Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a globally accepted technique in the preoperative evaluations of head and neck tumours; however, the effectiveness in the interpretation of salivary glands neoplastic lesions is still controversial. The objective of this study consisted of assessing the efficacy of FNAC in preoperative diagnosis of parotid tumours.
MethodsThis retrospective study was conducted using 93 patient samples with parotid gland tumoral pathology, treated at the Otorhinolaryngology Department in our institution during the 2007–2011 period. Preoperative FNAC was employed and the patients subsequently submitted to surgical excision with histopathological diagnosis of the specimen. Cytology results were classified as negative for malignancy, positive for malignancy or insufficient sample, and later compared with the definitive histological diagnosis.
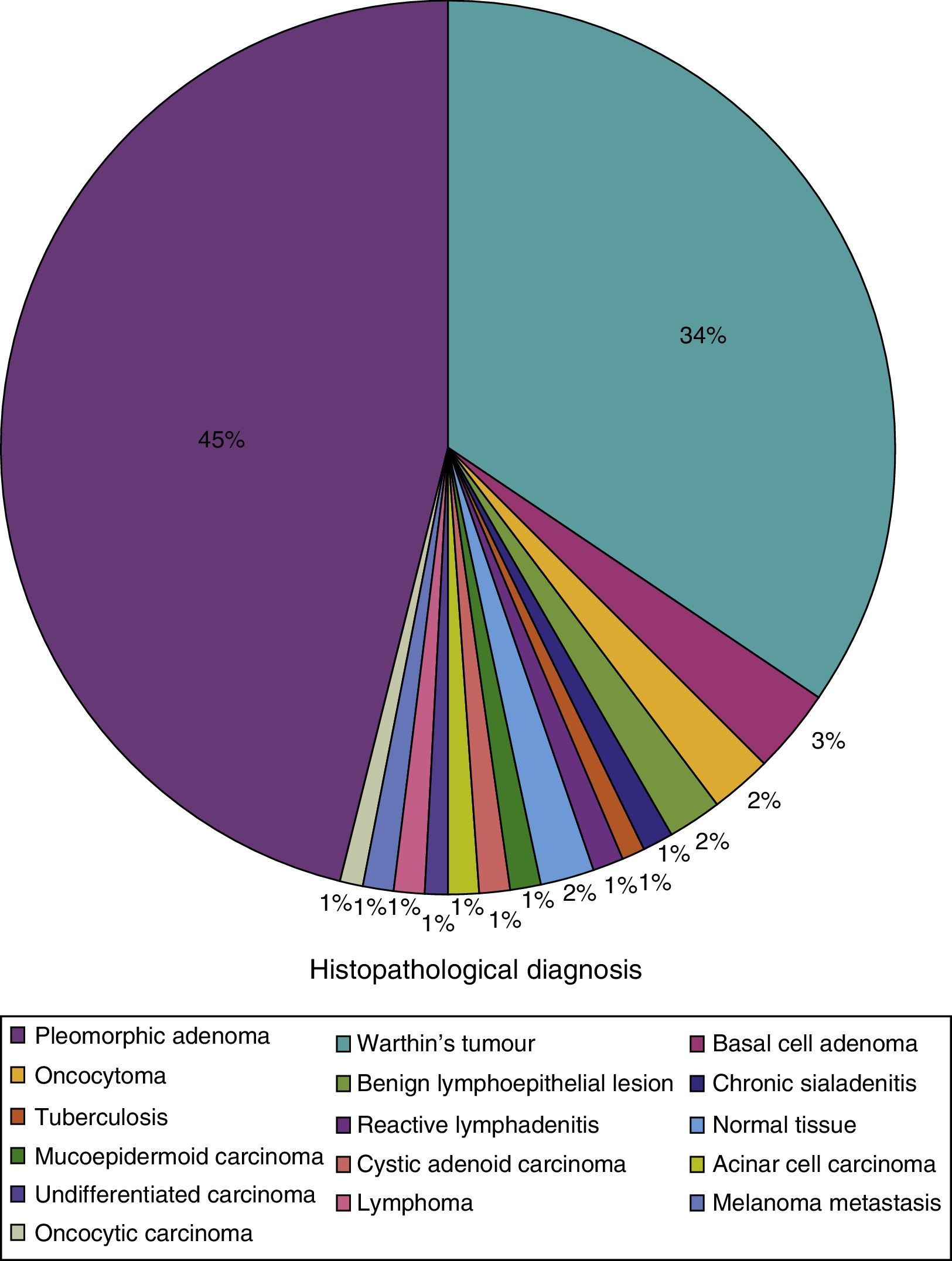
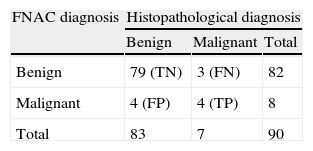
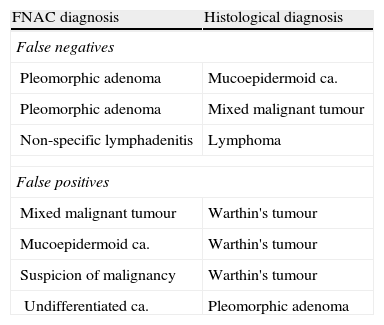
ResultsThe mean age of the studied sample was 52.9 years (range: 11–88 years); 55.9% were men. The FNAC showed significant sensitivity of 57.1%, with a specificity of 95.1%, for detecting malignancy in parotid gland tumours. The positive and negative predictive values for malignancy were 50 and 96.3%, respectively.
ConclusionsFNAC is considered a simple test but of limited use for diagnostic guidance in tumour pathology of the parotid gland in our environment, mainly because of its low sensitivity. However, the high specificity and high negative predictive value of FNAC make it a more accurate test in benign or negative result cases.
La citología por punción aspiración con aguja fina (PAAF) es un método globalmente aceptado en la evaluación preoperatoria de los tumores de cabeza y cuello, sin embargo, su efectividad en la interpretación de lesiones neoplásicas de las glándulas salivales es controvertida. El objetivo del presente estudio es evaluar la eficacia de la PAAF en el diagnóstico preoperatorio en los tumores de glándula parótida.
MétodosSe realizó un estudio retrospectivo de una muestra de 93 pacientes con enfermedad tumoral de la glándula parótida tratados en el Servicio de Otorrinolaringología de nuestra institución durante el período 2007–2011, que fueron sometidos a PAAF diagnóstica preoperatoria y posteriormente a exéresis quirúrgica y estudio anatomopatológico. Los resultados de la citología fueron clasificados como negativo o positivo para enfermedad maligna, o muestra insuficiente. Posteriormente, los resultados fueron comparados con el diagnóstico anatomopatológico definitivo.
ResultadosLa edad media de la muestra fue de 52,9 años, con un rango comprendido entre los 11 y los 88 años; el 55,9% eran hombres. La PAAF presentó una sensibilidad para detectar malignidad en tumores de la glándula parótida del 57,1% y una especificidad de 95,1%, con valores predictivo positivo y predictivo negativo para malignidad de 50 y 96,3%, respectivamente.
ConclusionesLa PAAF es una prueba sencilla pero de utilidad limitada para la orientación diagnóstica en la enfermedad tumoral de la glándula parótida en nuestro medio, debido principalmente a su baja sensibilidad; sin embargo, su alta especificidad y elevado valour predictivo negativo hacen de la misma una prueba con mayor precisión frente a un resultado benigno o negativo de la misma.