To compare perioperative outcomes and complications of robot assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) with extracorporeal (ECUD) vs. intracorporeal urinary diversion (ICUD) for bladder cancer.
Material and methodsRetrospective revision of 43 patients who underwent RARC for bladder cancer between 2015 and 2018 with at least 3 months of follow-up. The analysis included the initial series of RARC performed by one surgeon with extensive experience in open radical cystectomy.
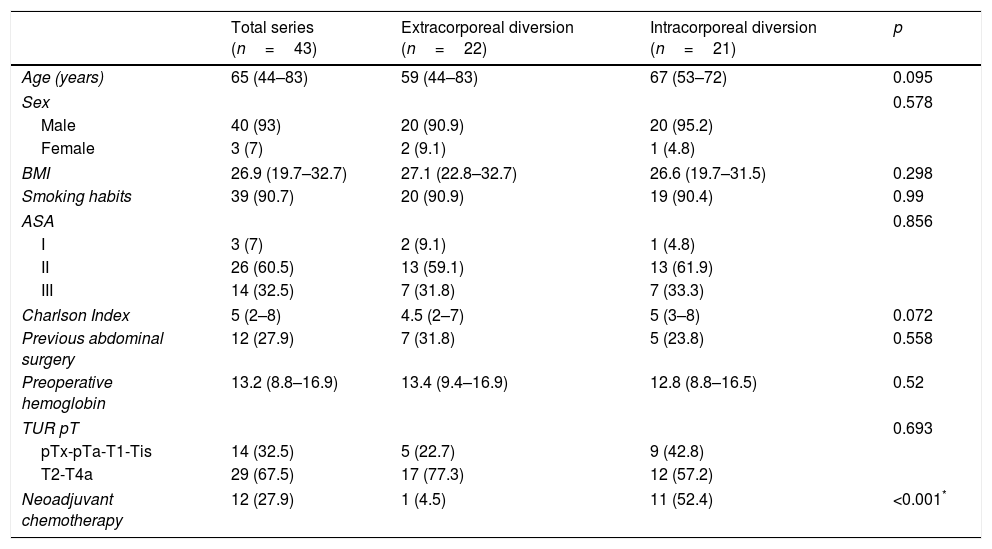
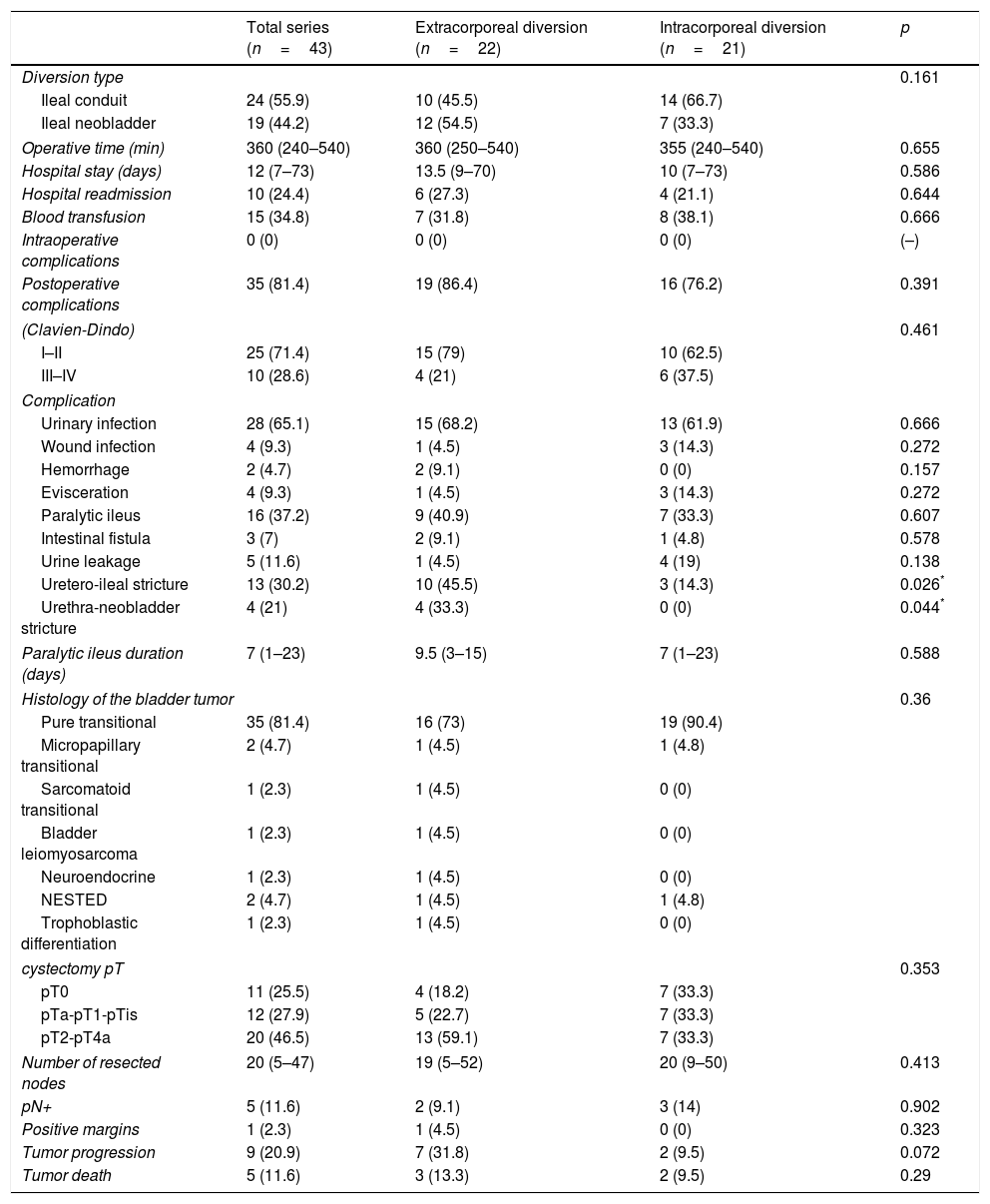
ResultsForty-three patients, 40 men (93%) and 3 women (7%), with a median age of 65 years (44–83) and mean follow-up of 27.7 months (±20.1) underwent RARC. A ECUD was performed in 22 cases (51%), of whom 10 were ileal conduits (45.5%) and 12 neobladders (54.5), and ICUD in 21 cases (49%), of whom 14 were ileal conduits (66.7%) and 7 neobladders (33.3%). Clinical and preoperative characteristics were similar in both groups. The median operative time was 360min (240–540) and length of hospital stay was 12 days (7–73). Thirty-five patients (81%) had postoperative complications, of whom 10 (23%) were major. Operative time, peroperative complications, pathological stage, positive margins, and number of lymph nodes removed did not significantly differ among groups. Patients who underwent ECUD had a higher rate of uretero-ileal strictures than those with ICUD (45.5% vs. 14.3%, p=0.026). Among the neobladders, the ECUD developed a higher rate of urethro-neobladder stricture than the ICUD (33% vs. 0%, p=0.044).
ConclusionsRARC with ICUD achieved peroperative outcomes and complication rates comparable than those with ECUD. The ICUD could reduce the risk of developing uretero-ileal and urethro-neobladder strictures.
Comparar los resultados perioperatorios y las complicaciones de la cistectomía radical asistida por robot (CRAR) con derivación urinaria extracorpórea (DUEC) vs. intracorpórea (DUIC).
Material y métodosRevisión retrospectiva de 43 pacientes sometidos a CRAR por tumor vesical entre 2015-2018 con seguimiento mínimo de 3 meses. Se analizó la serie inicial de CRAR realizada por un cirujano con amplia experiencia en cistectomía radical abierta.
ResultadosCuarenta y tres pacientes, 40 hombres (93%) y 3 mujeres (7%), con mediana de edad de 65 años (44-83) y seguimiento medio de 27,7 meses (±20,1) fueron sometidos a CRAR. Se realizó DUEC en 22 casos (51%), 10 conductos ileales (45,5%) y 12 neovejigas (54,5%), y DUIC en 21 (49%), 14 conductos ileales (66,7%) y 7 neovejigas (33,3%). Las características clínicas y preoperatorias fueron comparables entre grupos. La mediana de tiempo operatorio fue 360minutos (240-540) y de estancia hospitalaria 12 días (7-73). Treinta y cinco pacientes (81%) presentaron complicaciones postoperatorias, de las cuales 10 (23%) fueron mayores. No se encontraron diferencias en tiempo operatorio, complicaciones perioperatorias, estadificación patológica, márgenes y número de ganglios extirpados entre DUEC y DUIC. Los pacientes sometidos a DUEC presentaron mayor tasa de estenosis uretero-ileal en comparación con la DUIC (45,5% vs. 14,3%, p=0,026). En las neovejigas la DUEC presentó mayor tasa de estenosis uretroneovesical que la DUIC (33% vs. 0%, p=0,044).
ConclusionesLa CRAR con derivación urinaria intracorpórea ofrece resultados perioperatorios y complicaciones comparables a la extracorpórea. La derivación intracorpórea podría reducir el riesgo de desarrollar estenosis ureteroileal y uretroneovesical.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora