To assess the short-term compliance with fesoterodine treatment and to identify the reasons for lack of adherence and discontinuation in routine clinical practice. The secondary aim was to estimate the patient-reported outcomes.
MethodsThis was an observational retrospective, multicenter study conducted in a sample of women with overactive bladder on fesoterodine treatment for at least three months. Adherence to medication was assessed using the Morisky–Green test. Patient-reported outcomes were assessed using the Incontinence Questionnaire Short Form (ICIQ-SF), Overactive Bladder Questionnaire Short Form (OAB-qSF), and Treatment Benefit Scale (TBS).
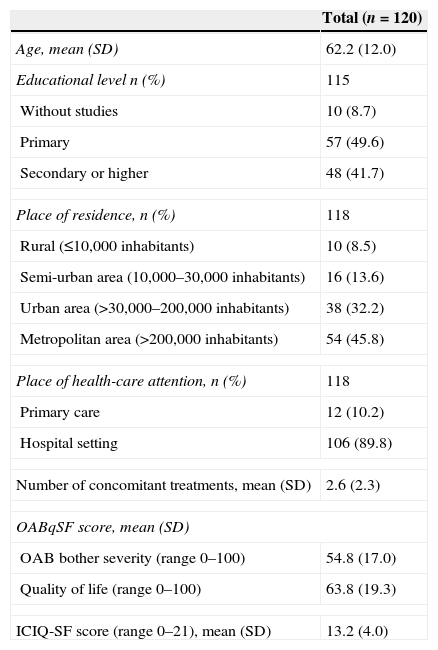
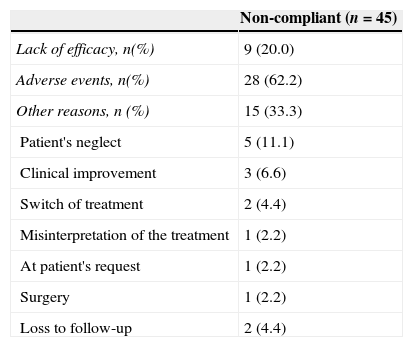
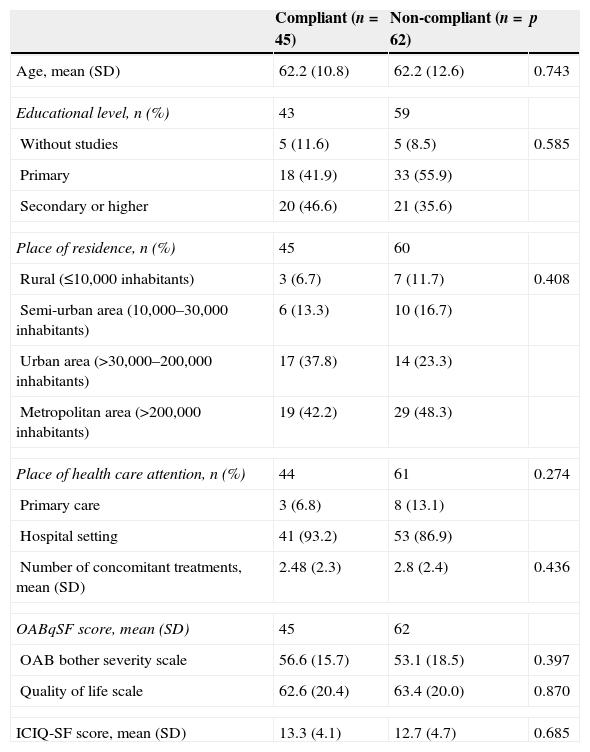
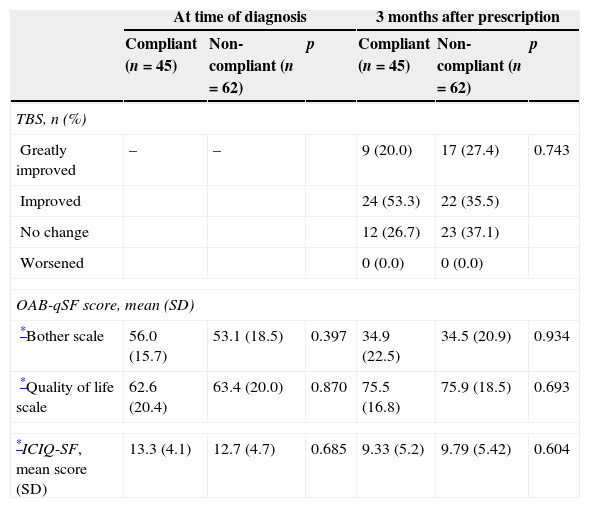
ResultsOne hundred and twenty women with a mean age [standard deviation (SD)] of 62.2 (12.0) years with severe OAB [mean (SD) ICIQ-SF score 13.2 (4.0)] were included. 42.1% of the patients were considered compliant with fesoterodine treatment. The main causes for non-compliance/discontinuation stated by the remaining 57.9% of the patients were adverse events (62.2%) and lack of clinical benefits (20.0%). The illness status as well as the patient-perceived bother occasioned by the OAB symptoms and their impact on the quality of life improved significantly after three months on fesoterodine treatment (p<0.0001). Most of the patients stated that the current state of their urinary problems had greatly improved/improved.
ConclusionIn routine clinical practice, a high percentage of patients were adherent to fesoterodine and perceived the benefit that the treatment provided them three months after starting treatment. However, more than half of the study population failed to comply or discontinued the treatment mainly due to intolerance or lack of efficacy.
Valorar a corto plazo la adherencia al tratamiento con fesoterodina e identificar las causas de la falta de adherencia o abandono en la práctica clínica diaria. El objetivo secundario fue estimar los resultados desde el punto de vista del paciente.
MétodosEste fue un estudio observacional, retrospectivo, y multicéntrico, llevado a cabo en una muestra poblacional de mujeres con vejiga hiperactiva (VH), en tratamiento con fesoterodina durante al menos 3 meses. La adherencia a la medicación se valoró mediante el test Morisky-Green. Los resultados desde el punto de vista del paciente fueron valorados empleando los cuestionarios cortos de incontinencia (ICIQ-SF) y vejiga hiperactiva (OAB-qSF) y la escala del beneficio del tratamiento (TBS).
ResultadosSe incluyeron 120 mujeres con una edad media (desviación estándar [DE]) de 62,2 (12,0) años con VH grave según la puntuación media (DE) del ICIQ-SF (13,2 [4,0]). El 42,1% de las pacientes fueron consideradas cumplidoras con el tratamiento de fesoterodina. Las principales causas de incumplimiento/abandono indicadas por el 57,9% restantes fueron los efectos adversos (62,2%) y la falta de beneficio clínico (20,0%). Tanto el grado de enfermedad como las molestias debidas a los síntomas de la VH percibidas por los pacientes y el impacto en su calidad de vida mejoraron significativamente después de 3 meses del tratamiento con fesoterodina (p<0,0001). La mayoría de los pacientes indicaron que sus problemas urinarios habían sufrido una gran mejora o habían mejorado.
ConclusiónEn la práctica clínica diaria un elevado porcentaje de pacientes fueron considerados cumplidores con el tratamiento de fesoterodina y percibieron los beneficios que dicho tratamiento proporcionaba después de 3 meses de iniciarlo. Sin embargo, más de la mitad de la población de estudio no cumplió o abandonó el tratamiento debido principalmente a intolerancia o falta de eficacia.