The low-intensity shockwave (LISW) therapy is a recently developed modality for treating erectile dysfunction.
ObjectiveTo assess the efficacy of LISW therapy for treating erectile dysfunction as described in the literature.
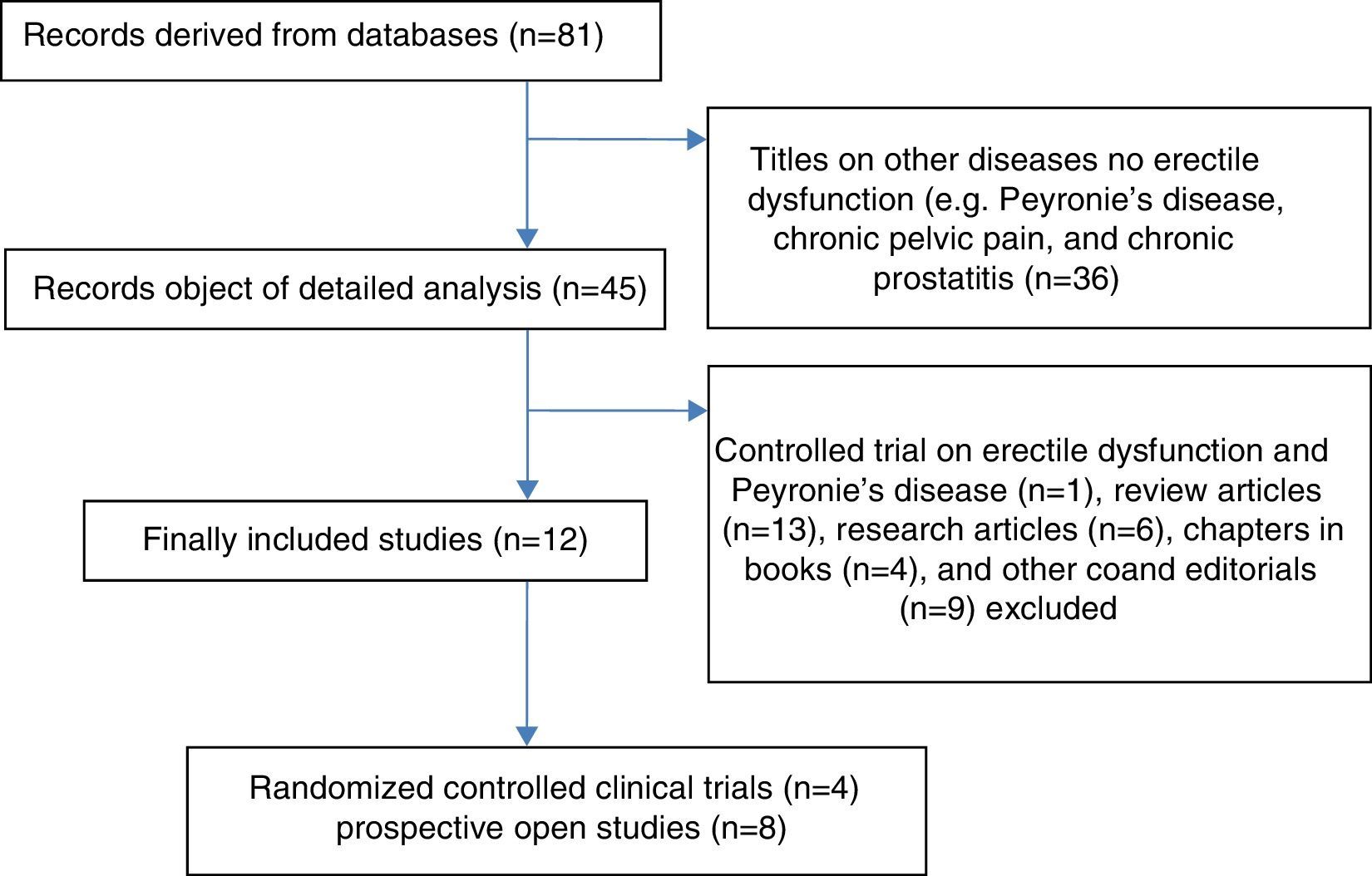
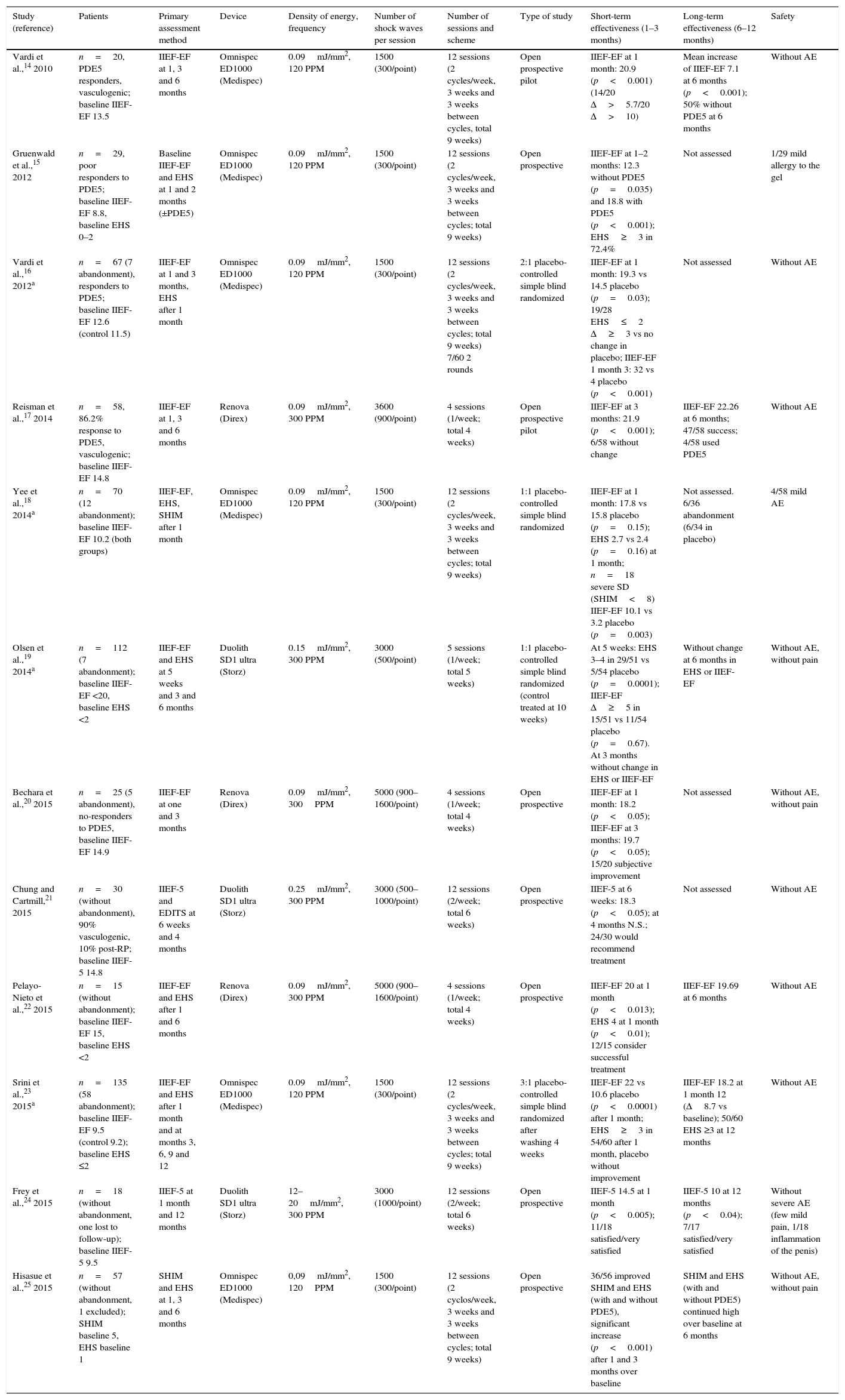
Acquisition of evidenceTwo independent reviewers identified studies eligible for a systematic review and meta-analysis of various sources written in English and Spanish, using the databases of PubMed, EMBASE and Web of Science. We excluded studies on Peyronie's disease. We employed the DerSimonian-Laird method for defining heterogeneity, calculating the grouped standard deviation of the mean (SDM). The primary objective of this review is to assess efficacy based on the change in the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-EF) over baseline at 1 month from the start of treatment, both for the treatment arm and the placebo arm. The secondary objective is focused on analysing IIEF-EF at 3–6 months from the start of the therapy.
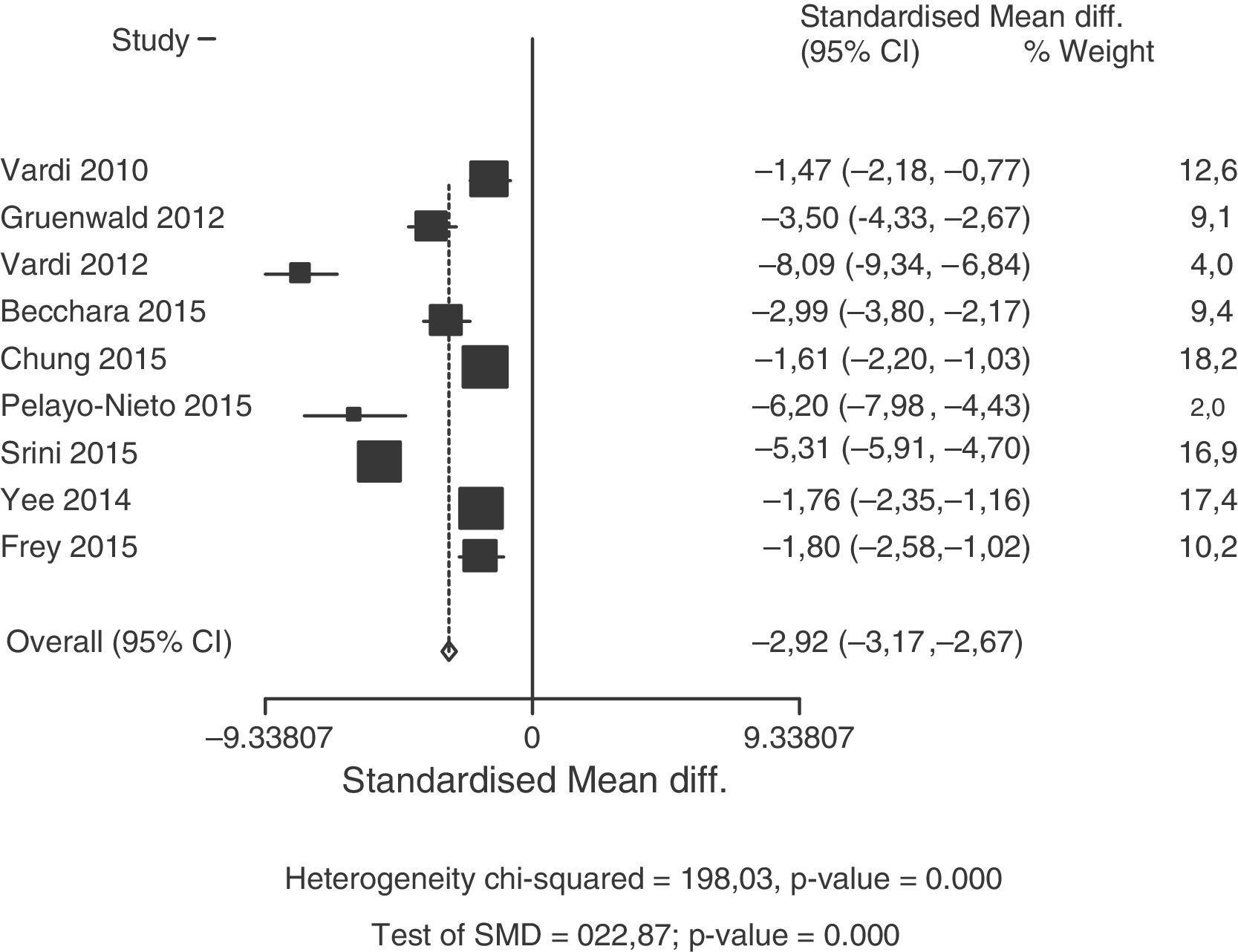
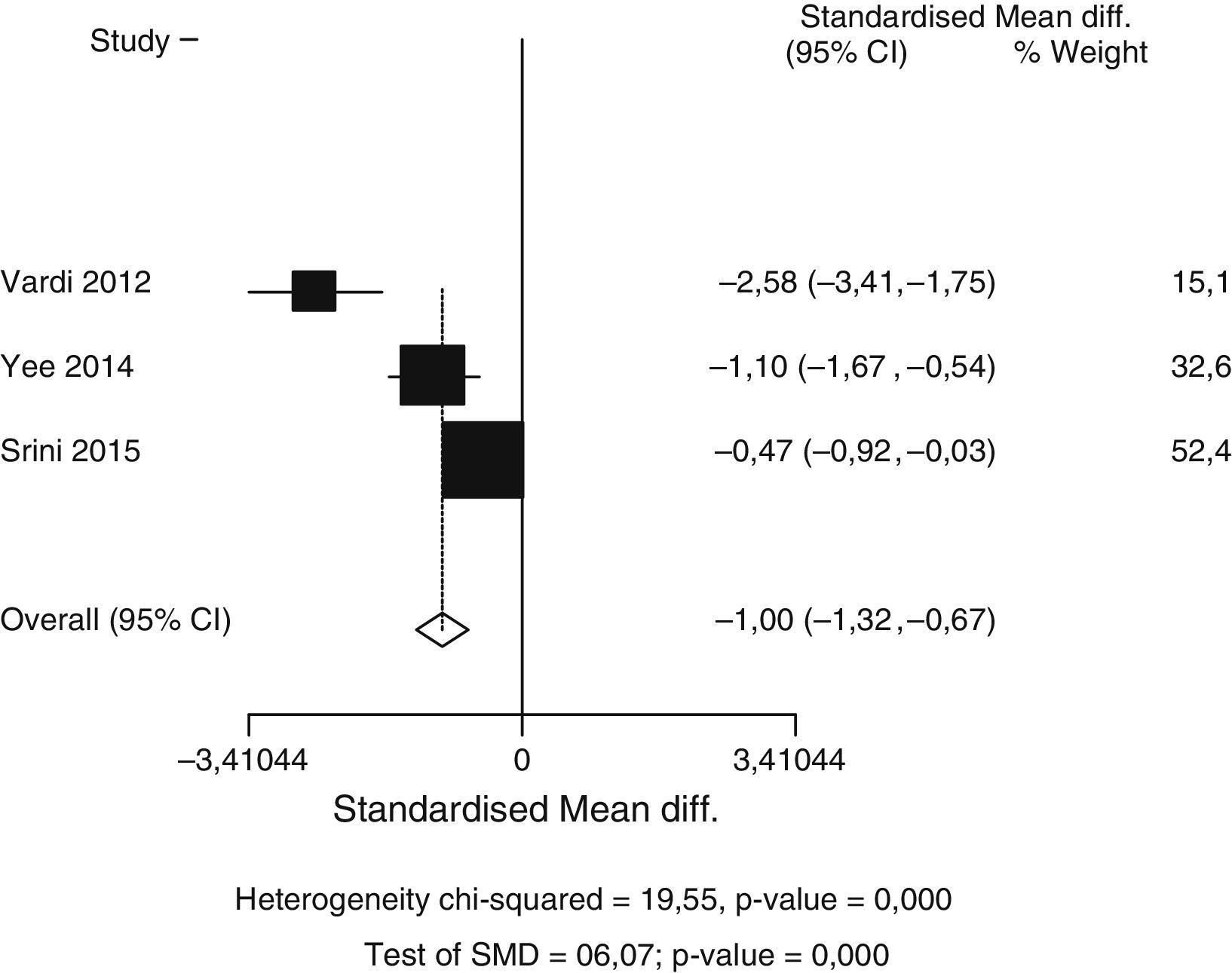
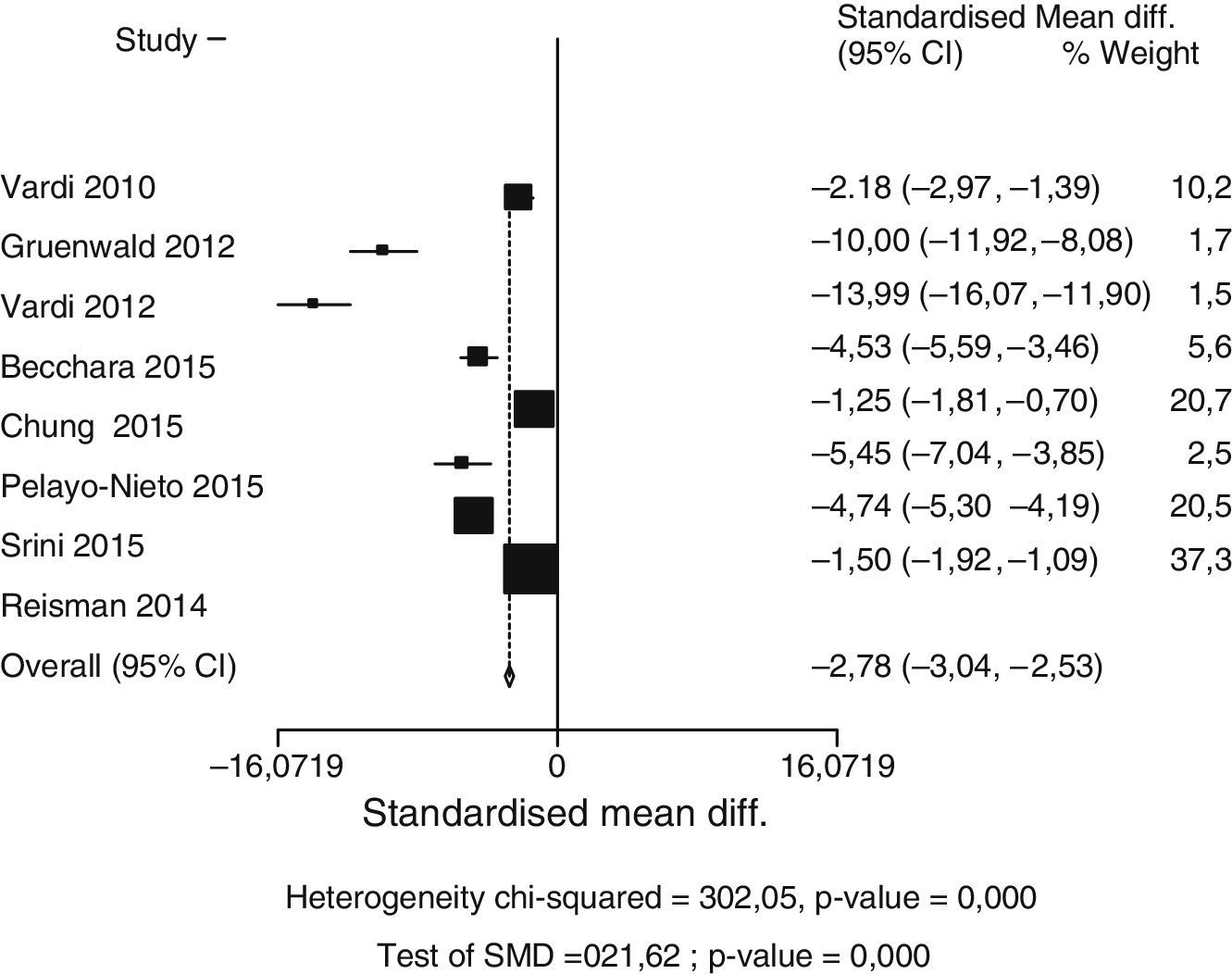
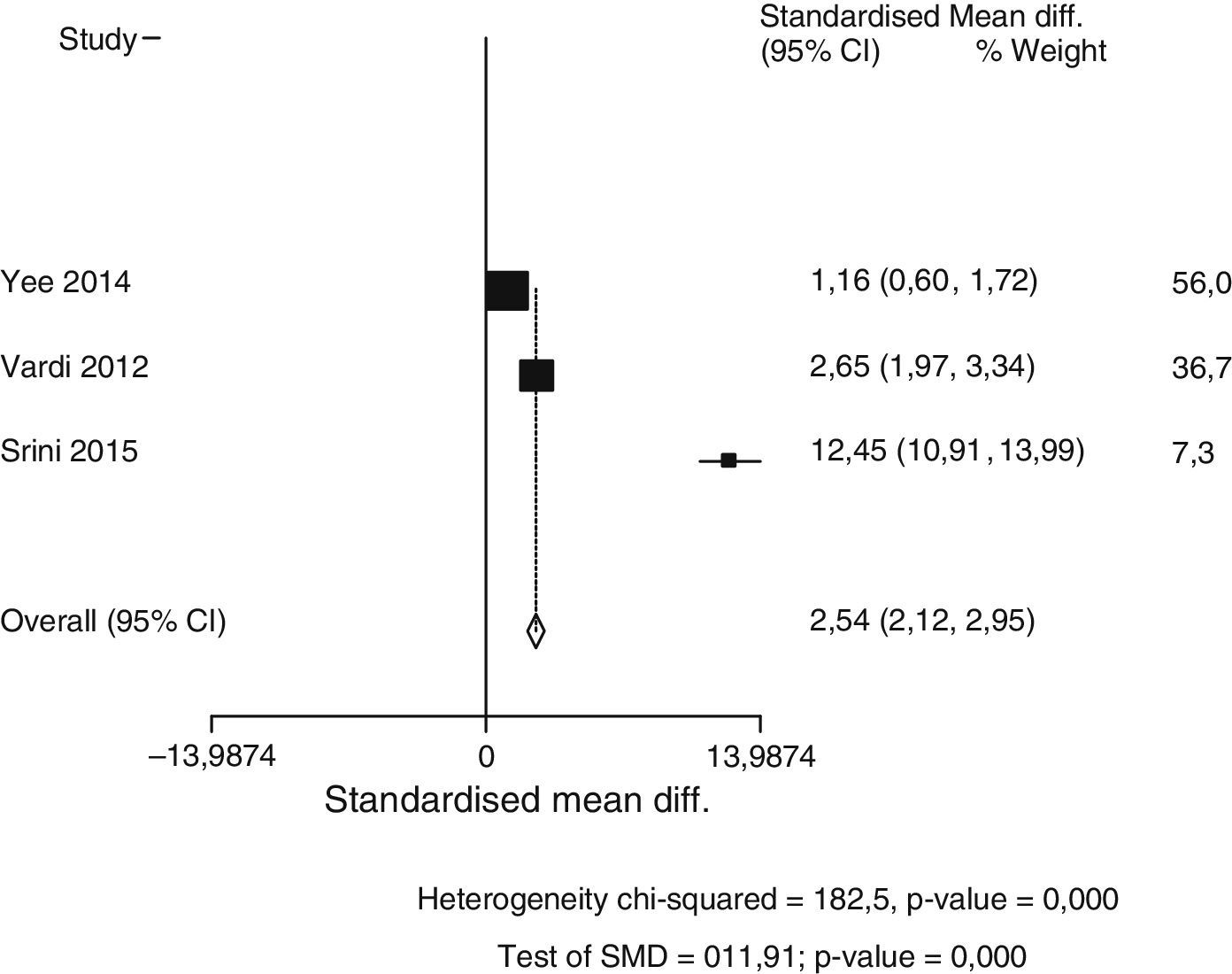
Summary of the evidenceThe pooled data of 636 patients from 12 studies showed that treatment with LISW resulted in a significant increase in IIEF-EF at 1 month with respect to baseline (SDM, −2.92; p=0.000), to a greater degree than placebo (SDM, −0.99; p=0.000). The IIEF-EF at 3–6 months for the treated patients was significantly greater than baseline (SDM, −2.78; p=0.000). Only one study compared the efficacy of placebo at 3–6 months vs baseline (SDM, −9.14). The comparison between LISW and placebo favors active treatment (SDM, 2.53; p=0.000) at 1 month. There are insufficient data in the literature to assess the response over placebo at 3–6 months.
ConclusionsAccording to the literature, treatment with LISW for erectile dysfunction is effective, both in the short and medium term. LISW has been described as more effective than placebo in the short term. The long-term efficacy data are insufficient. More studies are needed to explain the role of this therapy according to specific causes of erectile dysfunction.
La terapia con ondas de choque de baja intensidad (OCBI) es una modalidad de reciente uso en el tratamiento de la disfunción eréctil.
ObjetivoEvaluar la eficacia de la terapia con OCBI para el tratamiento de la disfunción eréctil según se describe en la literatura.
Adquisición de evidenciaDos revisores independientes identificaron estudios elegibles para llevar a cabo revisión sistemática y metaanálisis de diferentes fuentes escritas en inglés y español, utilizando las bases de datos de PubMed, Embase y Web of Science. Se excluyeron los estudios sobre la enfermedad de Peyronie. Se utilizó el método Der Simonian-Laird para definir la heterogeneidad calculando la desviación estándar de la media (DME) agrupada. El objetivo primario de esta revisión es evaluar la eficacia según el cambio del Índice internacional de función eréctil (IIEF-EF) sobre basal al mes de inicio de tratamiento, tanto para el brazo de tratamiento como para el brazo placebo. El objetivo secundario se centra en analizar IIEF-EF a 3-6 meses tras el inicio de la terapia.
Síntesis de evidenciaLos datos agrupados de 636 pacientes procedentes de 12 estudios mostraron que el tratamiento con OCBI conlleva un aumento significativo de IIEF-EF al mes con respecto a basal (DME = –2,92; p = 0,000), en un grado mayor que placebo (DME = –0,99; p = 0,000). El IIEF-EF a 3-6 meses en pacientes tratados fue significativamente mayor que basal (DME = –2,78; p = 0,000). Solo hay un estudio que compara eficacia de placebo a 3-6 meses vs basal (DME = –9,14). La comparación entre OCBI y placebo favorece el tratamiento activo (DME = 2,53; p = 0,000) al mes. No existen datos suficientes para evaluar respuesta sobre placebo a los 3-6 meses en la literatura.
ConclusionesEl tratamiento con OCBI para la disfunción eréctil según la literatura resulta eficaz, tanto a corto como a medio plazo. A corto plazo se ha descrito incluso más eficaz que placebo. Los datos sobre eficacia a largo plazo son insuficientes. También se necesitan más estudios para dilucidar el papel de esta terapia según las causas específicas de la disfunción eréctil.