La hiperplasia benigna de próstata se considera la causa más común de los síntomas del tracto urinario inferior. El sondaje vesical es el tratamiento urgente en pacientes con retención urinaria y la cirugía el de aquellos refractarios al tratamiento médico. Existe un grupo de personas con comorbilidades importantes no tributarias a cirugía. La embolización arterial prostática (EAP) podría presentarse como una alternativa segura y eficaz para conseguir el vaciamiento vesical y la micción espontánea, evitando así el sondaje vesical permanente en pacientes con comorbilidades importantes que contraindiquen la cirugía. En este estudio retrospectivo, evaluamos la eficacia de la EAP en pacientes portadores de sonda vesical permanente no tributarios de tratamiento quirúrgico.
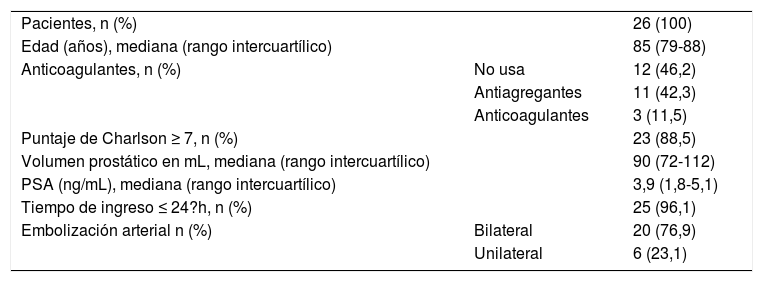
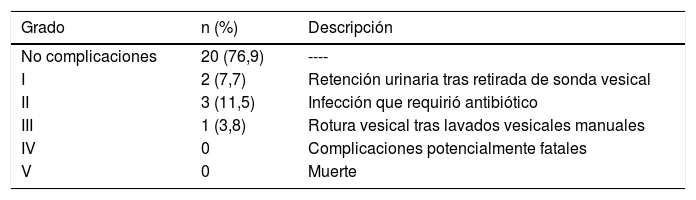
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo de 26 pacientes portadores de sonda vesical permanente a los que se les realizó una embolización prostática. Se revisaron los datos demográficos y clínicos (edad, uso de anticoagulación, volumen prostático, tiempo de ingreso, embolización unilateral o bilateral), la evaluación del índice de comorbilidad de Charlson y la clasificación de Clavien-Dindo para las complicaciones del procedimiento. Se analizó el éxito de la retirada de la sonda vesical permanente al mes del procedimiento.
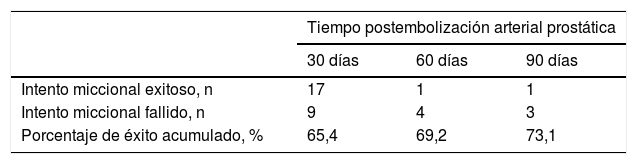
ResultadosUn total de 26 pacientes fueron incluidos en la revisión. La mediana de edad fue de 85 años, con un volumen prostático mediano de 90mL. El 88,5% de los sujetos puntuó más de 7 en la escala de comorbilidad de Charlson. Un único paciente presentó una complicación Clavien-Dindo III. De los 26 sujetos, 17 (65,4%) tuvieron una micción espontánea y un residuo posmiccional inferior a 100mL al mes del procedimiento. En total, se logró retirar la sonda vesical en 19 de los 26 sujetos (73,1%).
ConclusiónLa EAP es un procedimiento seguro y eficaz en el tratamiento de pacientes con sondaje vesical permanente no tributarios de tratamiento quirúrgico.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is considered the most frequent cause of lower urinary tract symptoms. Urinary catheterization is the emergency treatment for patients with urinary retention and surgery is indicated in patients refractory to medical treatment. There is a group of people with important comorbidities that make them ineligible for surgery. Prostatic arterial embolization (PAE) could be presented as a safe and effective alternative to achieve bladder emptying and spontaneous urination, thus avoiding permanent urinary catheterization in patients with significant comorbidities that represent a contraindication for surgery. In this retrospective study, we evaluated the efficacy of PAE in patients with permanent urinary catheterization who are ineligible for surgical treatment.
Material and methodsRetrospective study of 26 patients with permanent urinary catheter who underwent prostatic embolization. Demographic and clinical data (age, use of anticoagulation, prostate volume, length of hospital stay, unilateral or bilateral embolization), Charlson comorbidity index evaluation and Clavien-Dindo classification for procedural complications were reviewed. Successful removal of permanent urinary catheter was analyzed at one month after the procedure.
ResultsA total of 26 patients were included in the review. The median age was 85 years with a median prostate volume of 90mL. A Charlson comorbidity score above 7 was obtained in 88.5% of the subjects. Only one patient had one Clavien-Dindo III complication. Of the 26 subjects, 17 (65.4%) had spontaneous micturition and a postvoid residual lower than 100mL at one month post procedure. Overall, catheter removal was achieved in 19 out of 26 subjects (73.1%).
ConclusionPAE is a safe and effective treatment for patients with permanent urinary catheterization who are ineligible for surgical treatment.