This study evaluates expert opinion on laryngeal electromyography (LEMG).
MethodsA cross-sectional design was used to conduct an online survey of LEMG experts in 2021. They were questioned about the number LEMG performed annually, type of electrodes used, sector worked in, pain during the test, placement of the needle electrodes, interpretation of electrical muscle parameters, diagnosis of neuromuscular injury, prognostic sensitivity in vocal fold paralysis (VFP), laryngeal dystonia, tremor and synkinesis and quantifying LEMG.
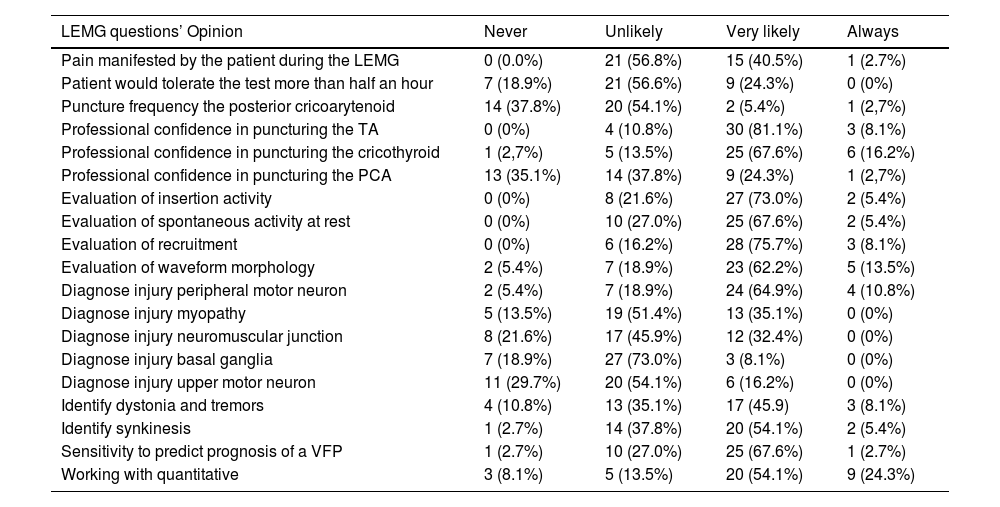
ResultsThirty-seven professionals answered (23 Spanish and 14 from other countries), with a response rate of 21.56%. All physicians used LEMG. 91.9% had one- or two-years’ experience and 56.8% performed 10–40 LEMG per year. 70.3% were otolaryngologists and 27%, neurologists. In 89.1% of cases, a team of electrodiagnostic physician and otolaryngologist performed LEMG. 91.3% of Spanish respondents worked in Public Health, 7.14% of other nationalities; 37.8% in a university department. Bipolar concentric needles electrodes were used by 45.9% and monopolar concentric by 40.5%. 57% professionals considered good patients’ tolerance to the test. LEMG sensitivity was regarded as strong, median and interquartile range were 80.0 [60.0;90.0] to diagnose peripheral nerve injuries, less for other levels of lesions, and strong to evaluate prognosis, 70.0 [50.0;80.0]. Respondents believe locate the thyroarytenoid and the cricothyroid muscles with the needle, 80.0 [70.0;90.0], as opposed to 20.0 [0.00;60.0] the posterior cricoarytenoid. The interpretation of the electrical parts of the LEMG was strong, 80.0 [60.0;90.0]. LEMG identify movements disorders, 60.0 [20.0;80.0], and synkinesis, 70.0 [30.0;80.0]. The professionals prefer quantitative LEMG, 90.0 [60.0;90.0].
ConclusionsThe experts surveyed consider LEMG that is well tolerated by patients. The insertional and spontaneous activity, recruitment and waveform morphology can be assessed easily. LEMG is mainly useful in the study of peripheral nerve injuries, and its value in VFP prognosis is considered strong.
El propósito de este estudio es evaluar la opinión de expertos en electromiografía laríngea (EMGL).
MétodosSe realizó una encuesta en línea a expertos EMGL en 2021 utilizando un diseño transversal. Se les preguntó sobre el número de EMGL realizados anualmente, el tipo de electrodos utilizados, el sector trabajado, el dolor durante la prueba, la colocación de los electrodos de aguja, la interpretación de parámetros eléctricos musculares, el diagnóstico de lesiones neuromusculares, la sensibilidad pronóstica en parálisis de cuerdas vocales (PCV), distonía laríngea, temblor y sincinesia, y la cuantificación de EMGL.
ResultadosUn total de 37 profesionales (23 españoles y 14 de otros países) respondieron, con una tasa de respuesta del 21,56%. Todos los médicos utilizaron EMGL, y el 91,9% tenía uno o dos años de experiencia. El 56,8% realizaba de 10 a 40 EMGL por año, y el 70,3% eran otorrinolaringólogos. El 89,1% de los casos se realizó EMGL en colaboración con un equipo de médico electrodiagnóstico y otorrinolaringólogo. Los electrodos de agujas bipolares concéntricos fueron utilizados por el 45,9%, y los monopolares concéntricos por el 40,5%. El 57% de los profesionales consideró buena la tolerancia de los pacientes al test. La sensibilidad EMGL se consideró fuerte para diagnosticar lesiones de los nervios periféricos, y fuerte para evaluar el pronóstico en casos de PCV. Los encuestados creen que la localización de los músculos tiroaritenoideo y cricotiroideo con la aguja es buena, pero menos efectiva para el cricoaritenoideo posterior. La interpretación de las partes eléctricas del EMGL fue fuerte, y EMGL identificó trastornos del movimiento y sincinesia. Los profesionales prefieren el EMGL cuantitativo.
ConclusionesSegún la opinión de los expertos encuestados, la electromiografía laríngea es bien tolerada por los pacientes, y la actividad de inserción y espontánea, el reclutamiento y la morfología de la forma de onda se pueden evaluar fácilmente. EMGL es principalmente útil en el estudio de lesiones de nervios periféricos, y su valor en el pronóstico de PCV se considera fuerte.