To assess the accuracy of targeted and systematic biopsies for the detection of prostate cancer (PCa) and clinically significant PCa (csPCa) in the everyday practice, evaluating the need for additional systematic biopsies at the time of targeted biopsy.
Patients and methodsFrom our multicentric database gathering data on 2115 patients who underwent fusion biopsy with Koelis™ system between 2010 and 2017, we selected 1119 patients who received targeted biopsies (a median of 3 for each target), followed by systematic sampling of the prostate (12–14 cores). Overall and clinically significant cancer detection rate (CDR) of Koelis™ fusion biopsies were assessed, comparing target and systematic biopsies. Secondary endpoint was the identification of predictors of PCa detection.
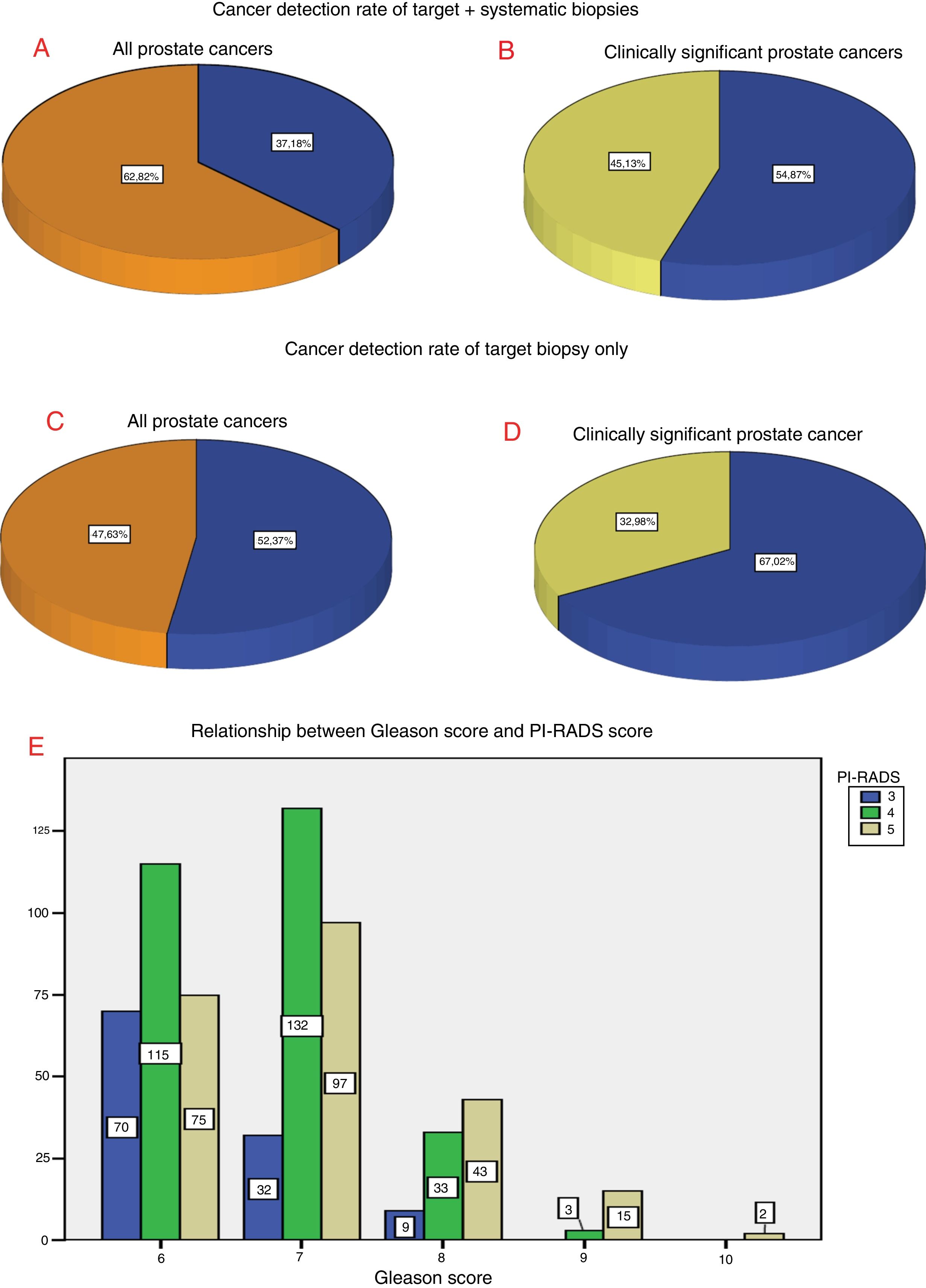
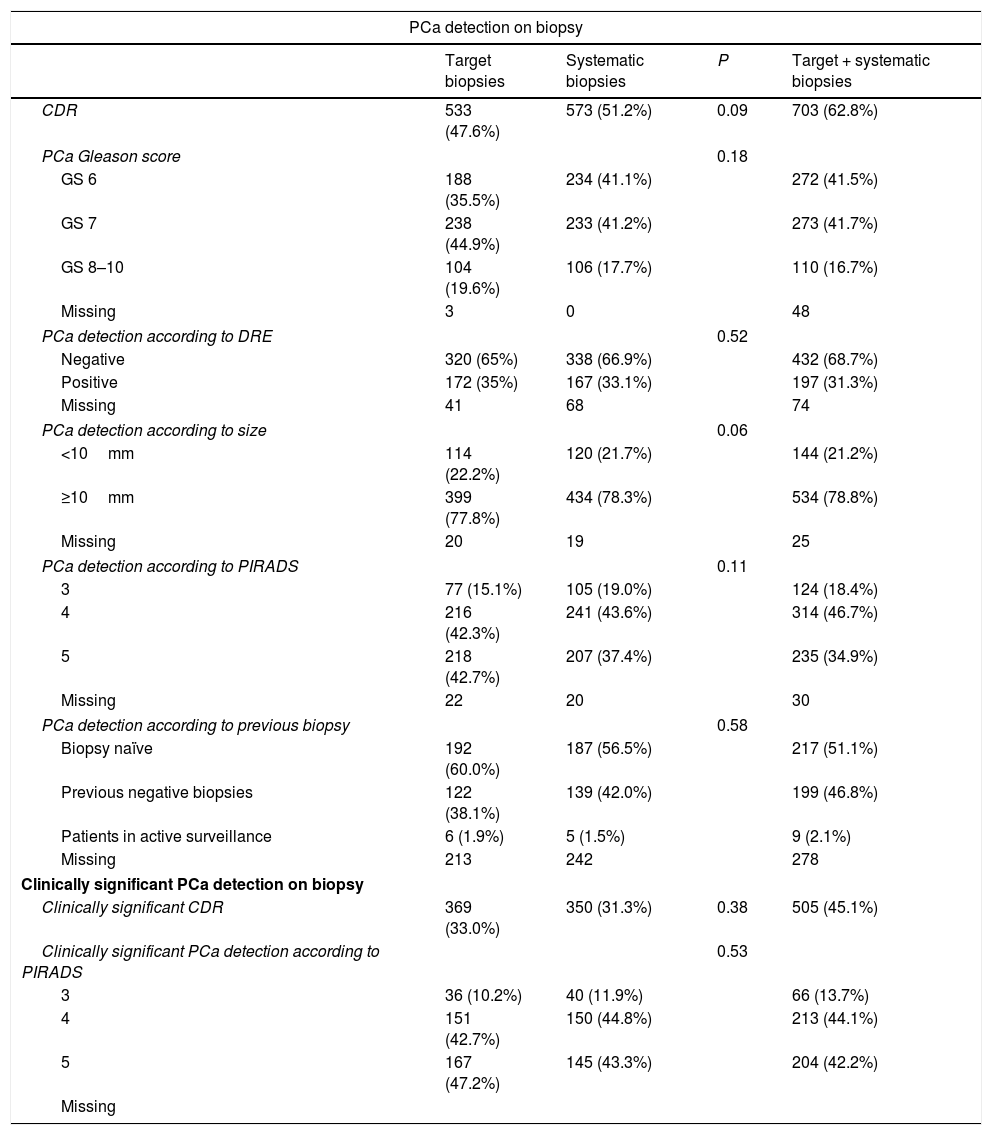
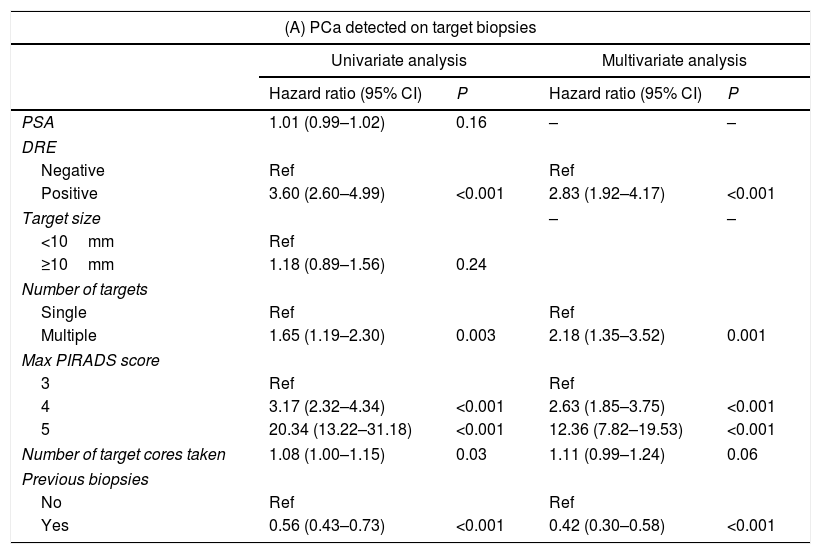
ResultsThe CDR of targeted biopsies only was 48% for all cancers and 33% for csPCa. The performance of additional, systematic prostate sampling improved the CDR of 15% for all cancers and of 12% for csPCa. PCa was detected in 35%, 69%, and 92% of patients with lesions scored as PI-RADS 3, 4 and 5, respectively. Elevated PI-RADS score and positive digital rectal examination were predictors of PCa, whereas biopsy-naïve status was associated with csPCa.
ConclusionIn the everyday practice target biopsy with Koelis™ achieves a good CDR for all PCa and csPCa, which is significantly improved by subsequent systematic sampling of the prostate. The outstanding outcomes of fusion biopsy are confirmed also in biopsy-naïve patients. Elevated PI-RADS score and positive digital rectal examination are strongly associated with presence of PCa.
Evaluar la precisión de las biopsias guiada y sistemática para la detección del cáncer de próstata (CP) y CP clínicamente significativo (CPCS) en la práctica diaria, analizando el requerimiento de biopsias sistemáticas adicionales en el momento de la biopsia guiada.
Pacientes y métodosDe nuestra base de datos multicéntrica que incluye 2.115 pacientes sometidos a biopsia de fusión con el sistema Koelis™ entre 2010 y 2017, seleccionamos 1.119 pacientes que recibieron biopsias guiadas (una mediana de 3 por cada lesión), con posterior muestreo sistemático (12 a 14 núcleos). Se evaluó la tasa de detección de cáncer (TDC) global y clínicamente significativa de las biopsias de fusión de Koelis™, comparando la biopsia guiada con la sistemática. Como objetivo secundario, está la identificación de los predictores de detección de CP.
ResultadosLa TDC de la biopsia guiada fue del 48% para todos los tipos de cáncer y del 33% para el CPCS. El muestreo de próstata sistemático adicional mejoró la TDC global en un 15% y en un 12% para CPCS. Se detectó CP en el 35, 69 y 92% de los pacientes con lesiones calificadas como PI-RADS 3, 4 y 5, respectivamente. Una puntuación elevada de PI-RADS y un examen rectal digital positivo fueron factores predictores de CP, y la condición «biopsia naïve» se asoció con CPCS.
ConclusiónEn la práctica diaria, la biopsia guiada con Koelis™ logra una buena TDC para todos los CP y CPCS, y mejora significativamente con el muestreo sistemático posterior de la próstata. Los excelentes resultados de la biopsia por fusión se confirman también en pacientes naïve. La puntuación PI-RADS elevada y el examen rectal digital positivo están altamente asociados con la presencia de CP.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora