Neurogenic detrusor hyperactivity (NDH) is a urodynamic observation characterized by involuntary detrusor contractions during the filling phase that are caused by an underlying neurological disease. The common and severe complications that can result from NDH warrant the preparation of healthcare protocols for the proper management of patients with NDH.
ObjectiveThe aim of this study is to standardize the criteria for the decision-making process in the management of patients with diagnosed or suspected NDH, providing personalized medical care.
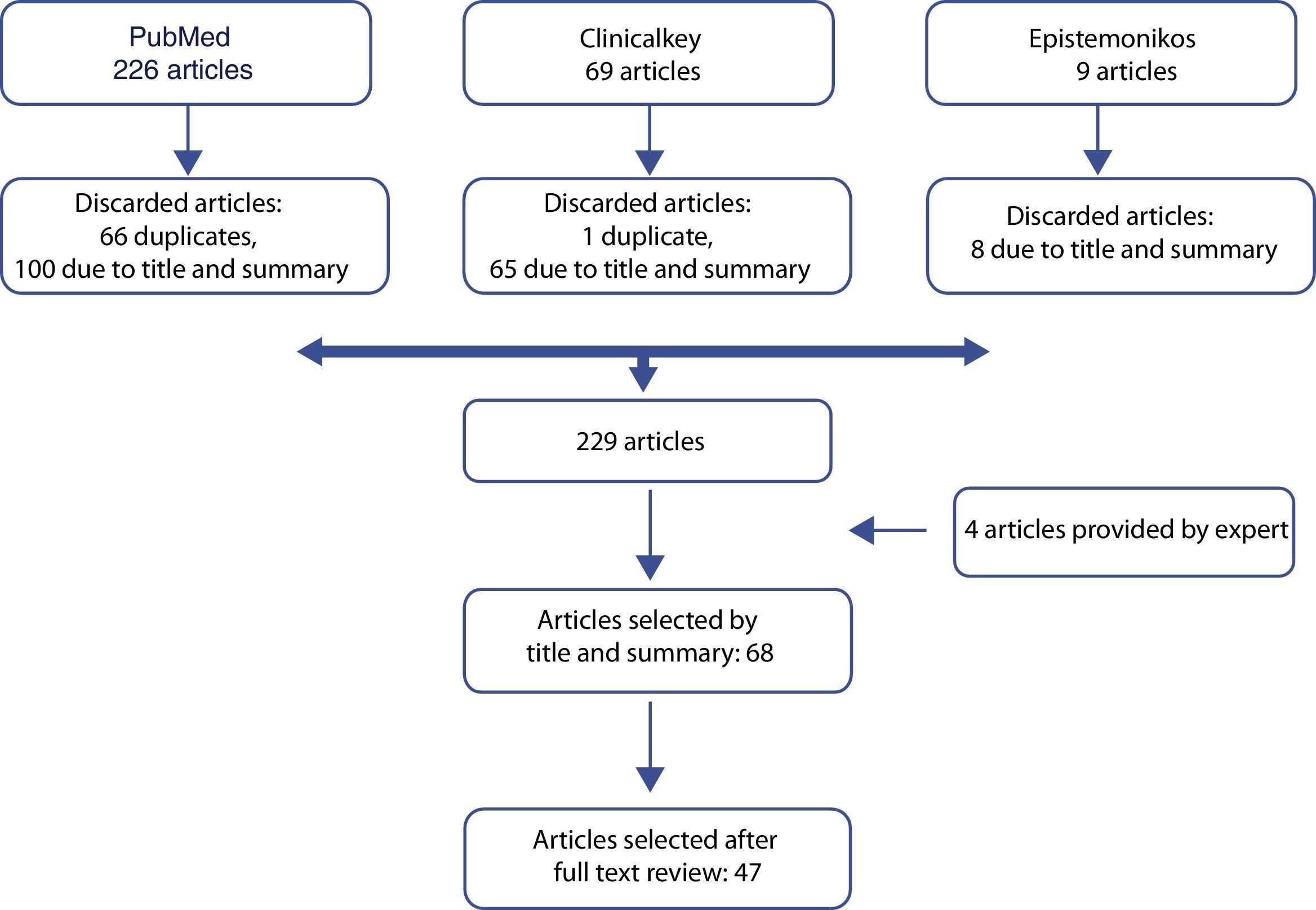
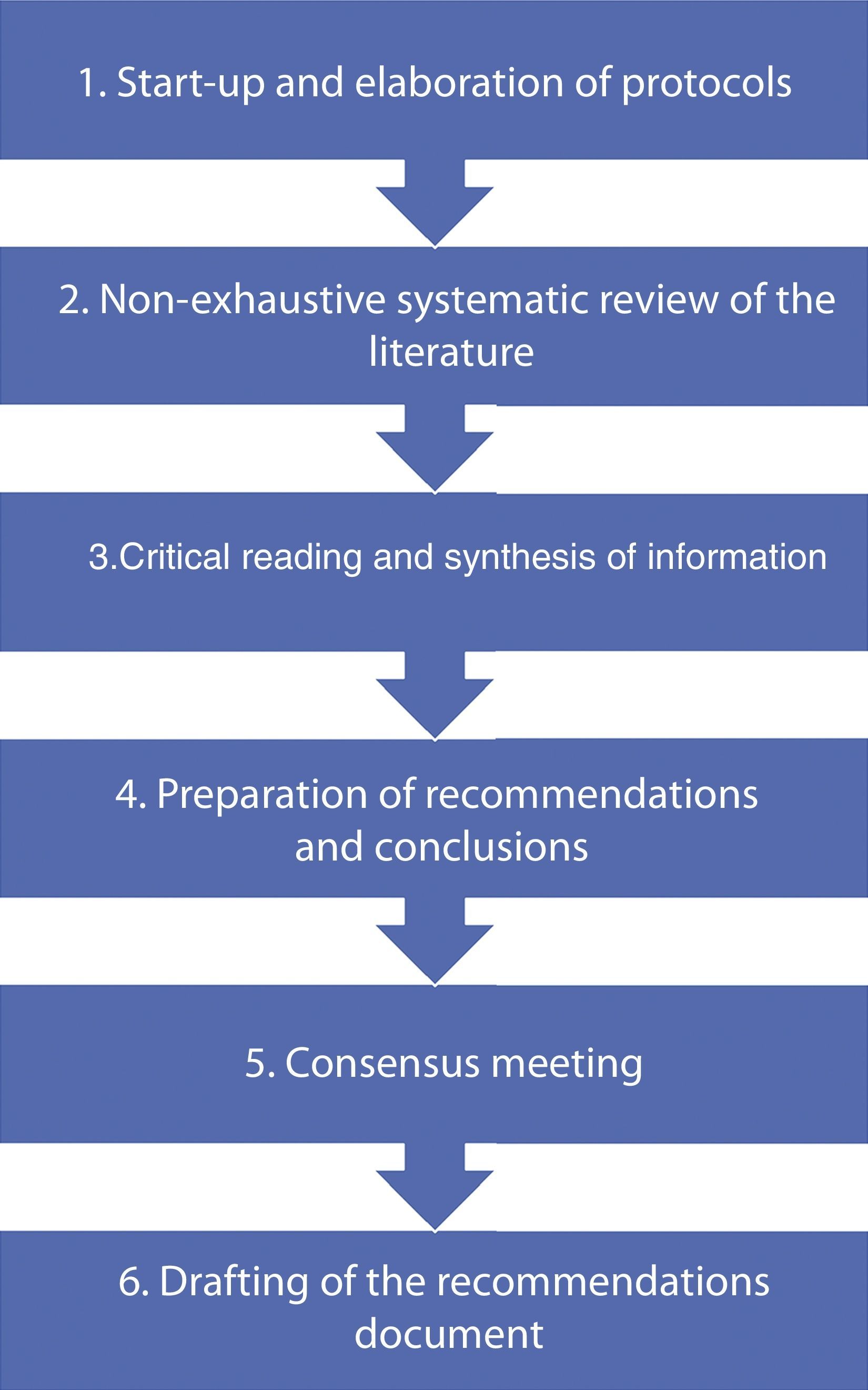
Acquisition of evidenceWe performed a systematic noncomprehensive literature review on the aspects of the diagnosis and treatment of NDH. Based on the review, recommendations were issued by nominal consensus of a group of urology specialists.
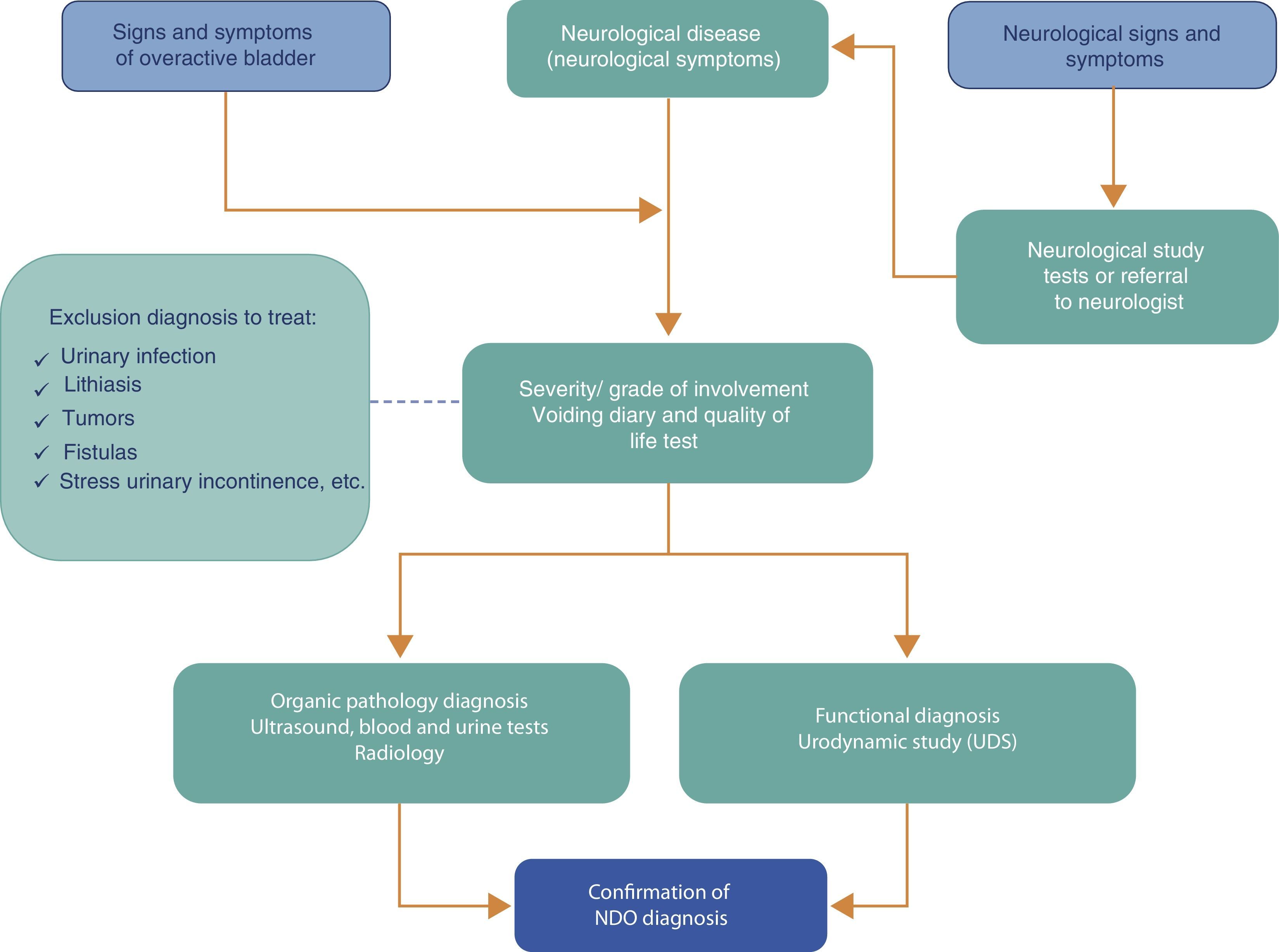
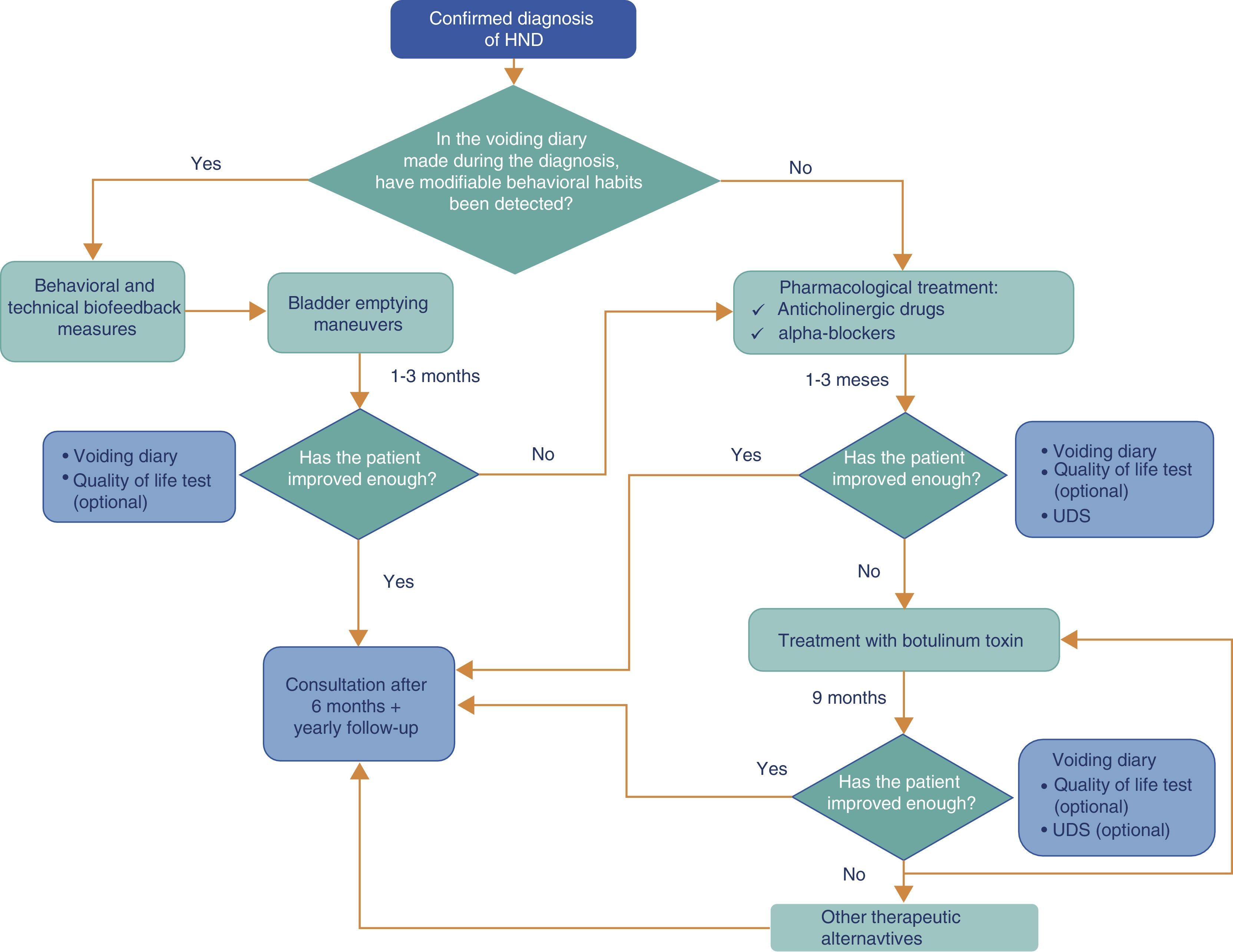
Synthesis of the evidenceIn general, the diagnosis of NDH is arrived at by a proper review of the medical history, physical examination and voiding diary before performing any diagnostic study. The main treatment objectives are to protect the upper urinary tract, restore function of the lower tract and improve these patients’ continence and quality of life. The treatment consists of several steps aimed at obtaining proper bladder storage that allows for sufficiently spaced voidings. The follow-up should be personalized based on each patient's needs.
ConclusionsThe identification and management of NDH is important for positively redirecting the function of the lower urinary tract, in terms of filling and voiding, thereby improving the patients’ quality of life.
La hiperactividad neurogénica del detrusor (HND) es una observación urodinámica caracterizada por contracciones involuntarias del detrusor durante la fase de llenado causada por una enfermedad neurológica subyacente. Las complicaciones frecuentes y graves que pueden derivar de la HND aconsejan la elaboración de protocolos asistenciales para el correcto manejo de enfermos con HND.
ObjetivoEl propósito de este trabajo es homogeneizar criterios para la toma de decisiones en el manejo de pacientes con diagnóstico o sospecha de HND, prestando atención a la medicina personalizada.
Adquisición de la evidenciaSe realizó una revisión sistemática no exhaustiva de la literatura sobre aspectos del diagnóstico y tratamiento de la HND; a partir de ella, se emitieron recomendaciones por consenso nominal de un grupo de especialistas en Urología.
Síntesis de la evidenciaEn general, el diagnóstico de HND vendrá dado por una correcta historia clínica, la exploración física y el diario miccional antes de realizar cualquier investigación diagnóstica. Los objetivos principales del tratamiento son proteger el tracto urinario superior, restaurar la función del tracto inferior y mejorar la continencia y la calidad de vida de estos pacientes. El tratamiento consiste en varios escalones encaminados a obtener un correcto almacenamiento vesical que permita micciones suficientemente espaciadas en el tiempo. El seguimiento debe personalizarse según las necesidades de cada paciente.
ConclusionesLa identificación y el manejo de la HND resultan importantes para reconducir positivamente la función del tracto urinario inferior, en cuanto a llenado y vaciado, y mejorar la calidad de vida de los pacientes con HND.