From 4 to 6% of males subjected to radical cystectomy due to urothelial carcinoma will have urethral recurrence (UR) during the follow-up.
ObjectiveTo analyze the diagnosis, treatment and course of the patients with UR following a cystectomy.
Acquiring of evidenceAnalysis of original articles and reviews related with the diagnosis, treatment, and course of patients subjected to radical cystectomy and who develop UR. The articles were obtained from a search in PubMed.
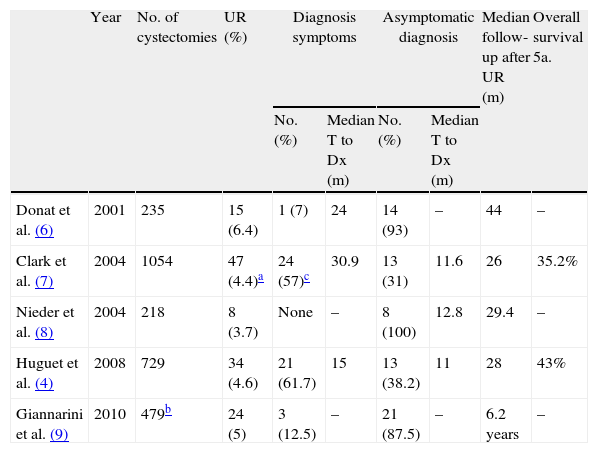
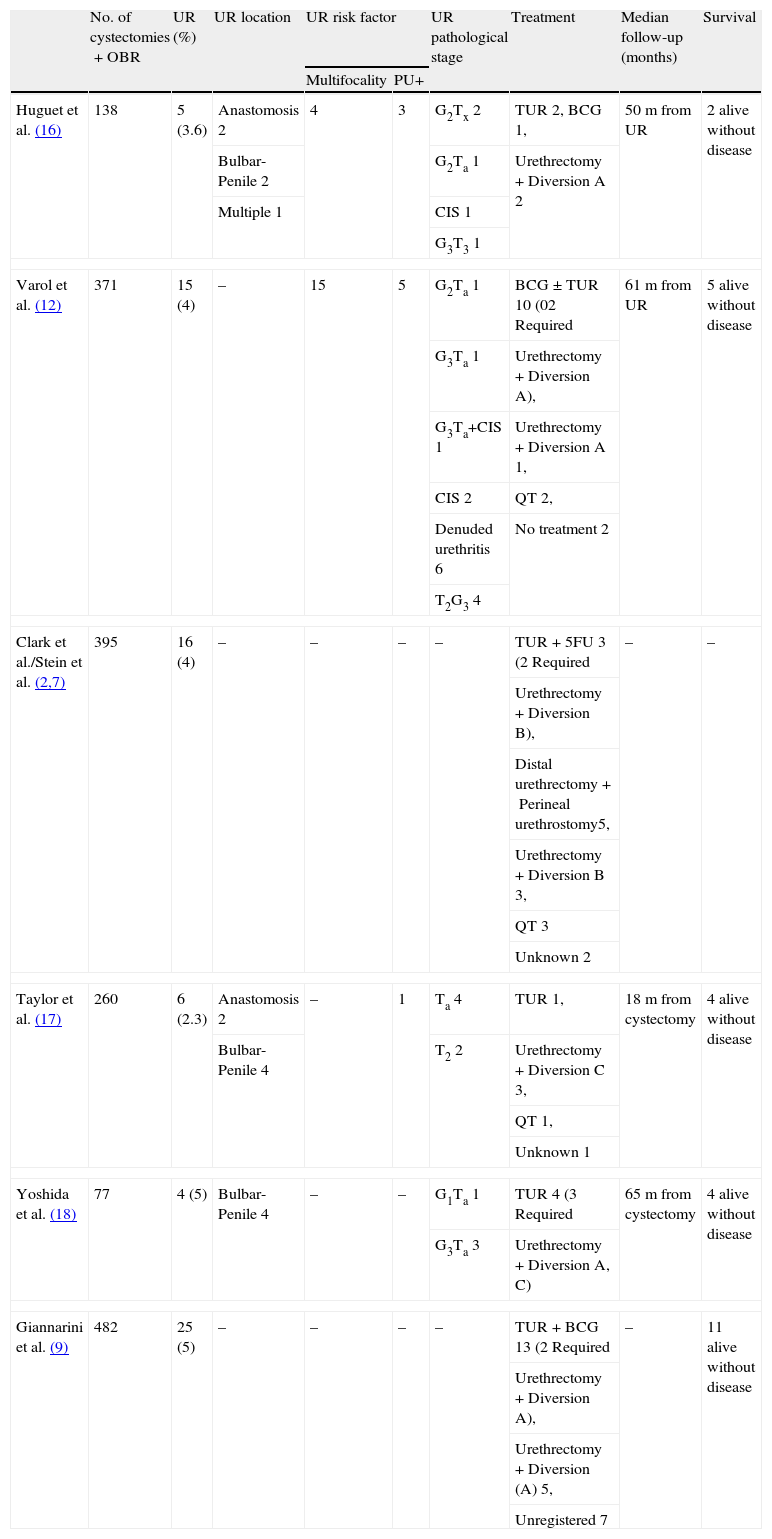
Synthesis of evidenceMost of the UR appear during the first 3 years of the cystectomy. Approximately 50% of the URs of contemporary series were diagnosed through urethral cytology, the patient being asymptomatic. The urethrectomy is the treatment of choice in patients with UR and cutaneous diversion. In patients with orthotopic bladder replacement (OBR): (1) the treatment of the intraurethral BCG can be useful in patients with carcinoma in situ (CIS), (2) papillary type conservative treatment in UR has contradictory results, and (3) when the uretrectomy is necessary, the ileal duct or conversion of the OBR in a continent urinary derivation can be used.
ConclusionsUrethral cytology is a test having high sensitivity and can contribute to the diagnosis of UR in the earliest stages. In patients with OBR, the diagnosis of a UR is a therapeutic challenge. The bladder tumor, urethral recurrence, and presence of an upper urinary tract tumor in 25% of the cases may be a cause of death in these patients.
Entre un 4-6% de los varones sometidos a cistectomía radical por carcinoma urotelial presentarán recidiva uretral (RU) durante el seguimiento.
ObjetivoAnalizar el diagnóstico, tratamiento y evolución de los pacientes con RU después de cistectomía.
Adquisición de evidenciaAnálisis de artículos originales y de revisión, relacionados con el diagnóstico, tratamiento y evolución de pacientes sometidos a cistectomía radical y que desarrollan RU. Artículos obtenidos de la búsqueda en PubMed.
Síntesis de evidenciaLa mayoría de las RU aparecen en los 3 primeros años después de la cistectomía. Cerca del 50% de las RU de series contemporáneas se diagnosticaron a través de citología uretral, estando el paciente asintomático. La uretrectomía es el tratamiento de elección en pacientes con RU y derivación cutánea. En pacientes con sustitución vesical ortotópica (SVO): 1) el tratamiento con BCG intrauretral puede ser útil en pacientes con carcinoma in situ (CIS); 2) el tratamiento conservador en RU de tipo papilar presenta resultados contradictorios, y 3) en caso de ser necesaria la uretrectomía, puede optarse por un conducto ileal o por la conversión de la SVO en una derivación urinaria continente.
ConclusionesLa citología uretral es una prueba con una elevada sensibilidad y puede contribuir al diagnóstico de RU en estadios más tempranos. En pacientes con SVO, el diagnóstico de una RU supone un reto terapéutico. El tumor vesical, la recidiva uretral, y la presencia de un tumor de vía urinaria alta en un 25% de los casos, pueden ser causa de fallecimiento en estos pacientes.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora