The effect of primary androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) in patients with localized prostate cancer (PCa) has not been well documented. The objective of the present study was to analyze the outcome of tumors treated with ADT as primary therapy in the Spanish Prostate Cancer Registry (19.4% of the series).
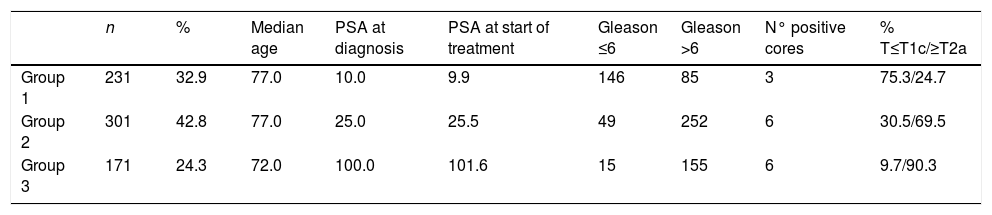
Patients and methodsPatients were classified in three groups: (1) with low/intermediate risk clinically localized tumors; (2) with high risk and locally advanced (T3-4) tumors; (3) with metastatic tumors. Time to castration resistance and overall cancer-specific survival were analyzed. In non-metastatic tumors, survivals in patients treated with ADT were compared with data from patients who underwent local treatments from the Spanish Prostate Cancer Registry.
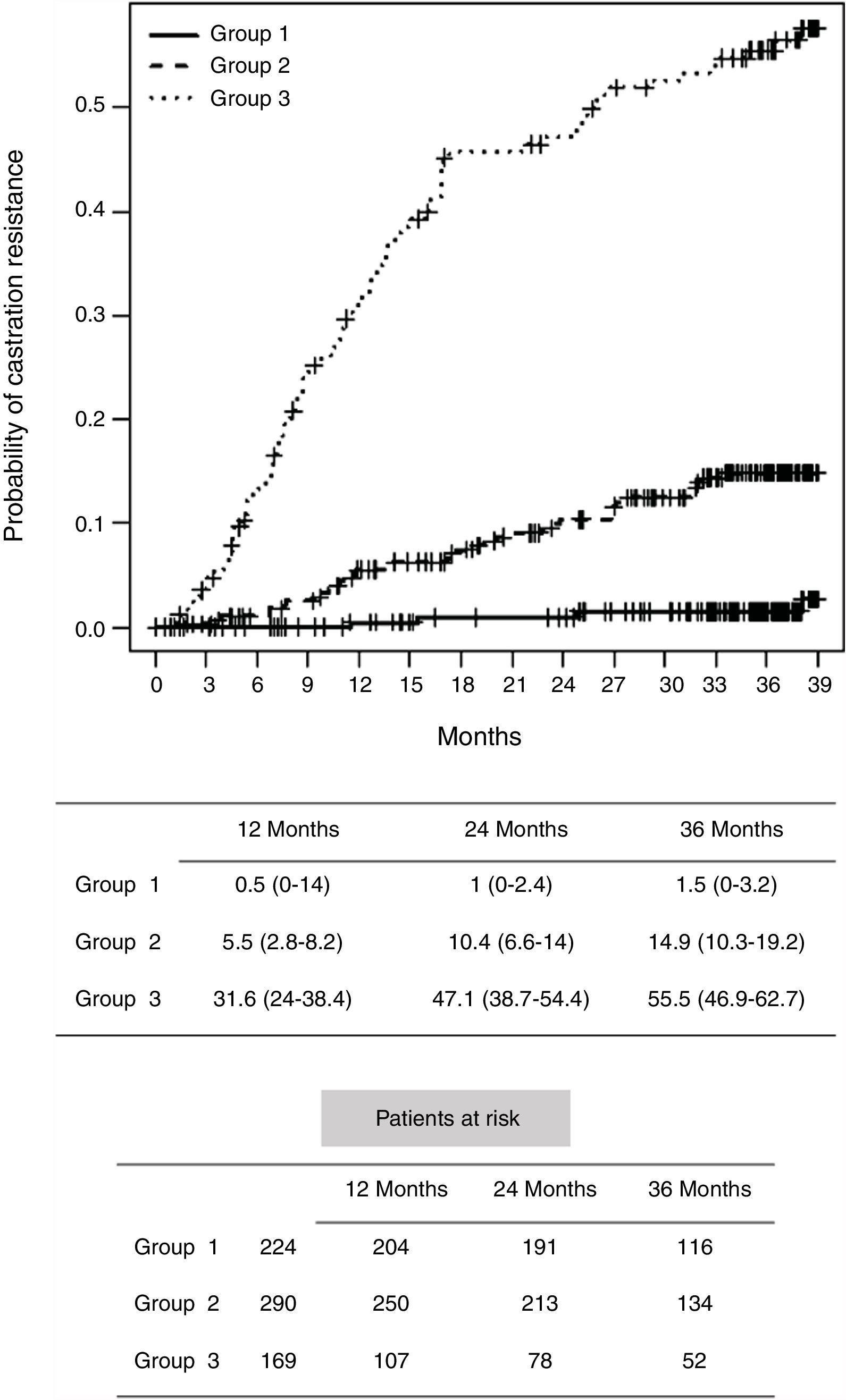
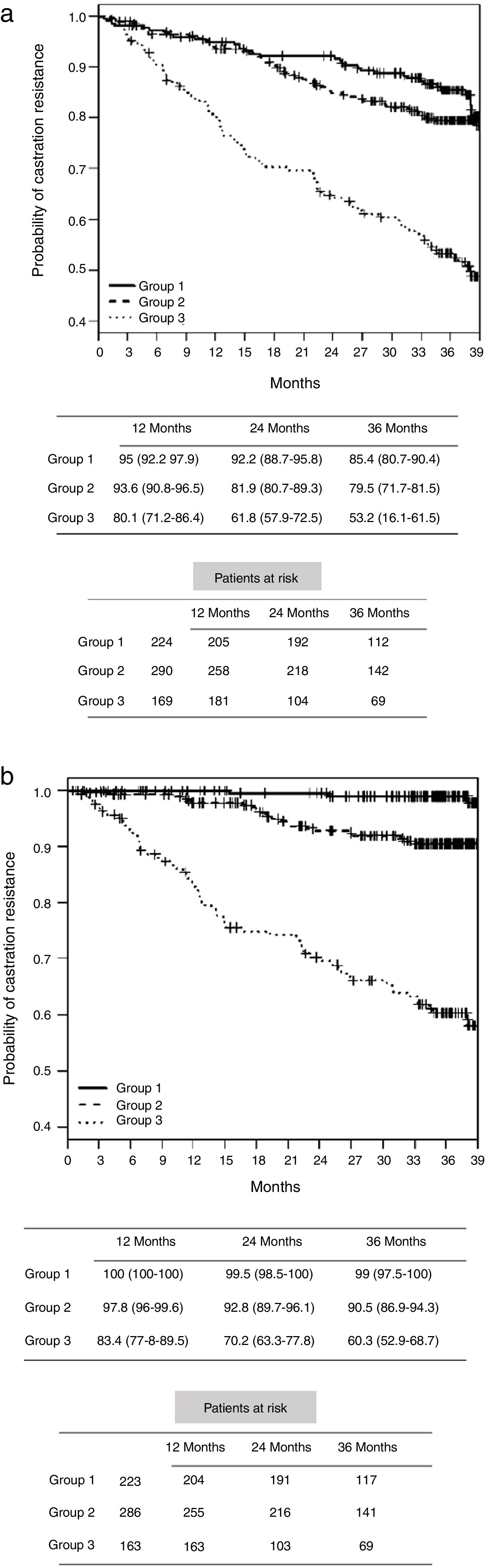
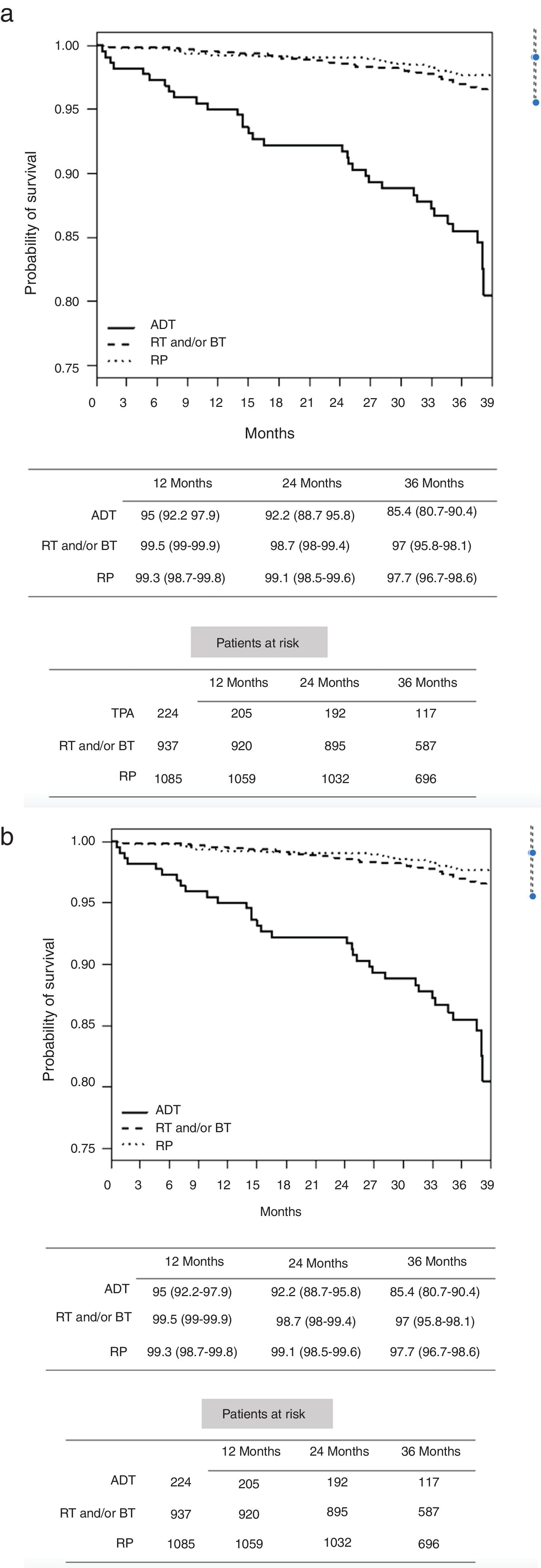
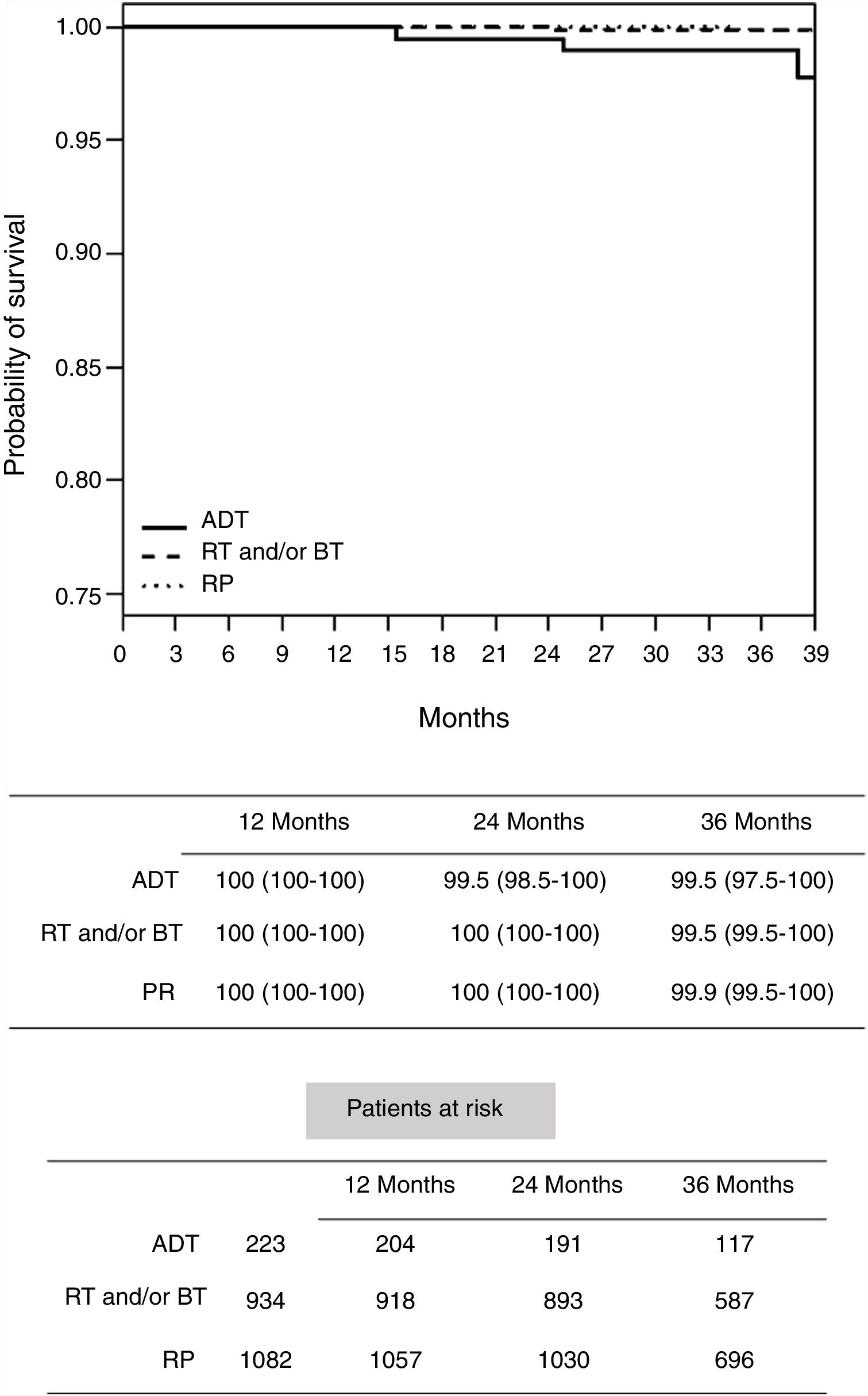
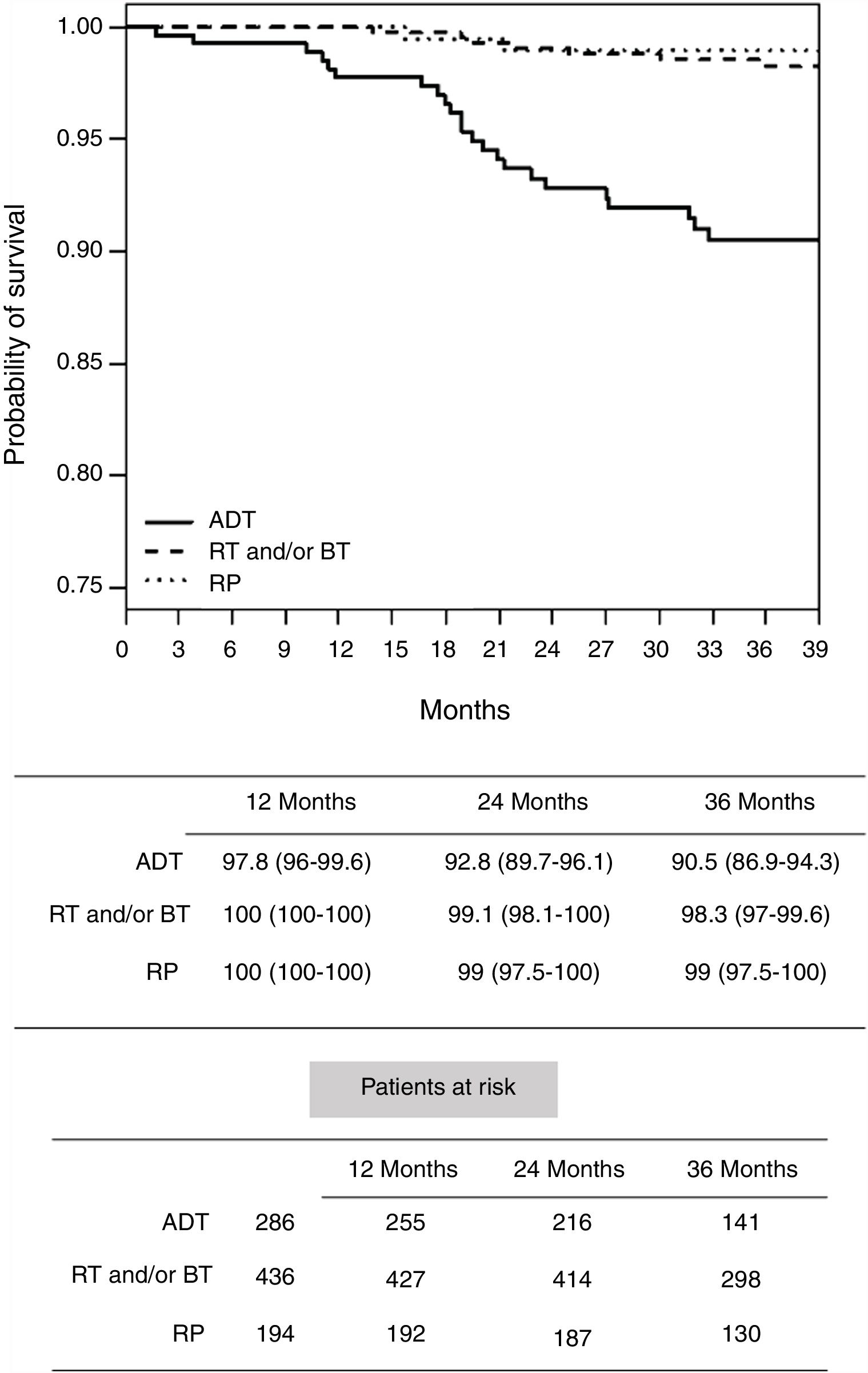
Results703 cases were analyzed. There were significant differences in the time to castration resistance, which was lower in the group of metastatic tumors. During follow-up, there were 179 deaths (25.5%) of which 89 (12.6%) were due to PCa. After 3 years of ADT, only 14.6% of patients in group 1 had died (1% due to PCa), 20.5% in group 2 and 46.8% in group 3 (9.2% and 31.3% due to PCa, respectively). Cancer-specific survival was significantly worse in group 1 using ADT than radical prostatectomy or radiotherapy. In high-risk and locally advanced tumors, ADT also had a lower cancer-specific survival than local treatments.
ConclusionA longer time until the castration resistance was observed in patients with well- and intermediate-risk localized tumors treated with ADT. Patients with metastatic tumors showed the shortest time to castration resistance.
Antecedentes El efecto del tratamiento primario de privación androgénica (TPA) en pacientes con cáncer de próstata (CP) localizado no está bien documentado. El objetivo del presente estudio fue analizar el resultado de los tumores tratados con TPA como terapia primaria en el Registro Español de Cáncer de Próstata (19,4% de la serie).
Pacientes y métodosLos pacientes se clasificaron en tres grupos: 1) con tumores clínicamente localizados de riesgo bajo/intermedio; 2) con tumores de alto riesgo y localmente avanzados (T3-4); 3) con tumores metastásicos. Se analizó el tiempo hasta la resistencia a la castración y la supervivencia general específica del cáncer. En tumores no metastásicos, las supervivencias en pacientes tratados con TPA se compararon con los datos de pacientes que recibieron tratamientos locales del Registro Español de Cáncer de Próstata.
ResultadosSe analizaron 703 casos. Hubo diferencias significativas en el tiempo de resistencia a la castración, que fue menor en el grupo de tumores metastásicos. Durante el seguimiento hubo 179 muertes (25,5%), de las cuales 89 (12,6%) se debieron a CP. Después de 3 años de TPA, solo el 14,6% de los pacientes en el grupo 1 fallecieron (1% debido a CP), el 20,5% en el grupo 2 y el 46,8% en el grupo 3 (9,2% y 31,3% debido a CP, respectivamente). La supervivencia específica del cáncer fue significativamente peor en el grupo 1 tratado con TPA que en el que recibió prostatectomía radical o radioterapia. En los tumores de alto riesgo y localmente avanzados, la TPA también tuvo una menor supervivencia específica al cáncer que los tratamientos locales.
ConclusiónSe observó un tiempo más largo hasta la resistencia a la castración en pacientes con tumores localizados de riesgo intermedio y bien tratados con TPA. Los pacientes con tumores metastásicos mostraron el menor tiempo hasta la resistencia a la castración.