La orquialgia es un trastorno andrológico frecuente y suele darse como resultado de un cambio patognomónico en los testículos y las estructuras adyacentes. Sin embargo, su causa sigue siendo desconocida en más de una cuarta parte de los pacientes.
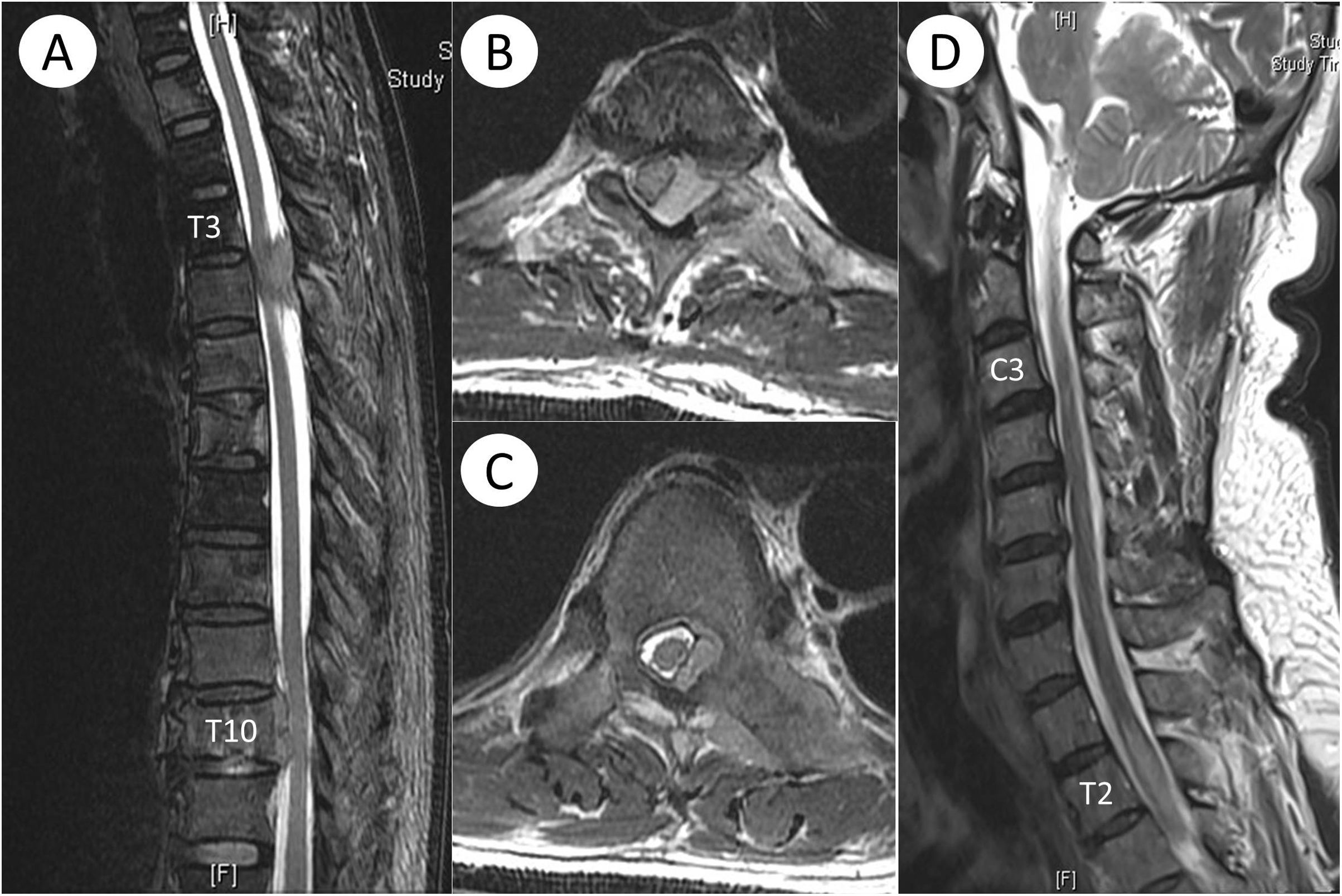
MétodosInformamos de 2varones que presentaron inicialmente una orquialgia aguda y aislada, que se complicó conduciendo posteriormente a una paraparesia. Los 2tenían antecedentes de cáncer de próstata y mielitis cervical. El examen urológico fue negativo en ambos. Finalmente, se identificó metástasis del cáncer de próstata y mielitis recurrente a nivel de T2 y T3, respectivamente. Aunque la orquialgia cedió progresivamente, las disfunciones urológicas, sexuales y neurológicas persistieron en los 2pacientes.
ConclusionesSegún la literatura existente, la enfermedad responsable de la orquialgia espinal se hallaba exclusivamente por debajo del nivel T10, lo que solía demorar el diagnóstico confirmatorio. Por lo tanto, en el caso de la orquialgia idiopática con una historia preexistente o riesgo de trastorno de la médula espinal y un estudio urológico negativo, se debe recomendar la evaluación exhaustiva de la médula espinal por encima del nivel T10.
Orchalgia is a common andrological disorder and usually results from pathognomonic change of testes and regional structures. However, responsible cause is still unknown in more than one-fourth of patients.
MethodsWe report 2men who initially suffered an acute, isolated orchalgia and posteriorly complicated with paraparesis. They had previous history of prostate cancer and cervical myelitis. The urological examination was negative in both of them. Finally, prostate cancer metastasis and recurrent myelitis at T2/3 level was identified, respectively. Although their orchalgia progressively subsided, their urological, sexual and neurological dysfunction persisted.
ConclusionsIn the literature, the responsible pathology of spinal orchalgia was exclusively found below T10 level, frequently delaying affirmative diagnosis. Therefore, a thorough evaluation of spinal cord above T10 level should be alerted for idiopathic orchalgia with a pre-existing history or risk of spinal cord disorder and a negative urological examination.