The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of diet induced obesity on semen parameters and serum antioxidant enzyme levels.
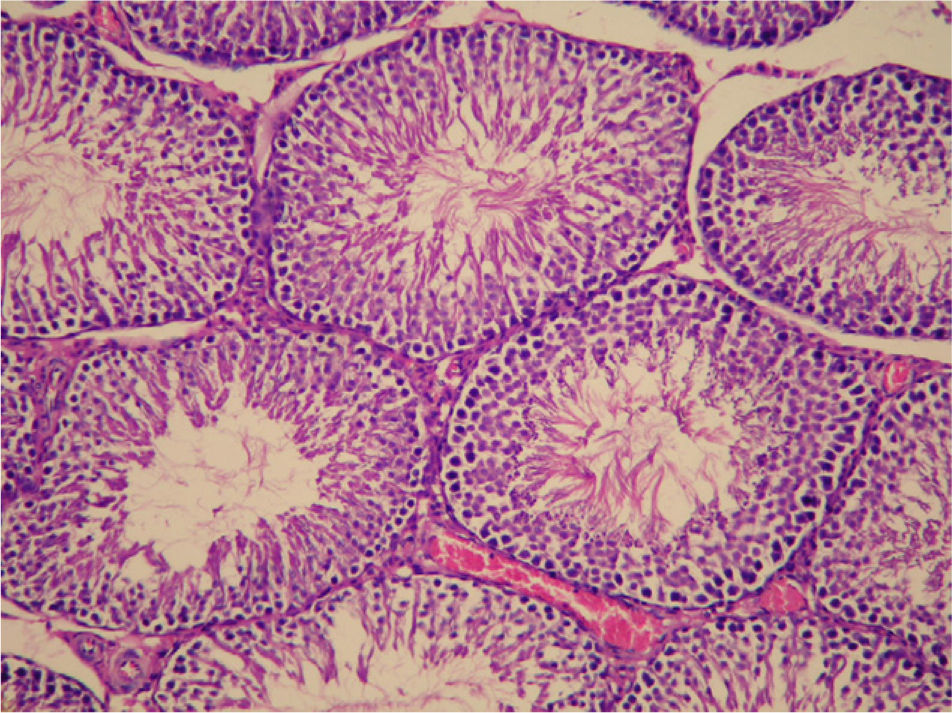
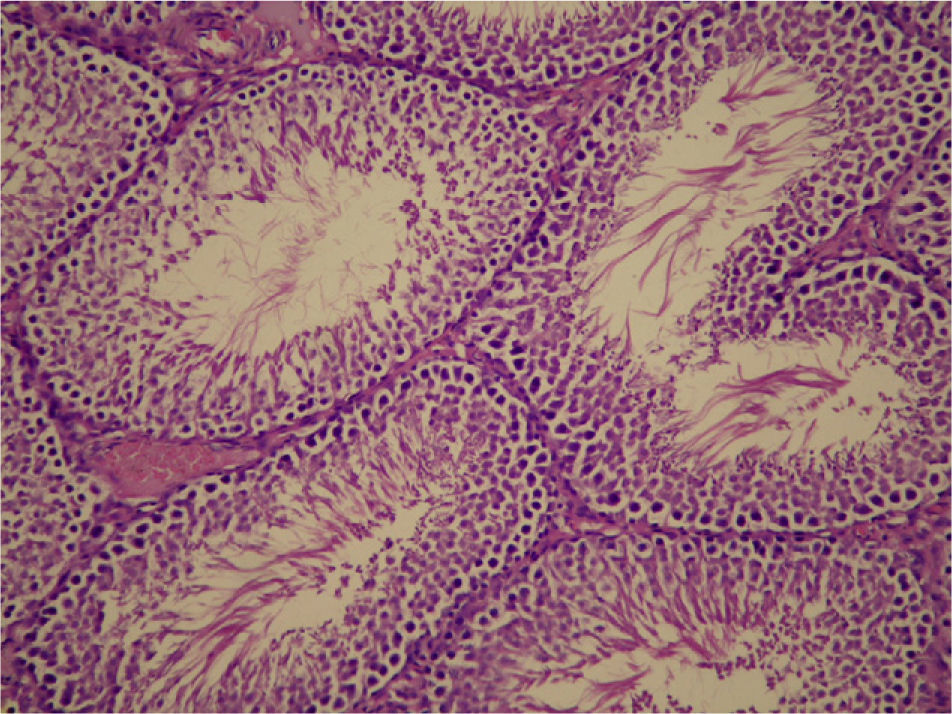
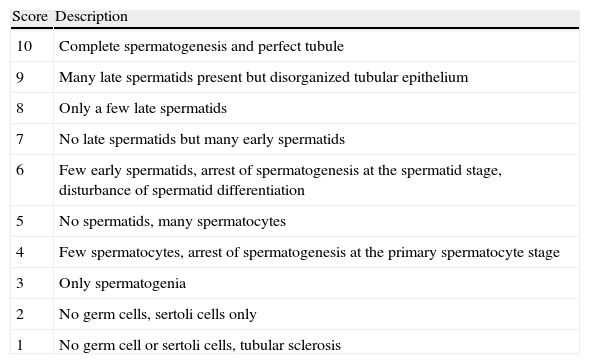
Material and methodsSix-week-old male rats were randomized into three groups as follows: group 1 (n=10) received a control diet, group 2 (n=9) received a high-fat diet and group 3 (n=11) received high-fat diet plus anastrozole. At the completion of a 10-week period, testicular tissues were obtained and spermatogenesis was evaluated with Johnsen Score System. The normal Johnsen Score was accepted as >9.39. In addition, serum antioxidant enzyme levels, triglyceride, cholesterol, testosterone, luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and estradiol levels were measured in serum.
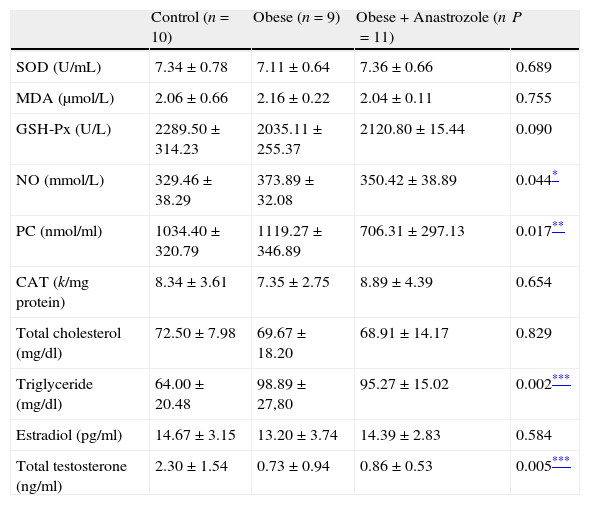
ResultsBody weights were significantly increased in mice fed with a high-fat diet compared to normal diet (P<.05). The mean triglyceride levels were 64.00±20.48mg/dl, 98.89±27.80mg/dl and 95.27±15.02mg/dl in group 1, group 2 and group 3, respectively (P<.05). Male rats fed with a high-fat diet had significantly lower levels of testosterone compared with the control diet male rats (P=.005). Testicular pathology revealed that Johnsen score were 9.60±0.15, 8.72±1.81 and 9.29 in group 1, group 2 and group 3, respectively (P=.169). In addition serum nitric oxide (NO) levels were higher in group 2 and group 3 compared to group 1 (P<.05).
ConclusionAs a result it may be concluded that obesity may induce oxidative stress and decrease testosterone levels. These changes may alter testicular functions and consequently it may be speculated that obesity can be an important causative factor in the etiology of the male infertility.
El objetivo de este estudio fue evaluar los efectos de la obesidad inducida por dieta en los parámetros de semen y los valores séricos de enzimas antioxidantes.
Material y métodosRatas macho de 6 semanas fueron distribuidas aleatoriamente en tres gru-pos: el grupo 1 (n = 10) recibió una dieta controlada; el grupo 2 (n = 9), una dieta alta en grasas, y el grupo 3 (n = 11), una dieta alta en grasas junto con anastrozol. A las 10 semanas se obtu-vieron los tejidos testiculares y se evaluó la espermatogénesis con el sistema de puntuación de Johnson. Se aceptó > 9,39 como puntuación normal. Además, se midieron los valores séricos de enzimas antioxidantes, los triglicéridos, el colesterol, la testosterona, la hormona luteini-zante (HL), la hormona estimulante del folículo (HEF) y el estradiol en el suero.
ResultadosEl peso corporal aumentó considerablemente en los ratones alimentados con una dieta alta en grasas en comparación con los que recibieron una dieta normal (p < 0,05). Los valores medios de triglicéridos fueron 64,00 ± 20,48, 98,89 ± 27,80 y 95,27 ± 15,02mg/dl en los grupos 1 2 y 3, respectivamente (p < 0,05). Las ratas macho alimentadas con una dieta alta en grasas presentaban valores de testosterona considerablemente más bajos en comparación con las que recibieron una dieta controlada (p = 0,005). La patología testicular reveló que la puntuación de Johnson fue 9,60 ± 0,15, 8,72 ± 1,81 y 9,29 en los grupos 1, 2 y 3, respectivamente (p = 0,169). Además, los valores de óxido nítrico (NO) en el suero fueron mayores en los grupos 2 y 3 que en el 1 (p < 0,05).
ConclusiónComo resultado, se puede concluir que la obesidad puede provocar estrés oxidativo y la disminución de los valores de testosterona. Estos cambios pueden alterar las funciones testiculares y, por lo tanto, se puede especular que la obesidad puede ser un factor causante importante en la etiología de la infertilidad masculina.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora