To assess therapeutic persistence and its relationship with concomitant medication in patients treated with fesoterodine versus tolterodine and solifenacin for overactive bladder (OAB) in standard clinical practice conditions.
Material and methodsAn observational, multicentre retrospective study was performed based on medical registries of patients followed-up in primary care (PC). Three study groups were analyzed. Persistence was defined as the time (in months) without withdrawing from the initial therapy or without changing to another medication for at least 30 days after the initial prescription. The concomitant medications were antidepressants, anxiolytic/hypnotic agents, antibiotics, antiseptic agents, laxatives and skin products. We employed the SPSSWIN program version 17 (statistical significance, p<.05).
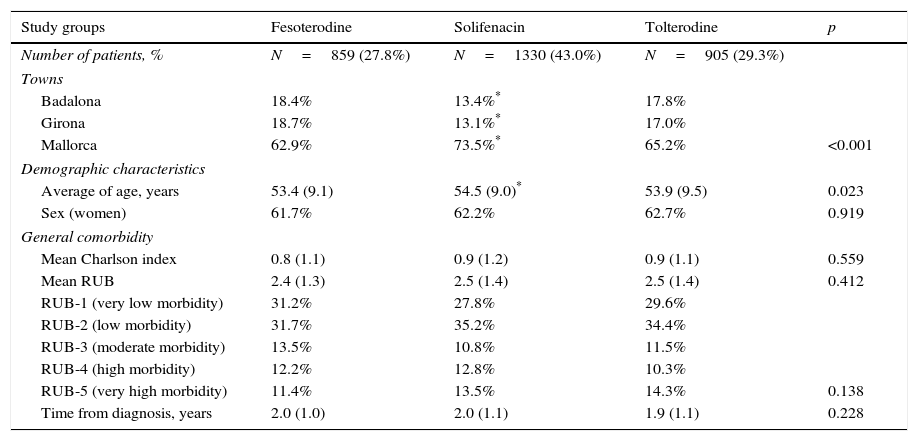
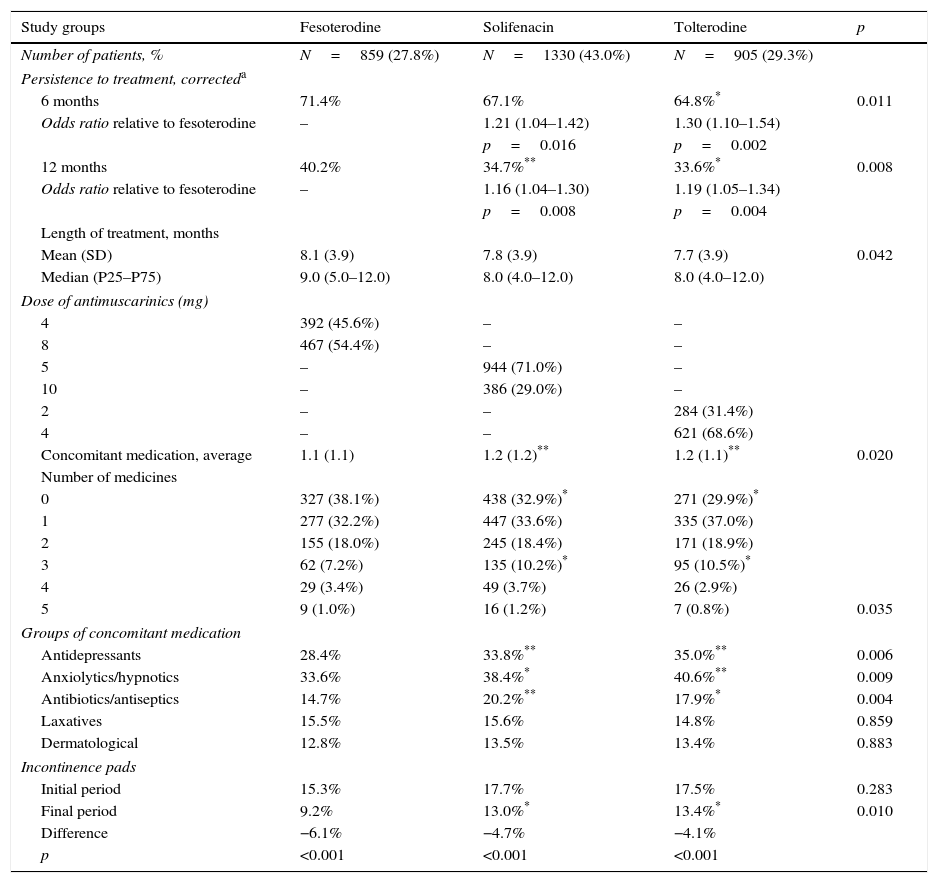
ResultsWe selected 3094 patients for the study. The median age was 54.0 years and 62.2% were women. The patients treated with fesoterodine shown greater treatment persistence (12 months) when compared with those who took solifenacin and tolterodine (40.2% vs. 34.7% and 33.6%, respectively; p=.008). They also showed a lower use of concomitant medication (1.1 vs. 1.2 and 1.2 drugs, respectively; percentages: 61.6% vs. 67.1% and 70.1%, respectively; p<.03).
ConclusionsThe patients undergoing OAB treatment with fesoterodine, when compared with those taking solifenacin and tolterodine, were associated with greater treatment persistence and a reduced use of concomitant medication.
Evaluar la persistencia terapéutica y su relación con la medicación concomitante en pacientes tratados con fesoterodina frente a tolterodina y solifenacina para el tratamiento de la vejiga hiperactiva en condiciones de práctica médica habitual.
Material y métodosSe efectuó un diseño observacional, multicéntrico, retrospectivo, realizado a partir de registros médicos de pacientes seguidos en atención primaria. Se analizaron los 3 grupos de estudio. La persistencia se definió como el tiempo (meses), sin abandono del tratamiento inicial o sin cambio a otra medicación al menos 30 días después de la prescripción inicial. La medicación concomitante fue: antidepresivos, ansiolíticos/hipnóticos, antibióticos, antisépticos, laxantes y productos-dermatológicos. Se utilizó el programa SPSSWIN versión 17 (significación estadística: p<0,05).
ResultadosSe seleccionaron para el estudio 3.094 pacientes. La media de edad fue de 54,0 años y el 62,2% fueron mujeres. Los pacientes tratados con fesoterodina mostraron mayor persistencia al tratamiento (12 meses) en comparación con solifenacina y tolterodina (40,2% frente al 34,7% y 33,6%; p=0,008), respectivamente. Además, también mostraron un menor uso de medicación concomitante (1,1 frente a 1,2 y 1,2 fármacos; porcentajes: 61,6% frente a 67,1% y 70,1%; p<0,03).
ConclusionesLos pacientes en tratamiento con fesoterodina frente a solifenacina y tolterodina para la vejiga hiperactiva se asociaron a una mayor persistencia al tratamiento, con una reducción de la medicación concomitante.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora