmoidal posterior fue de 7,1±1,02mm realizando un ángulo anterior a su salida de la órbita de 7,11±4,07°. La distancia desde la espina nasal hasta la arteria etmoidal anterior fue de 55,51±5,52mm. El ángulo realizado entre la espina nasal y el canal etmoidal anterior fue de 57,67±1,68°. La distancia entre el nasión y el canal etmoidal anterior fue de 29,31±2,53mm, de la arteria etmoidal anterior a la arteria etmoidal posterior fue de 11,24±2,14mm y de la arteria etmoidal posterior al nervio óptico de 7,26±1,33mm. Se apreciaron celdas supraorbitarias en el 15% (6/40) de las fosas.
ConclusionesLa técnica utilizada permitió realizar un análisis vascular completo del trayecto de las arterias etmoidales.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora