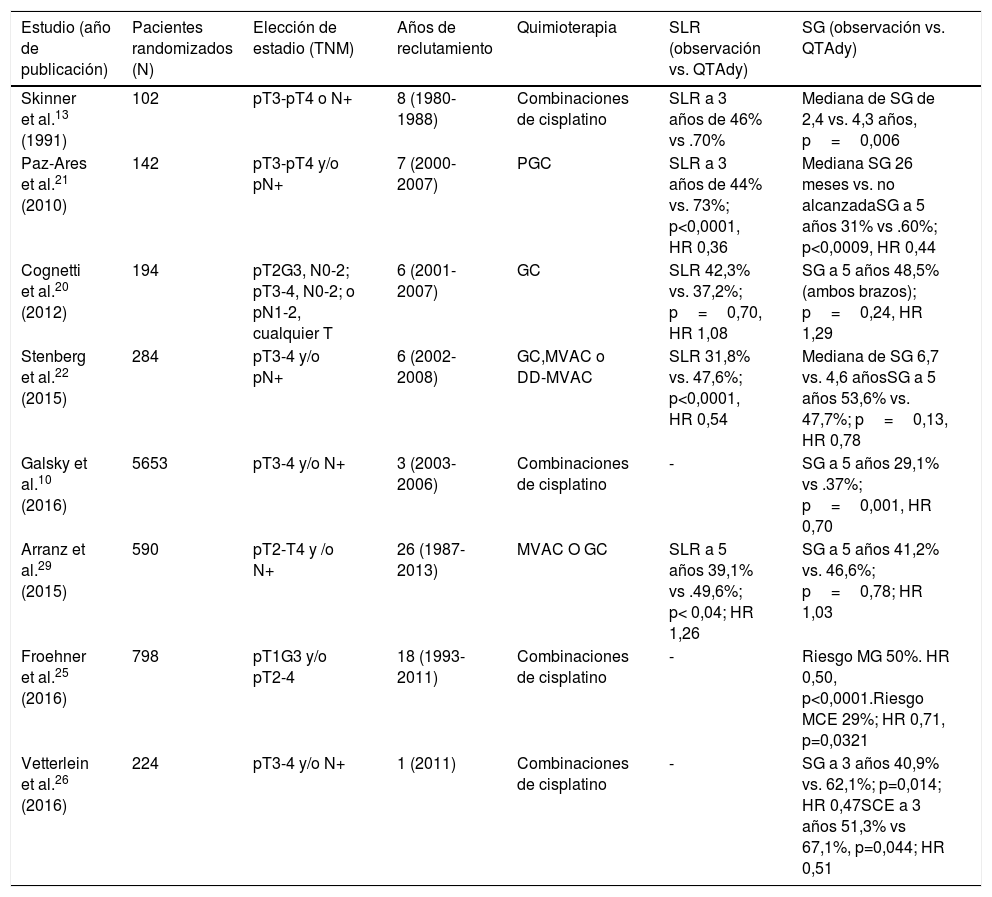
El papel de la quimioterapia adyuvante (QTAdy) en el tumor vesical músculo-invasivo sigue siendo controvertido actualmente.
ObjetivoEvaluar el efecto de la QTAdy en la supervivencia cáncer específica del tumor vesical músculo-invasivo tras cistectomía radical (CR).
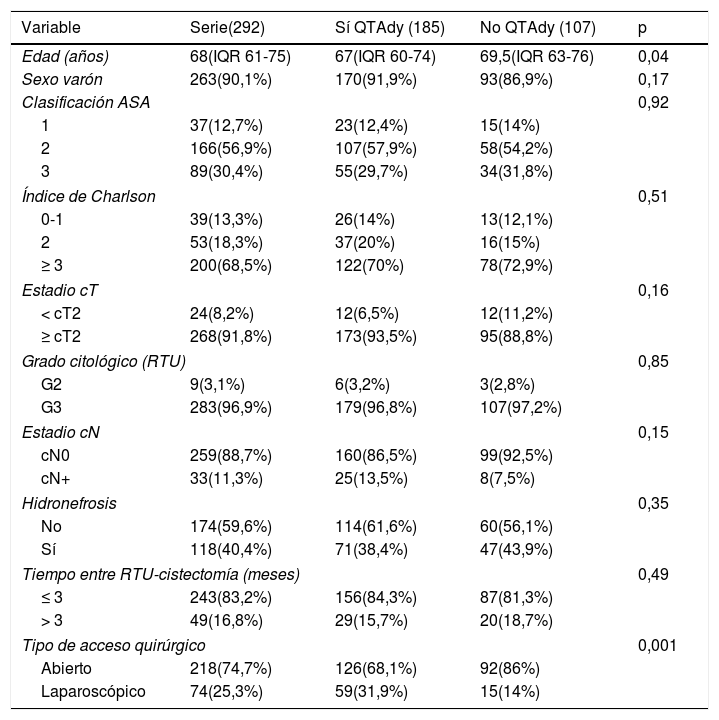
Material y métodosAnálisis retrospectivo de 292 pacientes diagnosticados de tumor vesical urotelial tratados con CR entre 1986-2009 con estadio pT3-4pN0/+cM0, divididas en dos cohortes:185(63,4%) pacientes tratados con QTAdy y otra con 107(36,6%) sin QTAdy. Mediana de seguimiento de 40,5 meses (IQR 55-80,5).
Análisis comparativo con test Chi cuadrado y t Student/ANOVA. Cálculo de supervivencia con el método de Kaplan-Meier y test de long-rank. Análisis multivariante (regresión de Cox) para identificar variables predictoras independientes de mortalidad cáncer específica (MCE).
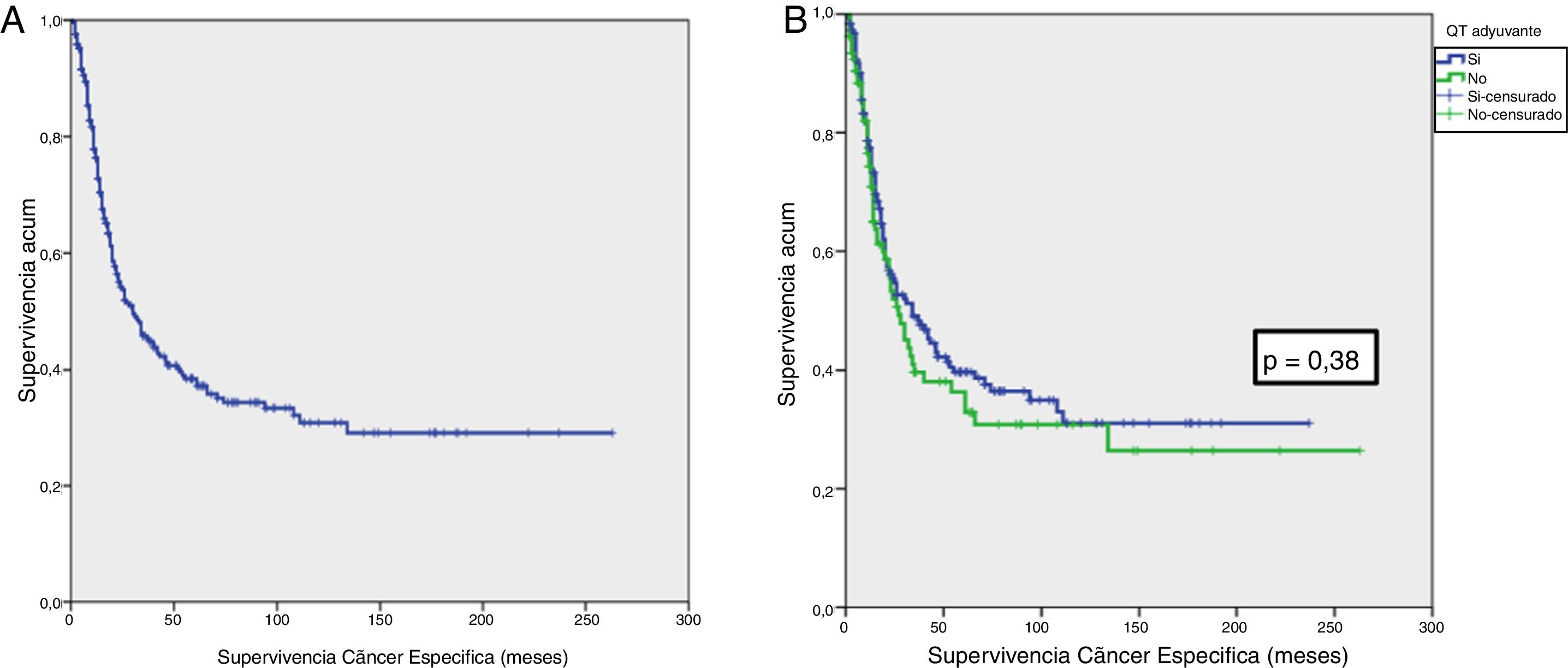
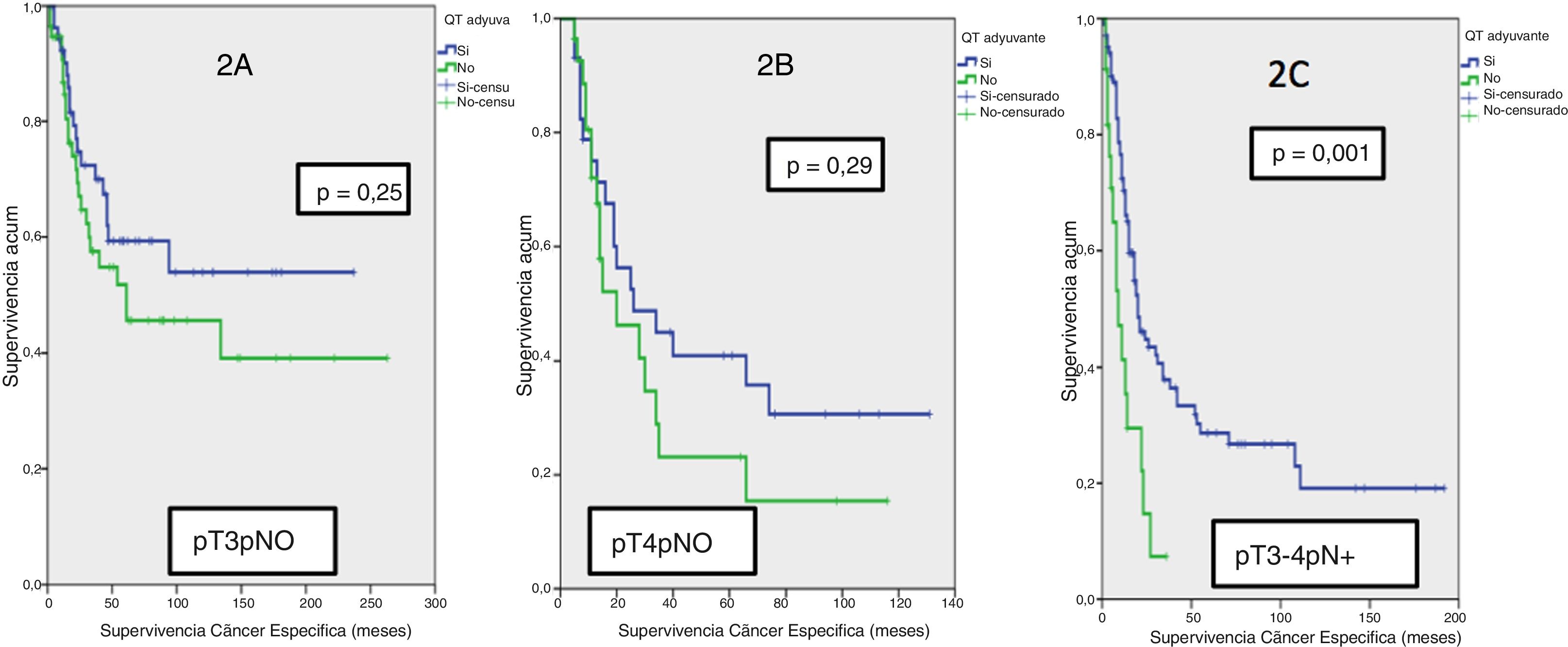
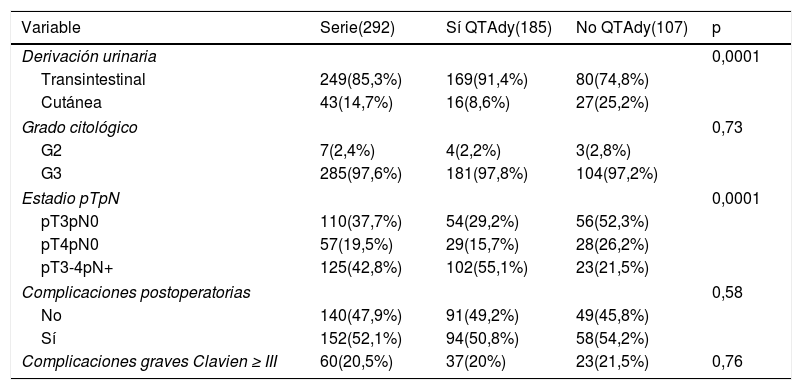
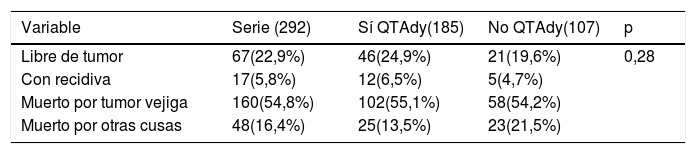
ResultadosEl 42,8% de la serie presentó afectación ganglionar tras CR. Al finalizar el seguimiento, 22,9% estaban libres de tumor vesical y 54,8% habían fallecido por esa causa. La mediana de supervivencia cáncer específica fue de 30 meses. No se observaron diferencias significativas en supervivencia cáncer específica en función del tratamiento con QTAdy en pacientes pT3pN0 (p=0,25) ni pT4pN0 (p=0,29), pero sí en pT3-4pN+ (p=0,001).
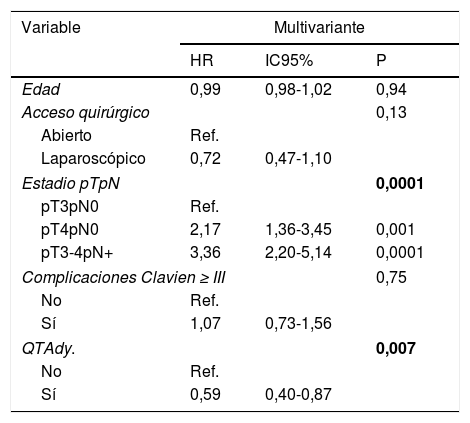
En el análisis multivariante se identificaron el estadio patológico (p=0,0001) y el tratamiento con QTAdy (p=0,007) como factores pronósticos independientes de MCE. La QTAdy redujo el riesgo de MCE (HR:0,59, IC95% 0,40-0,87, p=0,007).
ConclusionesEl estadio pT y pN se identificaron como variables predictoras independientes de MCE tras CR. La administración de QTAdy en nuestra serie se comportó como factor protector reduciendo el riesgo de MCE, aunque en el análisis por estadios, únicamente los pacientes pN+ se vieron beneficiados.
Currently, the role of adjuvant chemotherapy (ADJ) in muscle invasive bladder tumor remains controversial.
ObjectiveTo evaluate the effect of ADJ on cancer specific survival of muscle invasive bladder tumor after radical cystectomy (RC).
Material and methodsRetrospective analysis of 292 patients diagnosed with urothelial bladder tumor pT3-4pN0 / + cM0 stage, treated with RC between 1986-2009. Total cohort was divided in two groups: 185 (63.4%) patients treated with ADJ and 107 (36.6%) without ADJ. Median follow-up was 40.5 months (IQR 55-80.5).
Comparative analysis was performed with Chi-square test and Student's t test /ANOVA. Survival analysis was carried out with the Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test. Multivariate analysis (Cox regression) was made to identify independent predictors of cancer-specific mortality (CSM).
Results42.8% of the series presented lymph node involvement after RC. At the end of follow-up, 22.9% were BC-free and 54.8% had died due to this cause. The median cancer specific survival was 30 months. No significant differences were observed in cancer specific survival regarding the treatment with ADJ in pT3pN0 (p=.25) or pT4pN0 (p=.29) patients, but it was significant in pT3-4pN+ (p=.001).
Multivariate analysis showed pathological stage (p=.0001) and treatment with ADJ (p=.007) as independent prognostic factors for CSM. ADJ reduced the risk of CSM (HR:0.59,95% CI 0.40-0.87, p=.007).
ConclusionspT and pN stages were identified as independent predictors of CSM after RC. The administration of ADJ in our series behaved as a protective factor reducing the risk of CSM, although only pN+ patients were benefited in the stage analysis.