The objective of this paper is to study the etiology of vocal fold immobility with non-pathological LEMG.
MethodsA retrospective study was performed on patients who presented with vocal fold immobility and underwent LEMG from 2009 to 2017. Those patients with normal LEMG findings were selected. The different causes of vocal fold impairment were studied.
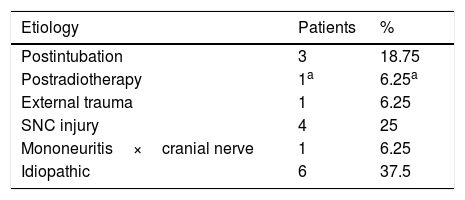
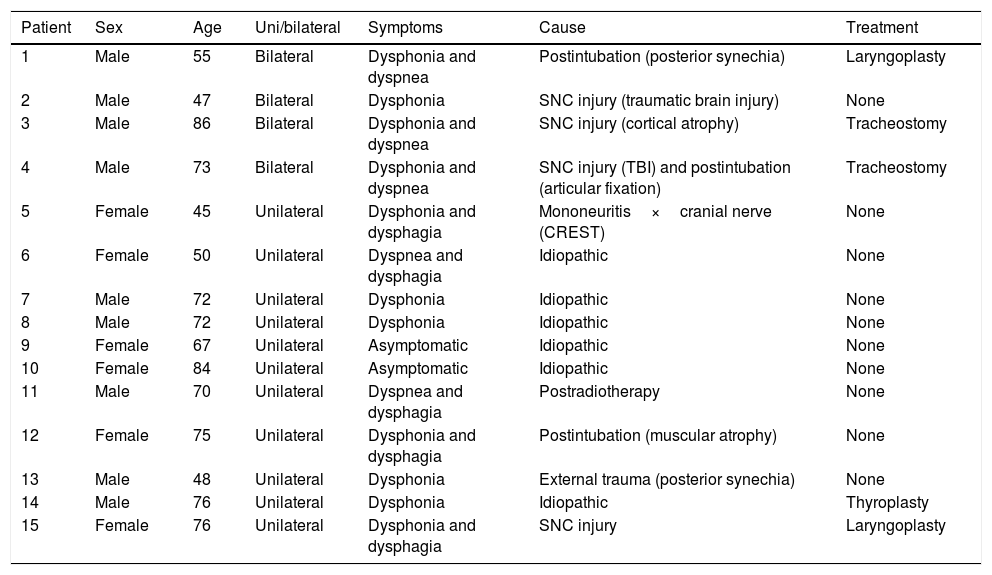
ResultsOf the 120 patients included in this study, 15 had a normal LEMG recording. The different etiologies of vocal fold immobility were idiopathic, central nervous system damage, iatrogenic, and external compression.
ConclusionsVocal fold immobility and vocal fold paralysis are not equal terms. Vocal fold immobility with normal LEMG has a heterogeneous group of causes. It is not correct to assume that the major cause of immobility in patients with normal LEMG is always cricoarytenoid joint fixation.
El propósito de este artículo es estudiar la etiología de la inmovilidad de las cuerdas vocales con una EMG laríngea no patológica.
MétodosSe ha realizado un estudio retrospectivo de pacientes con inmovilidad de cuerdas vocales a los que se les hizo EMG laríngea desde 2009 a 2017. Se seleccionaron los pacientes con EMG laríngea normal. Se estudiaron las diferentes causas de inmovilidad de las cuerdas vocales.
ResultadosDe los 120 pacientes incluidos en el estudio, 15 tuvieron un resultado de EMG laríngea normal. Las diferentes etiologías de inmovilidad de las cuerdas vocales fueron idiopáticas, lesiones del sistema nervioso central, causas iatrogénicas y compresión externa.
ConclusionesLa inmovilidad de cuerdas vocales y la parálisis de cuerdas vocales no son términos equivalentes. La inmovilidad de cuerdas vocales con EMG laríngea normal tiene un grupo de causas heterogéneo. No es correcto asumir que la principal causa de inmovilidad de cuerdas vocales en pacientes con EMG laríngea normal sea siempre la fijación cricoaritenoidea.