Throughout the years, clinicians dealing with pediatric urology disorders have resorted to bladder augmentation (BA), a demanding surgical procedure, to preserve renal functions in sundry congenital urinary tract defects. This study aimed to reveal the very long-term outcomes of BA in a large sample of pediatric patients and the role of underlying disease on renal prognosis after BA.
Materials and methodsA retrospective cross-sectional study was conducted on 54 children with congenital urinary defects who underwent BA. The utilized augmentation technique, the location of ureter implantation, complications, and ultrasonography findings were analyzed. Data on serum creatinine levels were collected from preoperative records and anniversaries following BA.
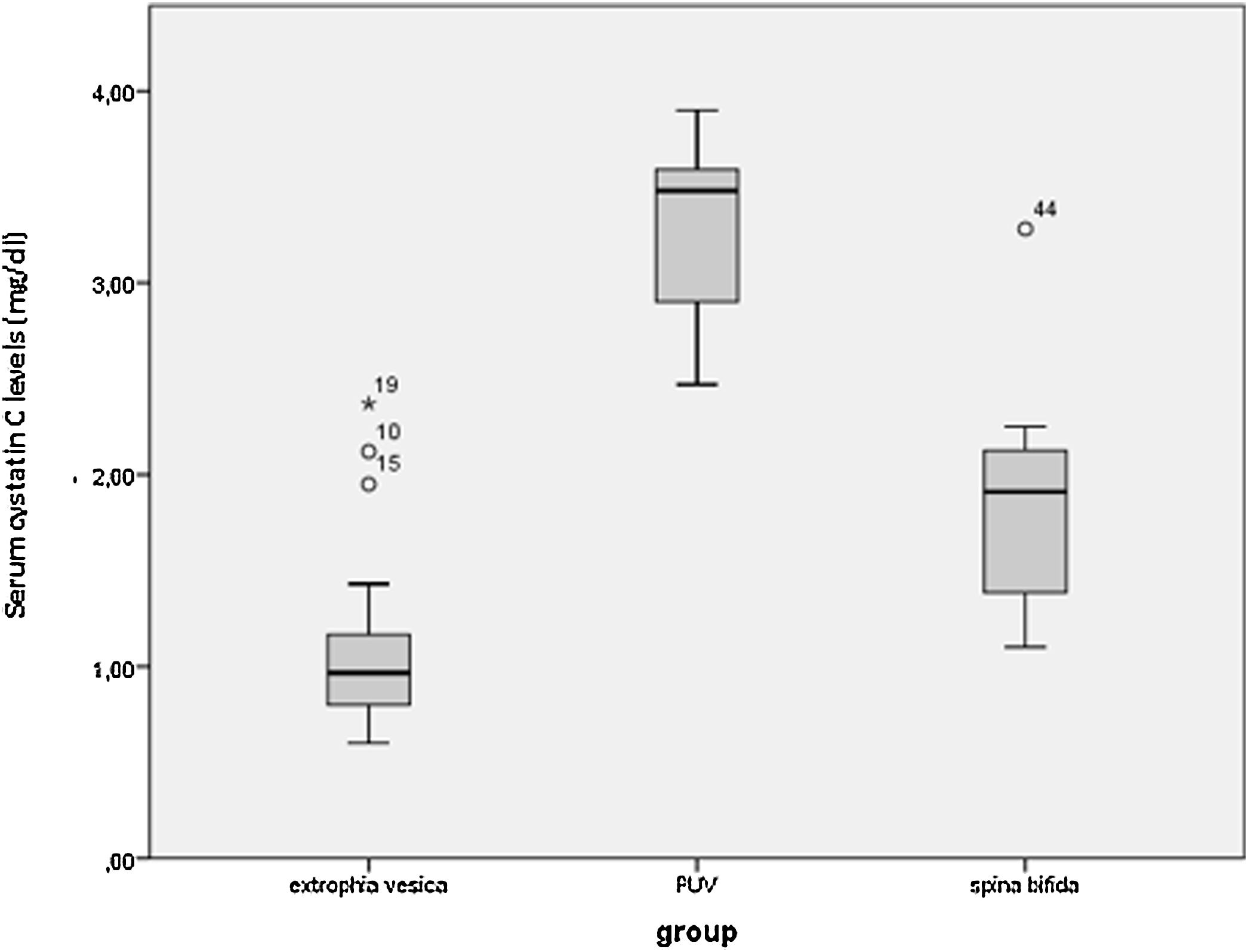
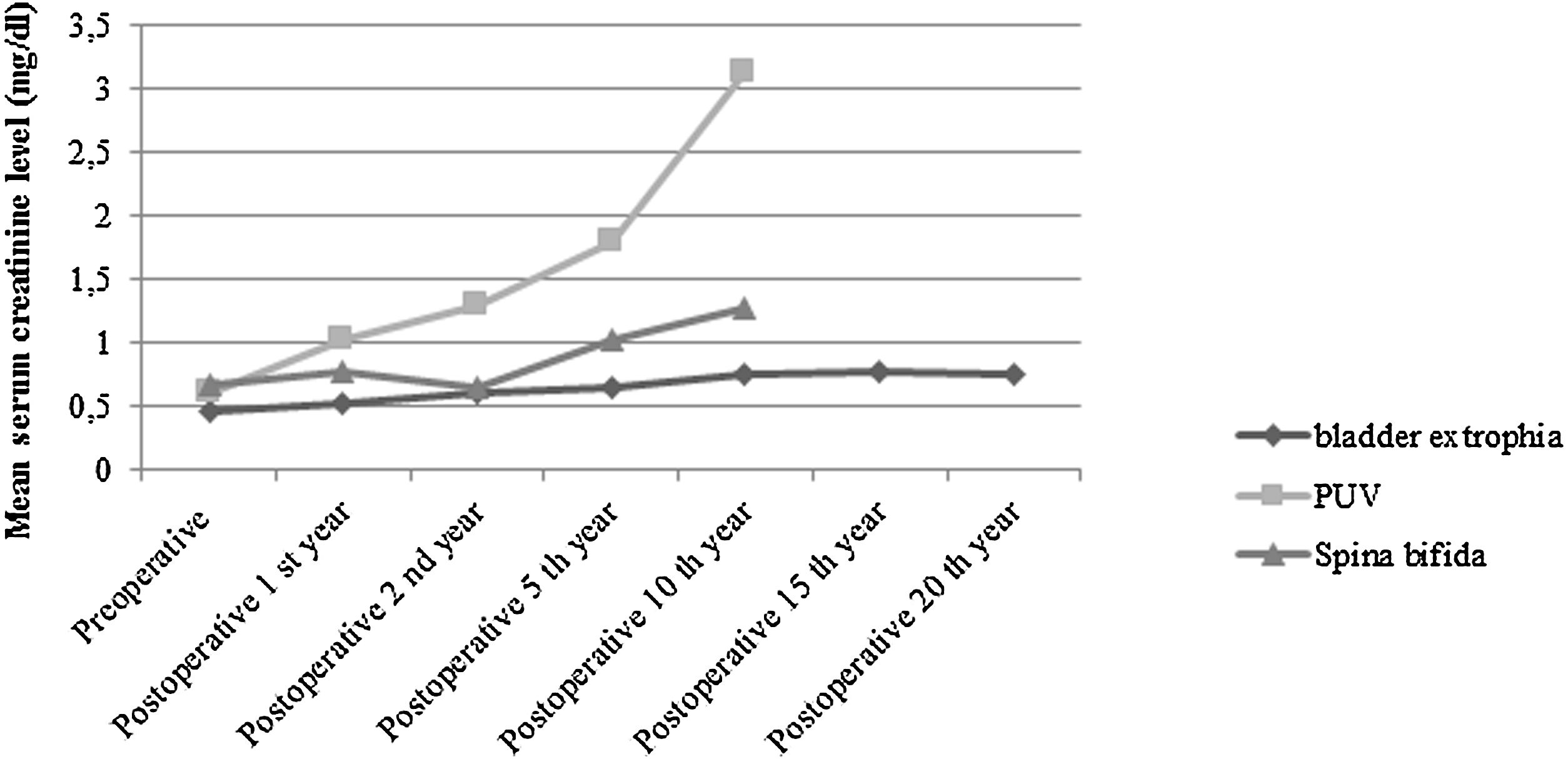
ResultsAmong 54 children, 33 (61.1%) were boys. Diagnoses were spinal dysraphism (SD) (n = 13), posterior urethral valve (PUV) (n = 8), bladder exstrophy (n = 32) and trauma (n = 1). The median follow-up duration was 18 (3–31) years. The comparisons of serum creatinine levels between groups revealed that, despite no meaningful difference was present between bladder exstrophy and PUV group in the preoperative period and postoperative 1st year, cases with PUV had significantly higher levels of serum creatinine levels in the following postoperative years. Therewithal compared with the SD group, subjects with PUV had significantly higher levels at the postoperative 2nd year (P = .035) and 10th year (P = .006).
ConclusionsIn our study, significantly long-term follow-up outcomes could facilitate the pre- and postoperative approach for enterocystoplasty in children. According to our results, it is noteworthy that kidney functions are at high risk of worsening in subjects with PUV and underwent BA.
A lo largo de los años, los médicos que se ocupan de los trastornos urológicos pediátricos han recurrido a la ampliación vesical (AV), un procedimiento quirúrgico altamente desafiante desarrollado para preservar las funciones renales en diversos casos de anomalías urinarias congénitas. Este estudio tiene como objetivo revelar los resultados de la AV a muy largo plazo en una amplia muestra de pacientes pediátricos, así como el papel de la enfermedad subyacente en el pronóstico renal tras la AV.
Materiales y métodosSe realizó un estudio transversal retrospectivo en 54 niños con anomalías urinarias congénitas que fueron sometidos a una AV. Se evaluó la técnica de ampliación utilizada, la localización de la implantación del uréter, las complicaciones y los hallazgos ecográficos. Se recogieron datos sobre los niveles de creatinina sérica en los registros preoperatorios y posteriores a la AV anuales.
ResultadosDe los 54 niños, 33 (61,1%) eran varones. Los diagnósticos fueron disrafismo espinal (DE) (n = 13), válvula uretral posterior (VUP) (n = 8), extrofia vesical (n = 32) y traumatismo (n = 1). La duración media del seguimiento fue de 18 (3–31) años. Las comparaciones de los niveles de creatinina sérica entre los grupos revelaron que, a pesar de que no existían diferencias significativas entre el grupo de extrofia vesical y el de VUP en el periodo preoperatorio ni en el primer año postoperatorio, los casos con VUP presentaban niveles de creatinina sérica significativamente más altos en los siguientes años posteriores a la cirugía. Además, en comparación con el grupo de DE, los sujetos con VUP tenían niveles significativamente más altos en el segundo (P = ,035) y décimo año (P = ,006) año del postoperatorio.
ConclusionesEn nuestro estudio, los resultados del seguimiento a largo plazo podrían facilitar el abordaje pre y postoperatorio de la enterocistoplastia en edad pediátrica. Debemos destacar que, según nuestros resultados, la función renal tiene un alto riesgo de empeoramiento en los sujetos con VUP sometidos a AV.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora