Elaborar un modelo predictivo de mortalidad cáncer específica (MCE) a 1, 3, y 5 años basándonos en variables clínicas precirugía y patológicas poscirugía en pacientes con tumor urotelial vesical tratados con cistectomía radical.
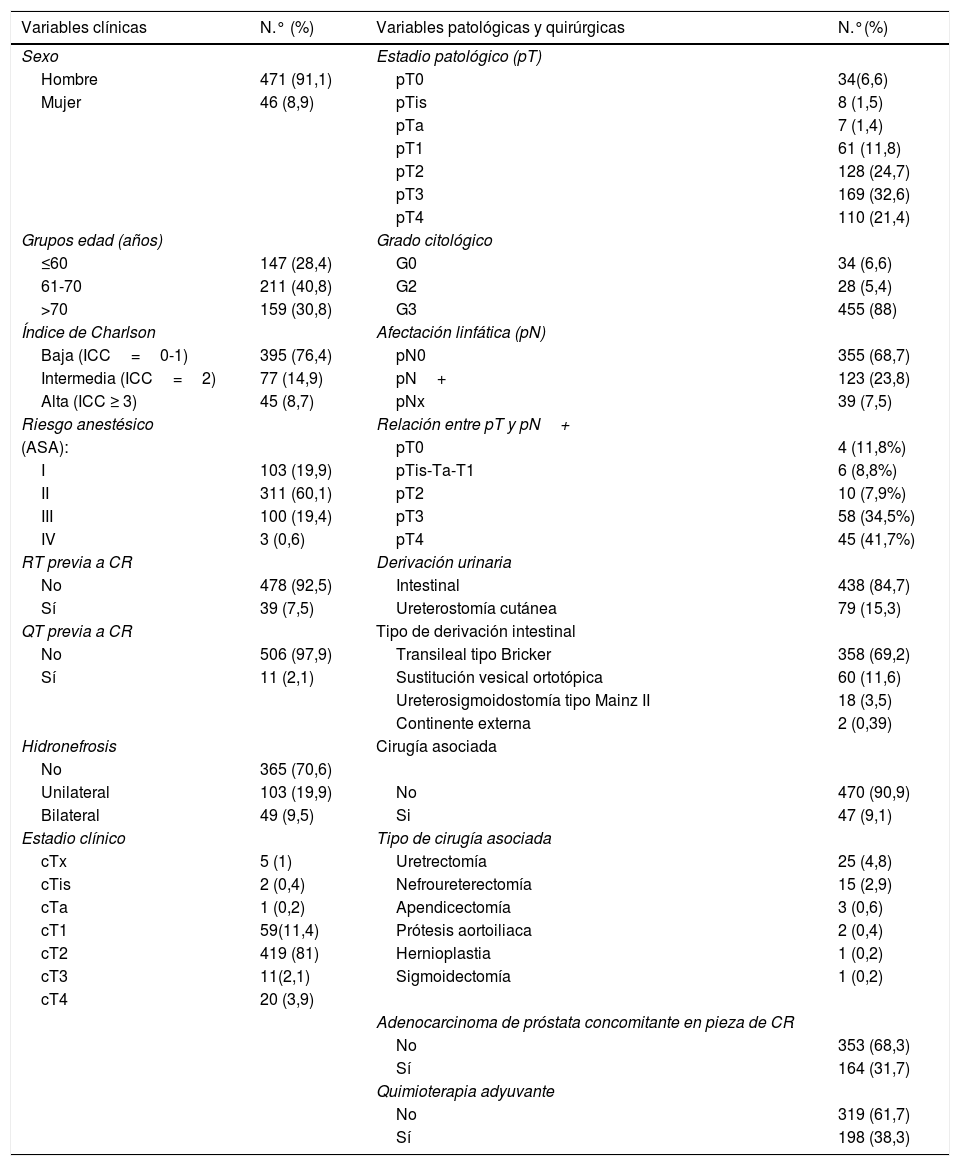
Material y métodosAnálisis retrospectivo de 517 pacientes diagnosticados de tumor urotelial vesical y tratados con cistectomía radical (1986 y 2009). Se recogieron variables demográficas, clínicas, quirúrgicas y patológicas, así como complicaciones acontecidas y evolución tras cistectomía radical.
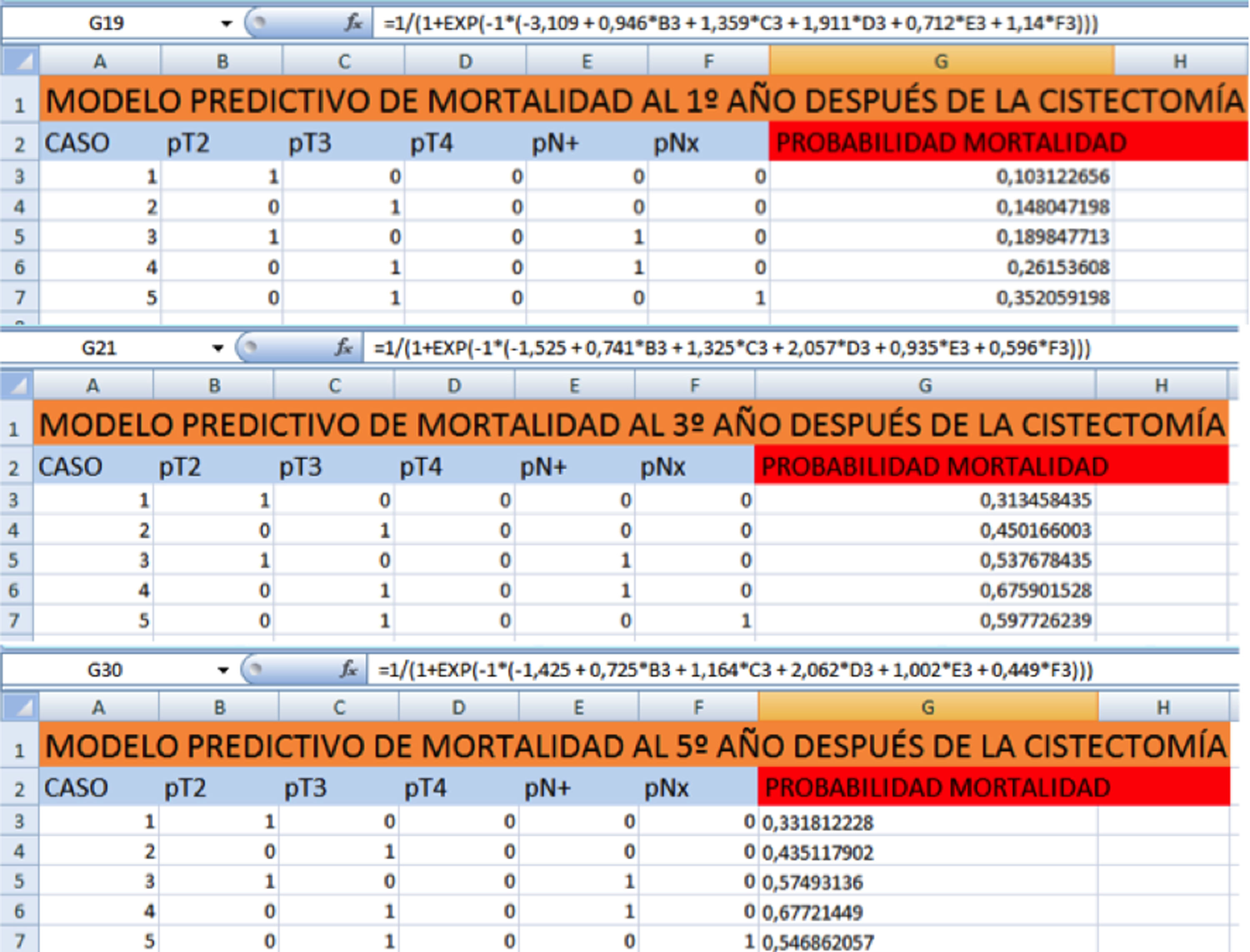
Análisis comparativo con test de Chi cuadrado y ANOVA. Cálculo de supervivencia con método de Kaplan-Meier y test de log-rank. Análisis univariante y multivariante mediante regresión logística para identificar las variables predictoras independientes de MCE. Se calculó la probabilidad individual de MCE a 1, 3 y 5 años según la ecuación general (función logística). La calibración se obtuvo mediante método de.
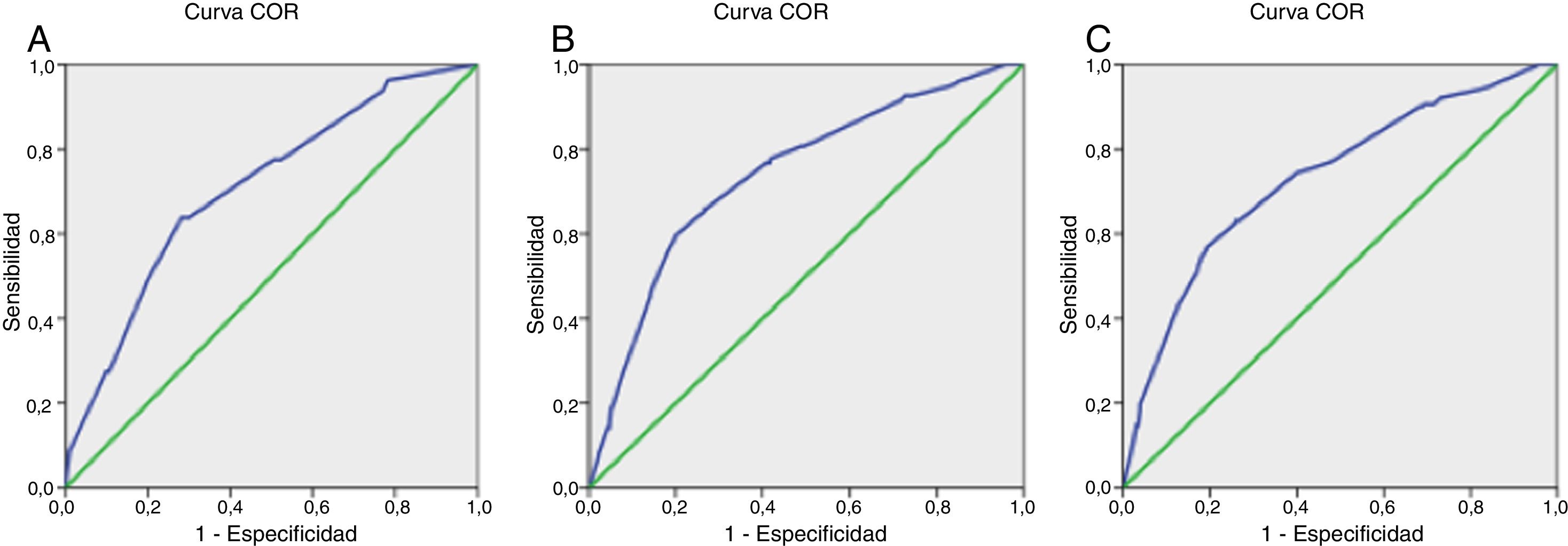
Hosmer-Lemeshow y la discriminación con elaboración de una curva ROC (área bajo la misma).
ResultadosEl tumor urotelial vesical fue la causa de muerte en 225 pacientes (45%). Se obtuvo una MCE el 1.°, 3.° y 5.° años del 17%, 39,2% y 46,3% respectivamente.
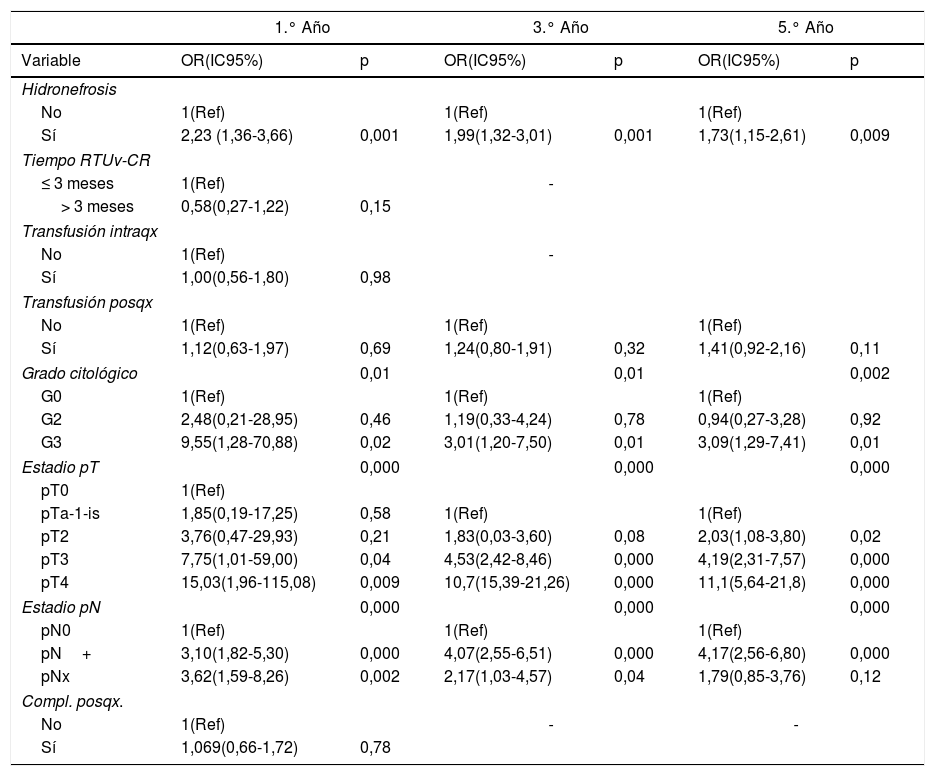
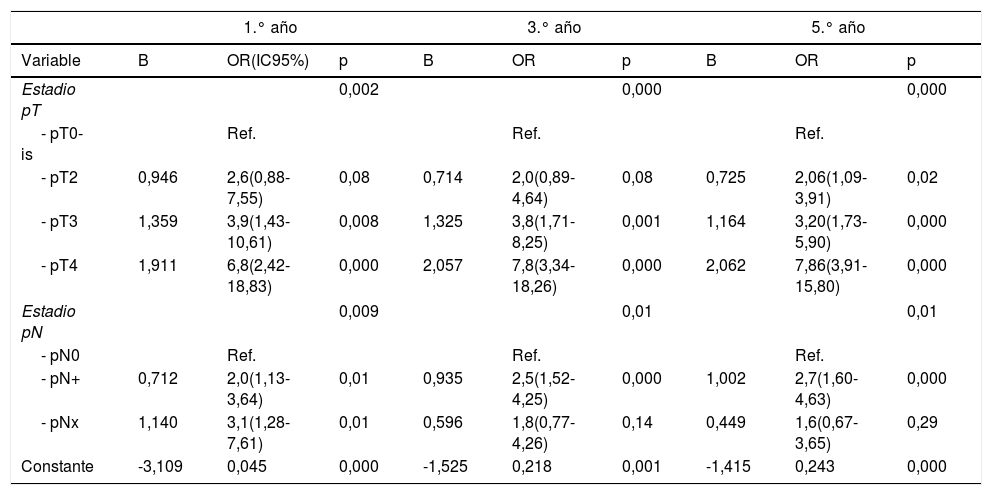
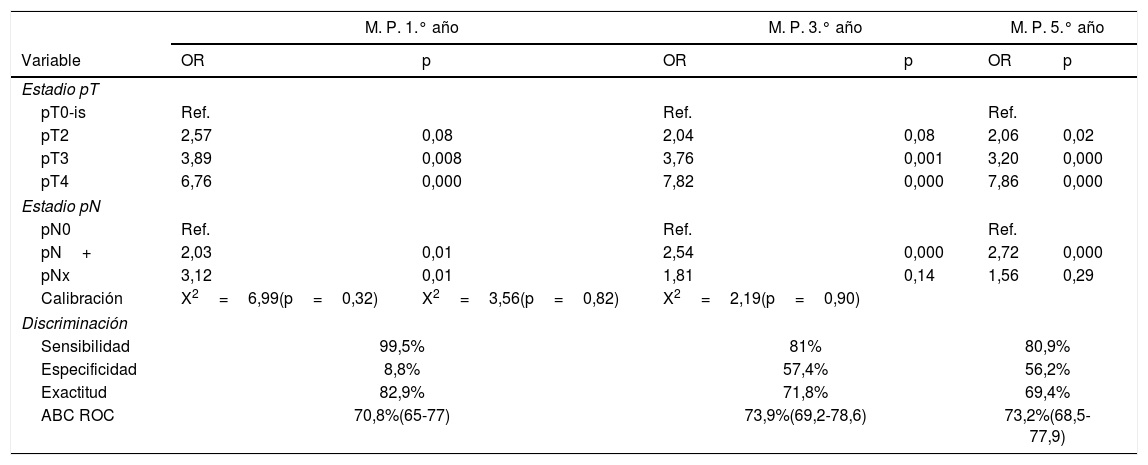
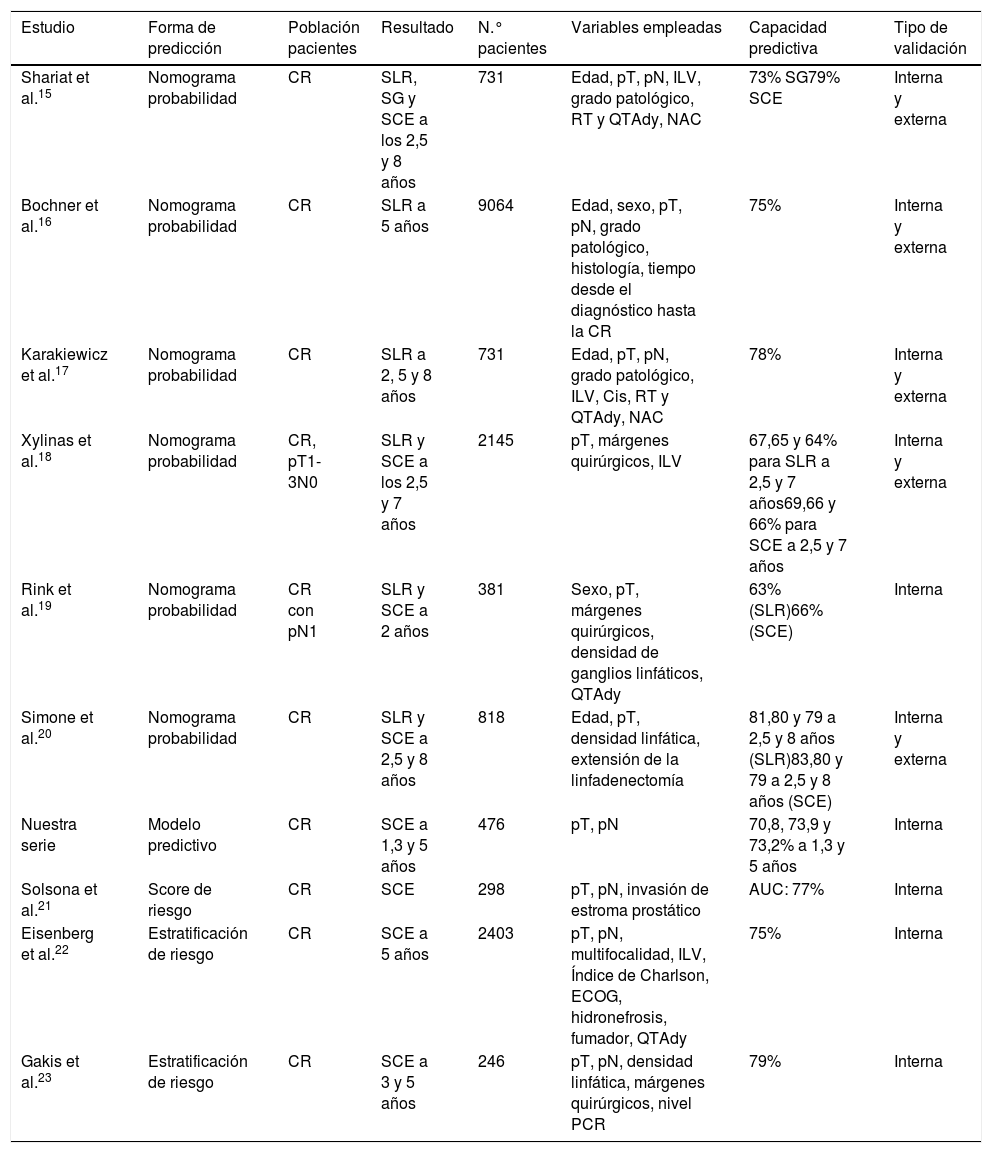
El estadio pT y pN se identificaron como variables pronósticas independientes de MCE al 1.°, 3.° y 5.° años. Se construyeron 3 modelos predictivos. La capacidad predictiva fue del 70,8% (IC95% 65-77%, p=0,000) para el 1.° año, del 73,9% (IC95% 69,2-78,6%, p=0,000) para el 3.° año y del 73,2% (IC95% 68,5-77,9%, p=0,000) para el 5.° año.
ConclusionesEl modelo predictivo permite estimar el riesgo de MCE a los 1, 3 y 5 años con fiabilidad del 70,8, 73,9 y 73,2% respectivamente.
Based on preoperative clinical and postoperative pathological variables, we aim to build a prediction model of cancer specific mortality (CSM) at 1, 3, and 5 years for patients with bladder transitional cell carcinoma treated with RC.
Material and methodsRetrospective analysis of 517 patients with diagnosis of cell carcinoma treated by RC (1986-2009). Demographic, clinical, surgical and pathological variables were collected, as well as complications and evolution after RC.
Comparative analysis included Chi square test and ANOVA technique. Survival analysis was performed using Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed using logistic regression to identify the independent predictors of CSM. The individual probability of CSM was calculated at 1, 3 and 5 years according to the general equation (logistic function). Calibration was obtained by the Hosmer-Lemeshow method and discrimination with the elaboration of a ROC curve (area under the curve).
ResultsBC was the cause of death in 225 patients (45%). One, three and five-year CSM were 17%, 39.2% and 46.3%, respectively.
The pT and pN stages were identified as independent prognostic variables of CSM at 1, 3 and 5 years. Three prediction models were built. The predictive capacity was 70.8% (CI 95% 65-77%, p=.000) for the 1st year, 73.9% (CI95% 69.2-78.6%, p=.000) for the third and 73.2% (CI% 68.5-77.9%, p=.000) for the 5th.
ConclusionsThe prediction model allows the estimation of CSM risk at 1, 3 and 5 years, with a reliability of 70.8, 73.9 and 73.2%, respectively.