To evaluate the rate of residual tumor, understaging and perioperative complications in patients with high grade non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer who underwent second transurethral resection (re-TUR).
Materials and methodsA retrospective review of 47 patients with high grade non-muscleinvasive bladder cancer who underwent second TUR from January 2007 to December 2009 at our institution. We evaluated the rate of residual tumor and understaging detected by re-TUR, complications, and the cost of the surgery.
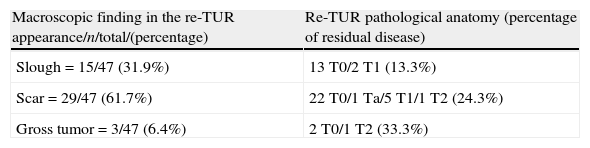
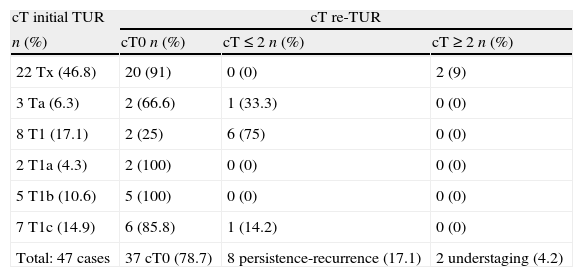
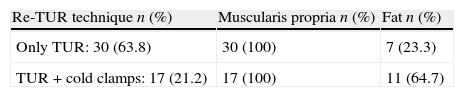
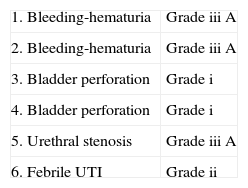
ResultsTwenty-two patients underwent second TUR because of the absence of muscle in the initial resection specimen (cTx). We observed residual disease in 8/47 patients (17%) and understaging in 2 cases (4.2%); in only 2 patients understaged, muscularis propria was not present in the sample of initial TUR. The other 20 cTx (90%) were cT0 in the re-TUR. We did not identify any case of cT1 understaged in the re-TUR (≥cT2). Six patients (12.6%) reported complications related with the second TUR (one urethral stricture, two patients required reintervention because of bleeding, one febrile urinary infection and two bladder perforations).
ConclusionsOur findings show that the absence of muscle in the initial resection specimen is the only risk factor for understaging. Therefore, we consider re-TUR is mandatory in these cases. On the other hand, when complete TUR has been performed and the muscularis propria is present and tumor free (cTa-T1), we consider that systematic re-TUR is not necessary and only indicated in selected patients, even more if we consider that re-TUR is not exempt from complications.
Evaluar la tasa de persitencia, infraestadificación y complicaciones perioperatorias en pacientes con tumor no músculo-invasivo de alto grado que han sido sometidos a re-resección transuretral (re-RTU).
Material y métodosRevisión retrospectiva de 47 pacientes con estadio clínico de tumor vesical de alto grado no músculo-invasivo sometidos a re-RTU entre enero de 2007 y diciembre de 2009 en nuestro centro. Evaluamos la tasa de tumor residual (persistencia) y de infraestadificación, así como las complicaciones quirúrgicas y el coste de la re-RTU.
ResultadosEn 22 casos se indicó la re-RTU por ausencia de muscular propia en el espécimen (cTx). Observamos tumor residual en 8/47 pacientes (17%) e infraestadificación en 2 casos (4,2%), en los 2 únicos pacientes infraestadificados no se había observado muscular propia en el espécimen de la RTU inicial. Los 20 cTx restantes (90%), fueron cT0 en la re- RTU. No observamos ningún caso de cT1 en los que en la re-RTU apareciera infraestadiaje (≥cT2). Seis pacientes (12,6%) presentaron complicaciones secundarias a la re-RTU (una estenosis uretral, 2 reintervenciones por sangrado, una infección urinaria febril y 2 perforaciones vesicales).
ConclusionesEn nuestro estudio la ausencia de muscular en el espécimen de la RTU es el único factor de riesgo de infraestadificación. Es por ello que en estos casos consideramos que la re-RTU es obligatoria. Por el contrario, en los casos donde la RTU ha sido completa y la muscular se encuentra libre de tumor (cTa-T1) creemos que la re-RTU sistemática es innecesaria, solo indicada en casos concretos y más no estando exenta de complicaciones.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora