The expression of PD-L1 in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is associated with worse survival and prognostic clinical-pathological features. However, they seem to respond better to new therapeutic agents. Knowing the behavior of RCC according to the presence of PD-L1 has implications for medical counseling and therapeutic approaches.
ObjectiveTo identify the presence of PD-L1 in renal tumor cells and analyze its association with patients’ prognostic factors, overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS).
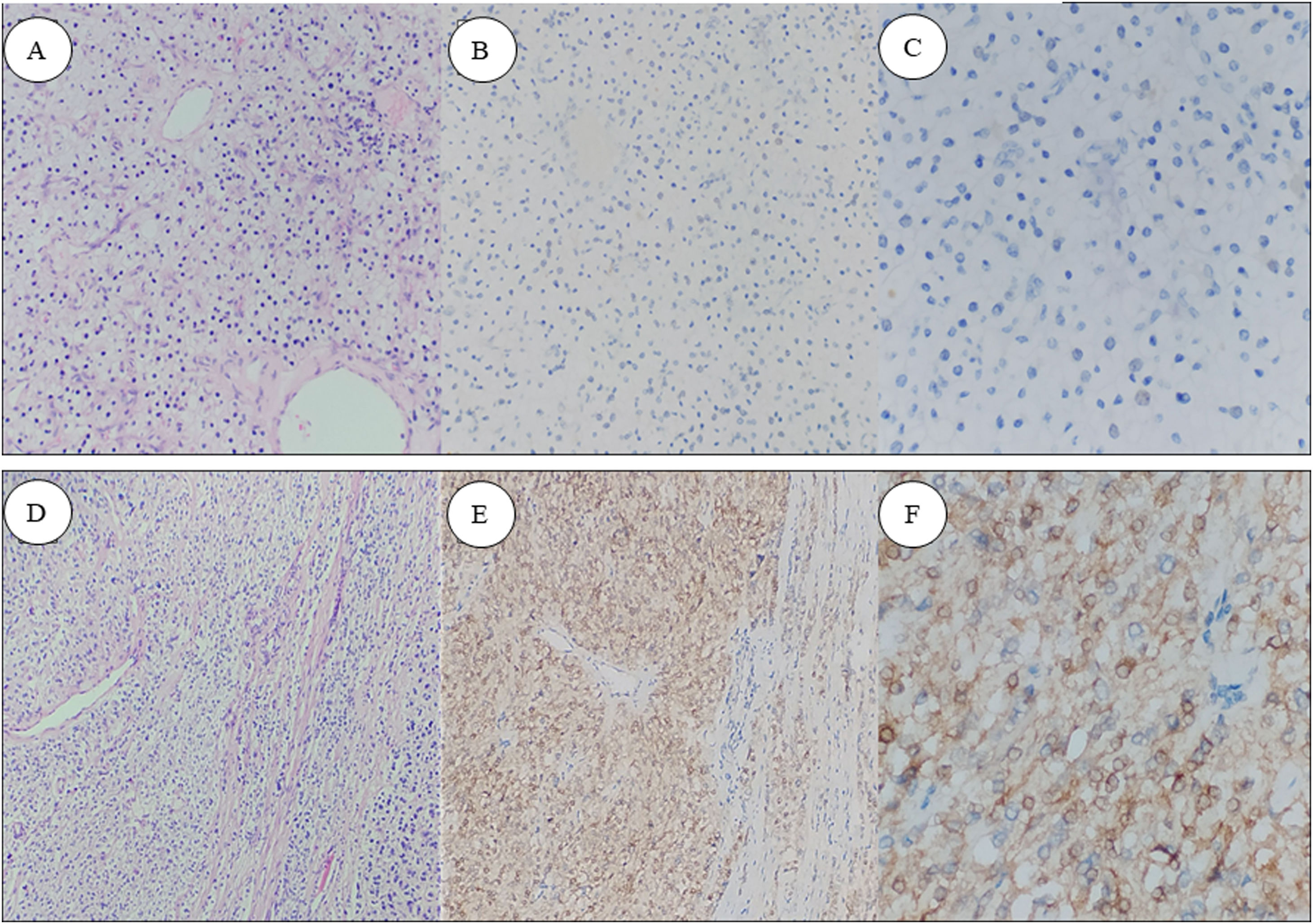
MethodologyRetrospective analysis of RCC tissue samples, obtained between 2018 and 2021. Immunohistochemistry analysis with mouse monoclonal Anti PD-L1, clone 22C3. Definition of PD-L1 “positive” as a Tumor Proportion Score ≥1%. Comparison of prognostic factors according to the presence or absence of PD-L1, and univariate analysis for OS and CSS.
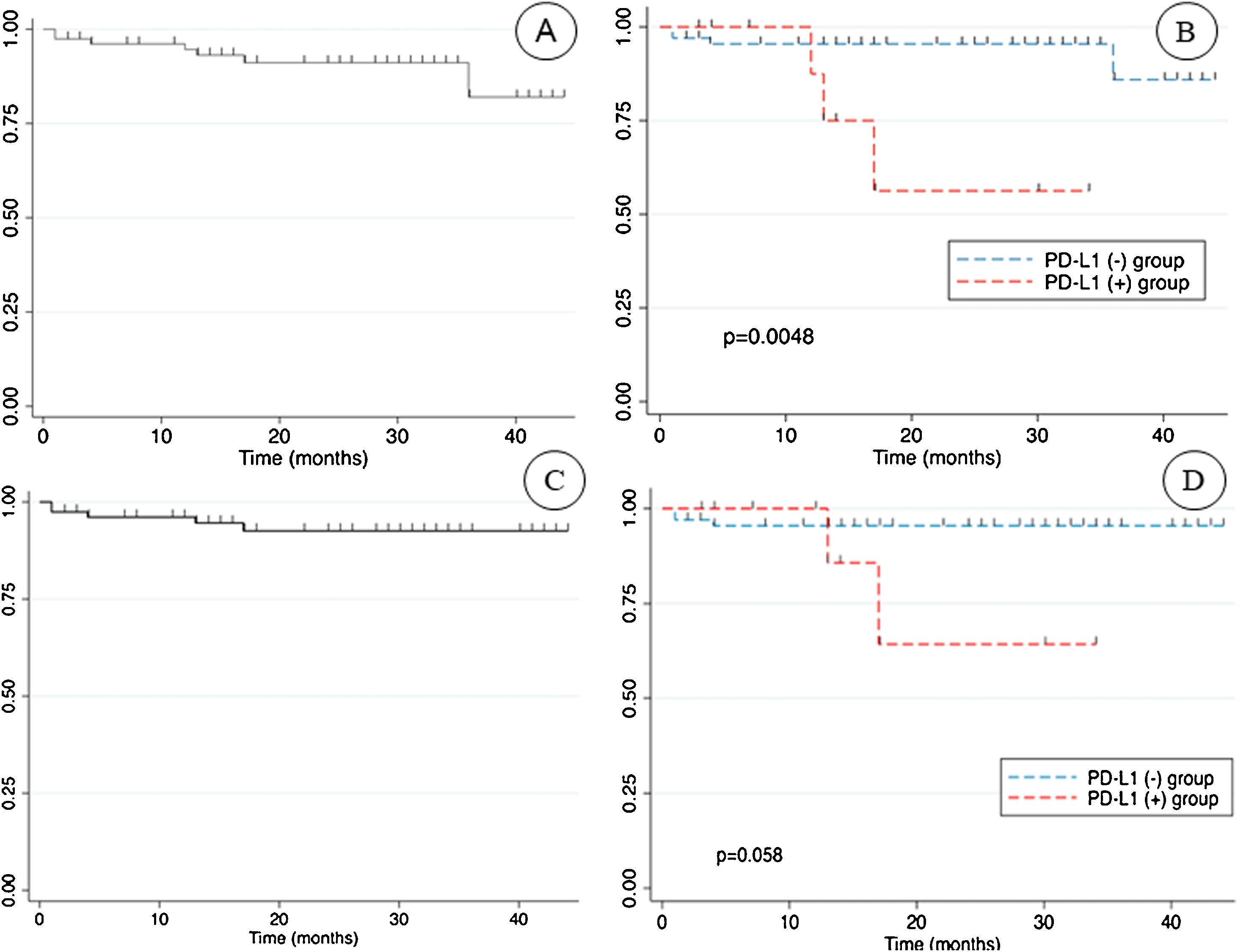
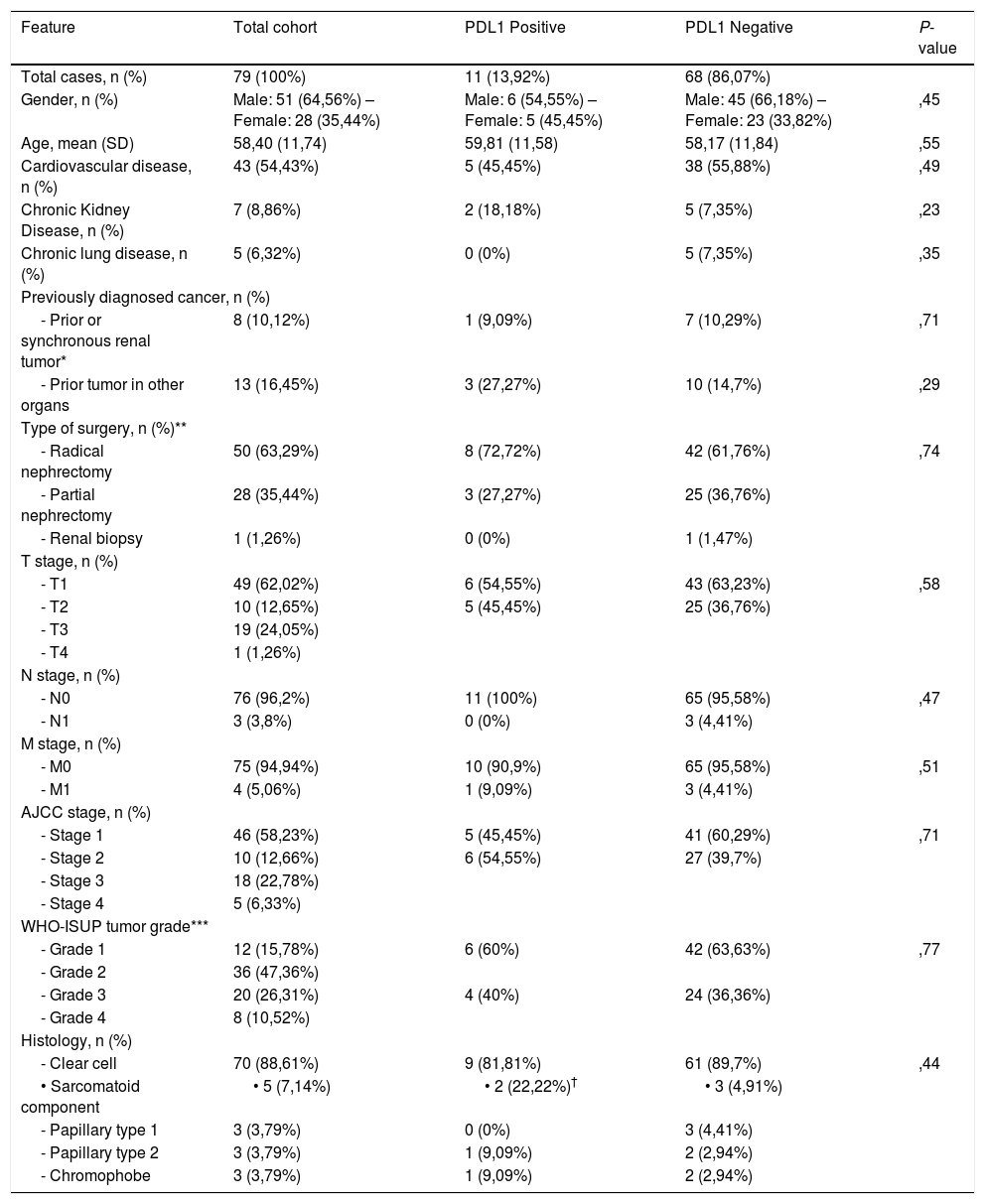
Results14% (n = 11) of the sample were PD-L1(+). Average age was 59 years. There were no statistically significant differences between PD-L1 status and TNM stages, nuclear grade and histology. PD-L1(+) had worse OS with a HR of 5.27 (CI: 1.1–23.7; P = .03) and CSS showed a unfavorable tendency for PD-L1(+) with a HR of 4.79 (CI: 0.79–28.95; P = .08).
ConclusionThe prevalence of PD-L1 in RCC is considerable. In this study PD-L1(+) was associated with unfavorable OS and CSS. It seems reasonable to incorporate its routine use in RCC.
La expresión de PD-L1 en el carcinoma de células renales (CCR) se asocia a tasas de supervivencia y características clínico-patológicas pronósticas peores. Sin embargo, estas parecen responder mejor ante nuevos agentes terapéuticos. Conocer el comportamiento del CCR según la presencia de PD-L1 tiene implicaciones sobre el asesoramiento de los pacientes y el abordaje terapéutico.
ObjetivoIdentificar la presencia de PD-L1 en las células tumorales renales y analizar su asociación con los factores pronósticos de los pacientes, la supervivencia global (SG) y la supervivencia cáncer-específica (SCE).
MetodologíaAnálisis retrospectivo a partir de muestras de tejido de CCR obtenidas entre 2018 y 2021. Estudio inmunohistoquímico con monoclonal de ratón anti PD-L1, clon 22C3. Se definió PD-L1 “positivo” como una puntuación de proporción tumoral ≥1%. Comparación de factores pronósticos según la presencia o ausencia de PD-L1, y análisis univariante para la SG y la SCE.
ResultadosUn 14% (n = 11) de la muestra era PD-L1(+). La edad media era de 59 años. No hubo diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre el estatus de PD-L1 y el estadio TNM, el grado nuclear y el tipo histológico. Los pacientes PD-L1(+) tuvieron peor SG con un HR de 5,27 (IC: 1,1–23,7; P = ,03) y la SCE mostró una tendencia desfavorable para PD-L1(+) con un HR de 4,79 (IC: 0,79–28,95; P = ,08).
ConclusiónLa prevalencia de PD-L1 en el CCR es considerable. En este estudio, PD-L1(+) se asoció con una SG y SCE desfavorables, lo que justifica incorporar su uso rutinario en el CCR.