To determine the clinical utility and limitations of guided prostate biopsy power Doppler in patients with elevated serum PSA levels.
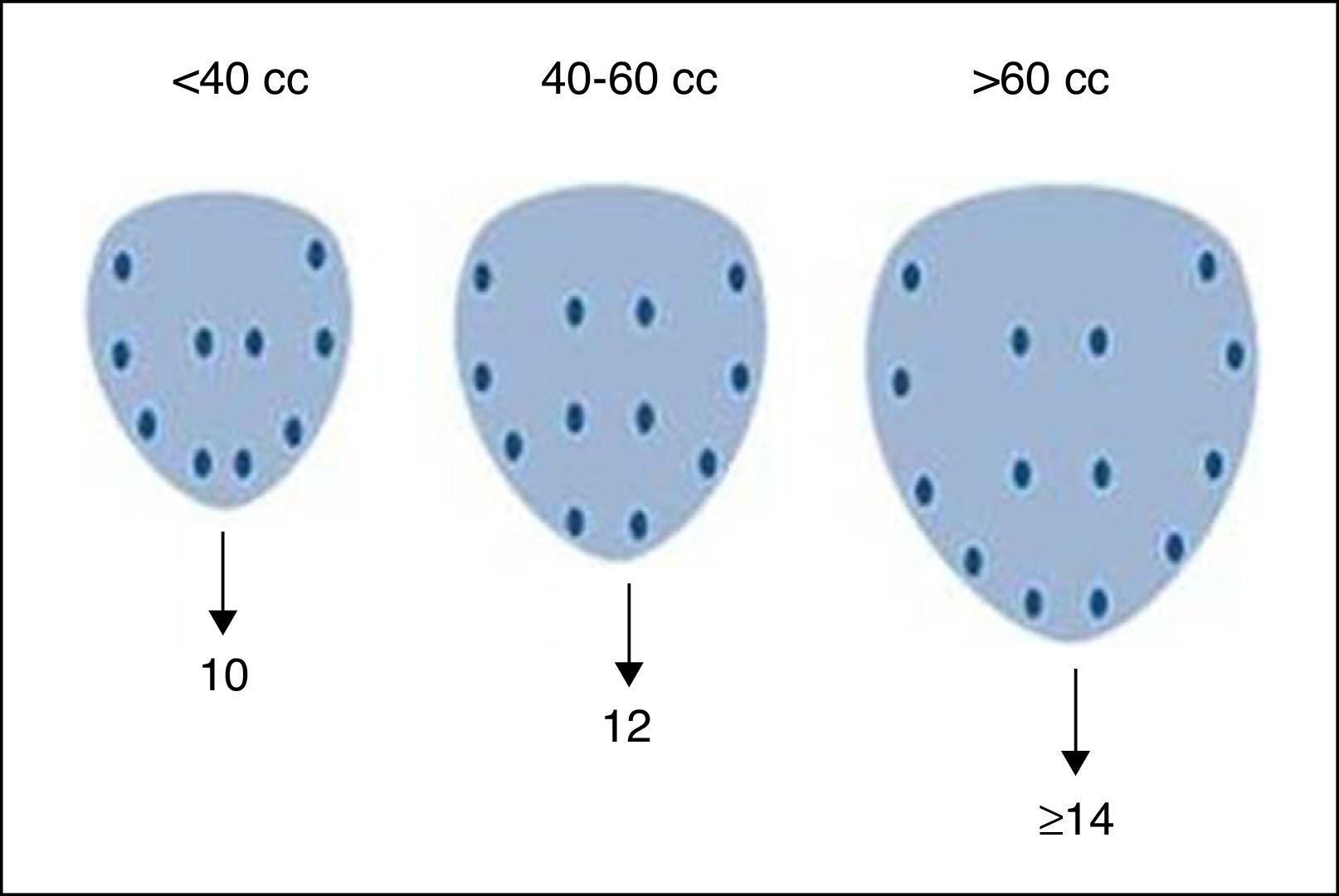
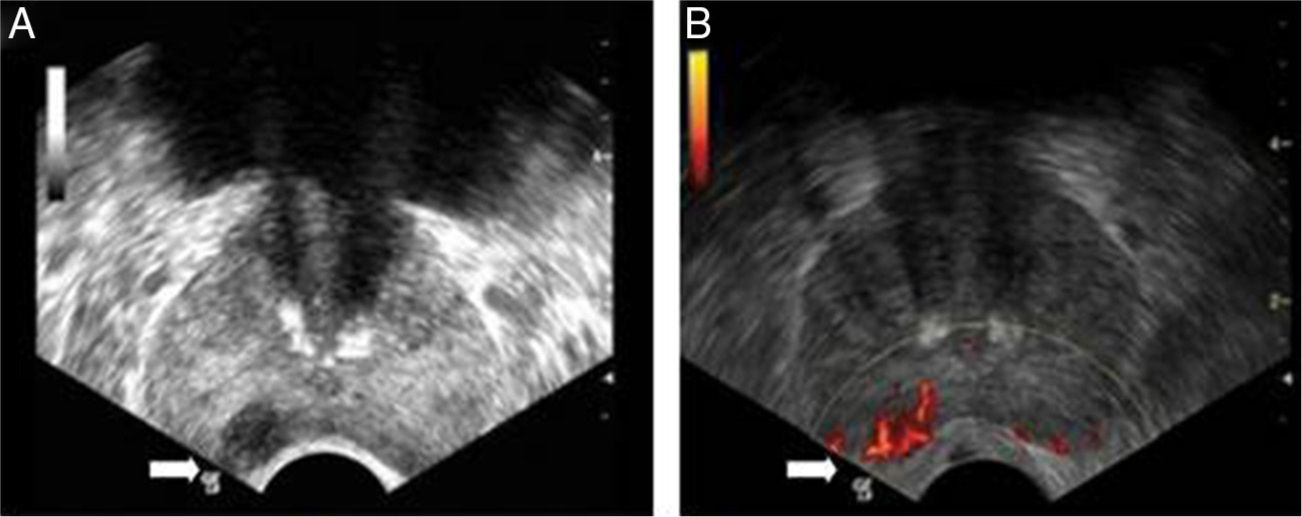
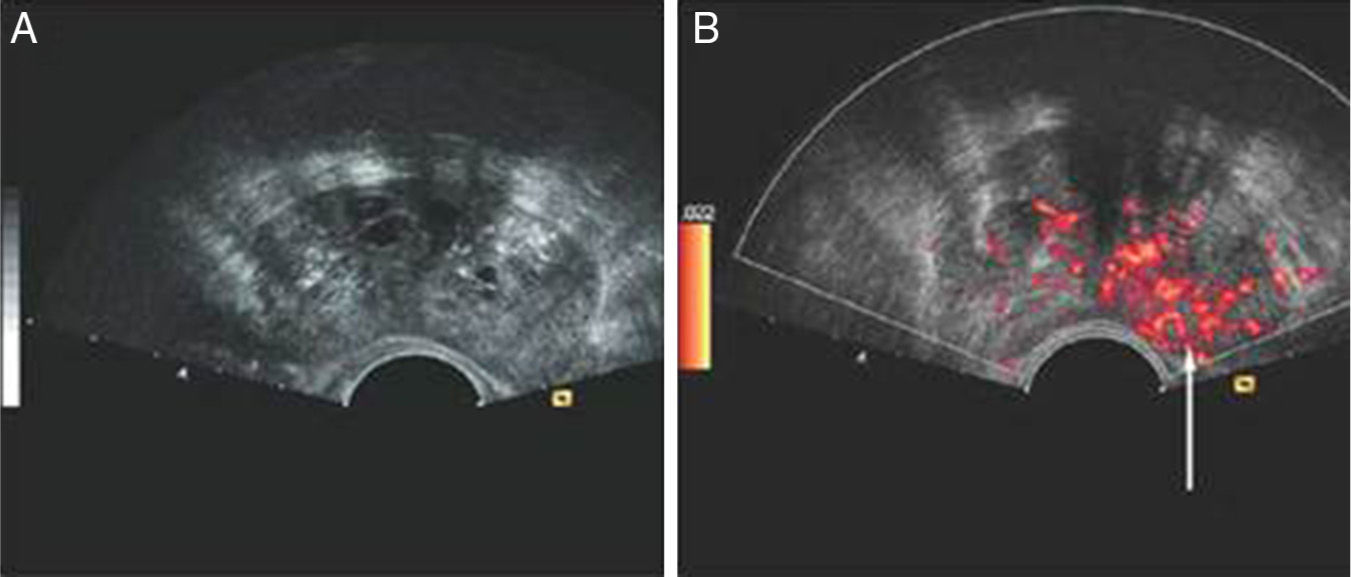
Materials and methodsProspective study. From April 2012 to May 2013, 111 men over 45 years of age with serum PSA level greater than 4.0ng/dl who underwent a transrectal prostate biopsy were included. The hypoechoic nodules in the peripheral region were considered positive on the gray scale. Subsequently, the study was conducted with the power Doppler, where the vascularization of suspicious images was analyzed for sampling. In addition, samples were taken from the suspected areas when performing the digital rectal examination. We calculated sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of the three tests (digital rectal examination, standard gray scale ultrasound and power Doppler).
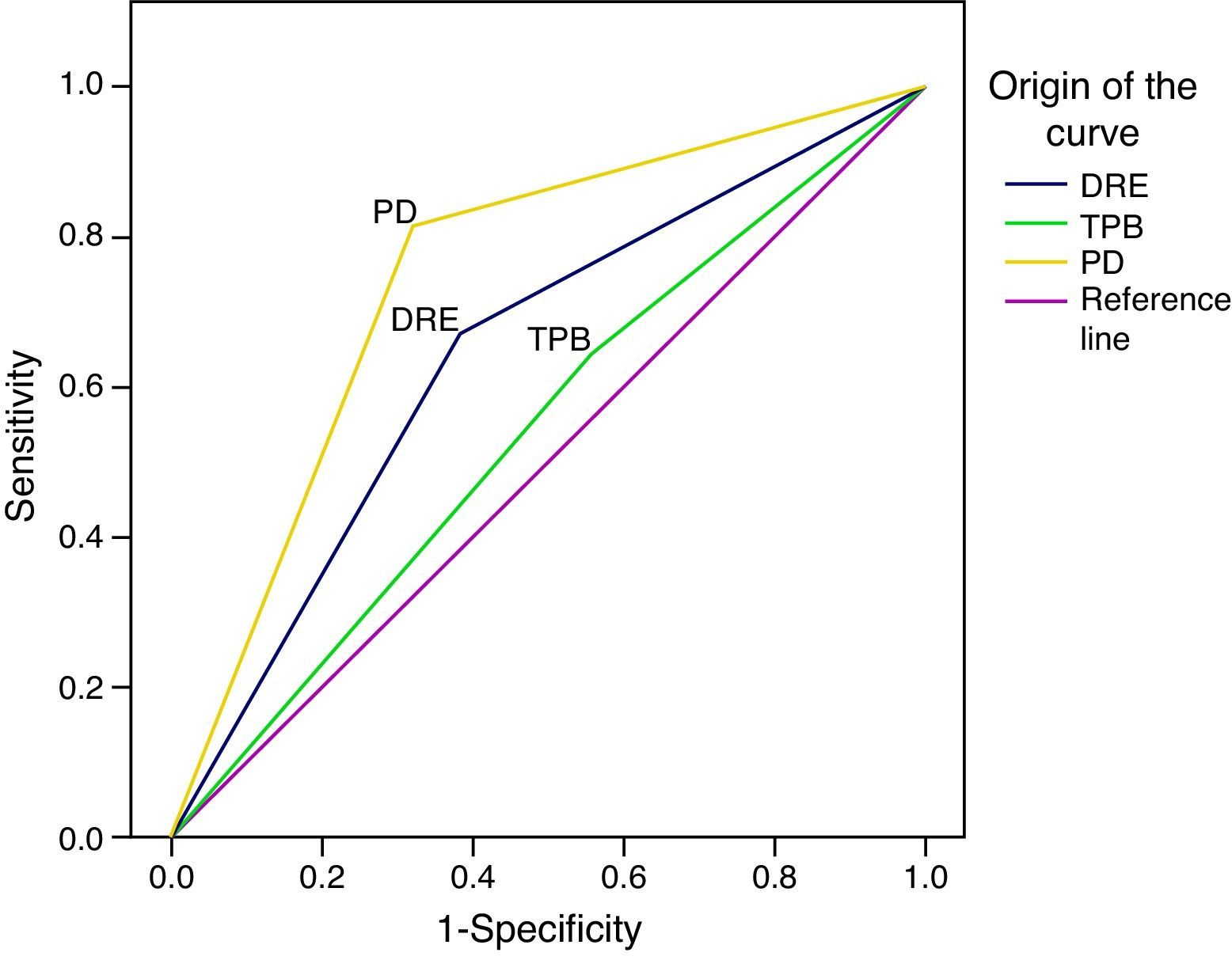
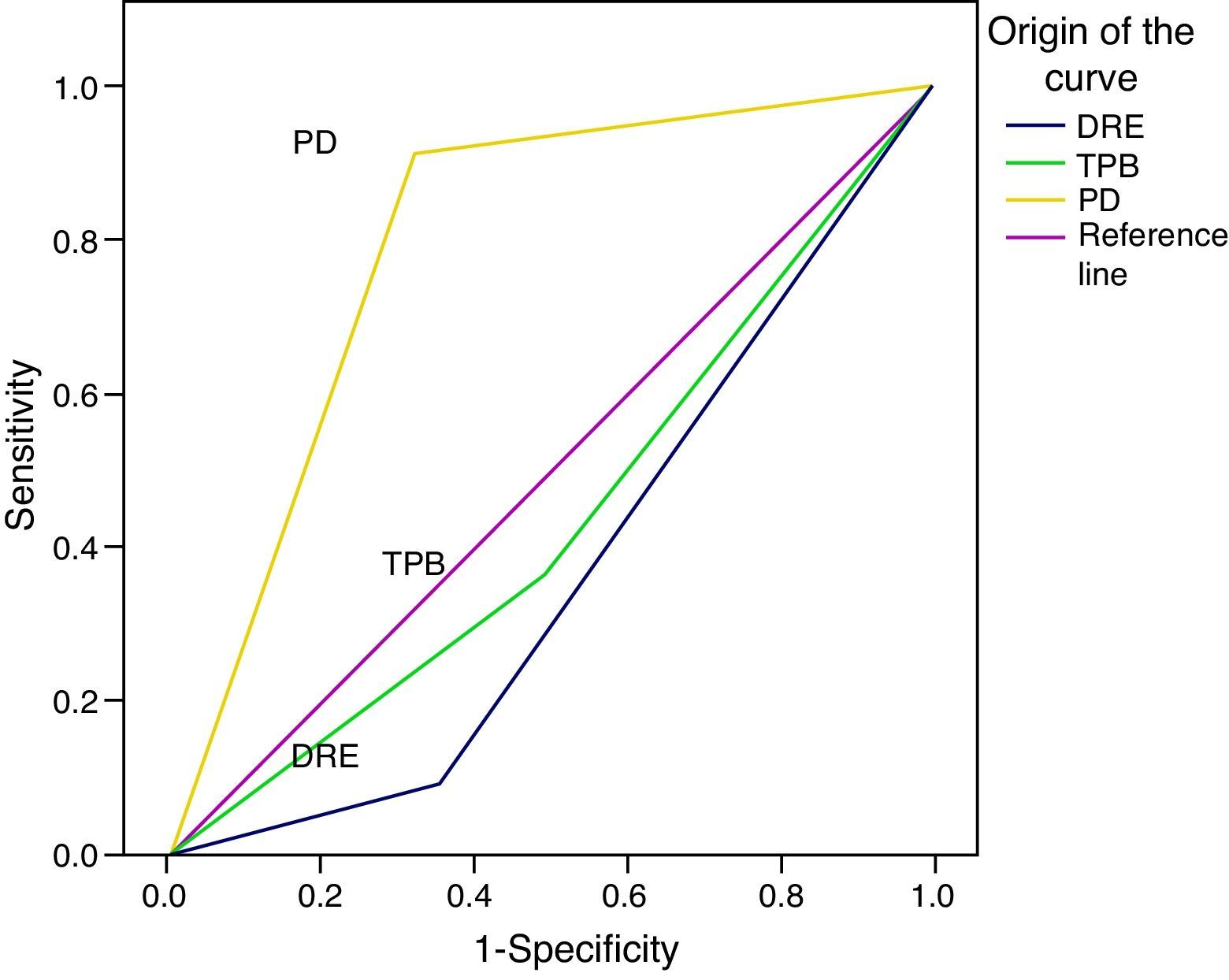
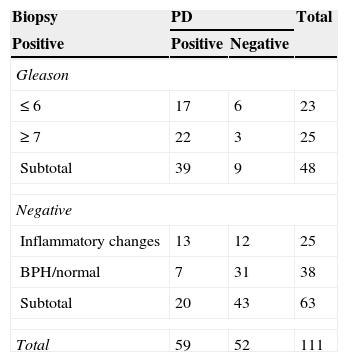
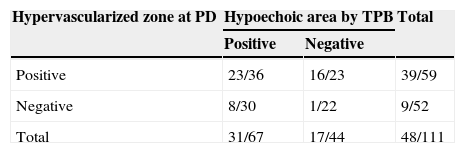
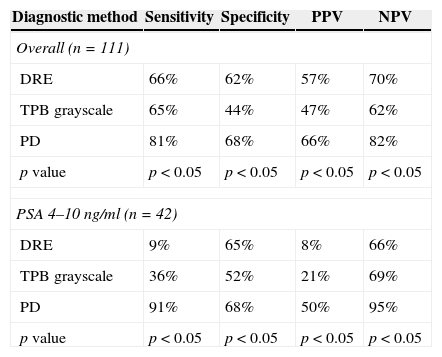
ResultsProstate cancer was diagnosed in 48 of the 111 patients (43%). Fifty-nine cases (53%) were defined as positive with the power Doppler. Of these, 39 (66%) corresponded to a diagnosis of prostate adenocarcinoma. The power Doppler was positive in 39 cases of the 48 patients diagnosed with cancer and the gray scale ultrasound was positive in 31 cases. Overall sensitivity of the power Doppler was 81%, specificity 68%, PPV 66% and NPV 82%, which was higher compared to the other methods (p<.05).
ConclusionCurrently, prostate biopsy using power Doppler does not seem to identify prostate cancer with sufficient accuracy to omit the guided systematic biopsy gray scale, the combined use of these methods.
Determinar la utilidad clínica y limitaciones de la biopsia de próstata guiada por power doppler en pacientes con elevación de los niveles séricos de PSA.
Materiales y métodoEstudio prospectivo. Desde abril del 2012 a mayo del 2013 se incluyeron un total de 111 hombres mayores de 45 años con un nivel de PSA sérico mayor a 4,0ng/dl, los cuales fueron sometidos a una biopsia prostática transrectal. Los nódulos hipoecogénicos en la zona periférica fueron considerados positivos en la escala de grises. Posteriormente se efectuó el estudio con el power doppler, donde la vascularización de las imágenes sospechosas fue analizada para tomar las muestras. Además se tomó muestra de las zonas sospechosas al examen digitorrectal. Se calculó la sensibilidad, especificidad, valor predictivo positivo y valor predictivo negativo de las 3 pruebas (examen digitorrectal, ecografía estándar con escala de grises, y power doppler).
ResultadosEl diagnóstico de cáncer de próstata fue hallado en 48 pacientes (43%) del total de 111. Cincuenta y nueve casos (53%) fueron definidos como positivo al power doppler, y de estos 39 (66%) correspondieron a un diagnóstico de adenocarcinoma de próstata. Del total de los 48 pacientes con diagnóstico de cáncer el power doppler fue positivo en 39 casos y la ecografía en escala de grises fue positiva en 31 casos. La sensibilidad global del power doppler fue del 81%, especificidad del 68%, VPP 66% y VPN 82%, lo cual resultó superior en comparación con los otros métodos (p<0,05).
ConclusiónEn la actualidad la biopsia prostática utilizando power doppler no parece identificar el cáncer de próstata con una precisión suficiente para omitir la biopsia sistemática guiada por escala de grises, siendo preferible el uso combinado de estos métodos being preferable.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora