The aim of our study is to correlate the CT adipose tissue distribution and recurrence risk of Prostatic Cancer (PCa) after Radical Prostatectomy (RP). Furthermore, we evaluated the association of adipose tissue and PCa aggressiveness.
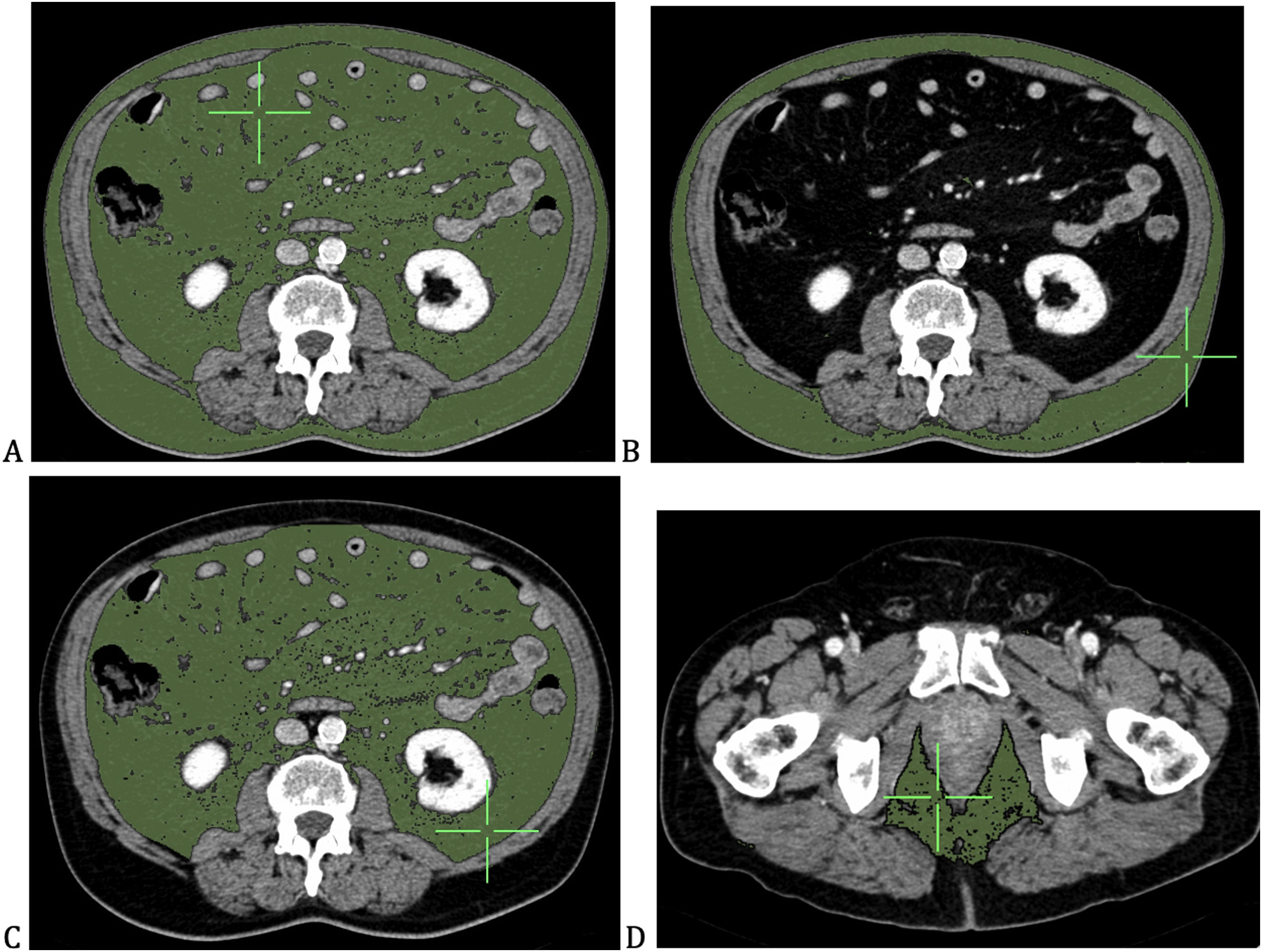
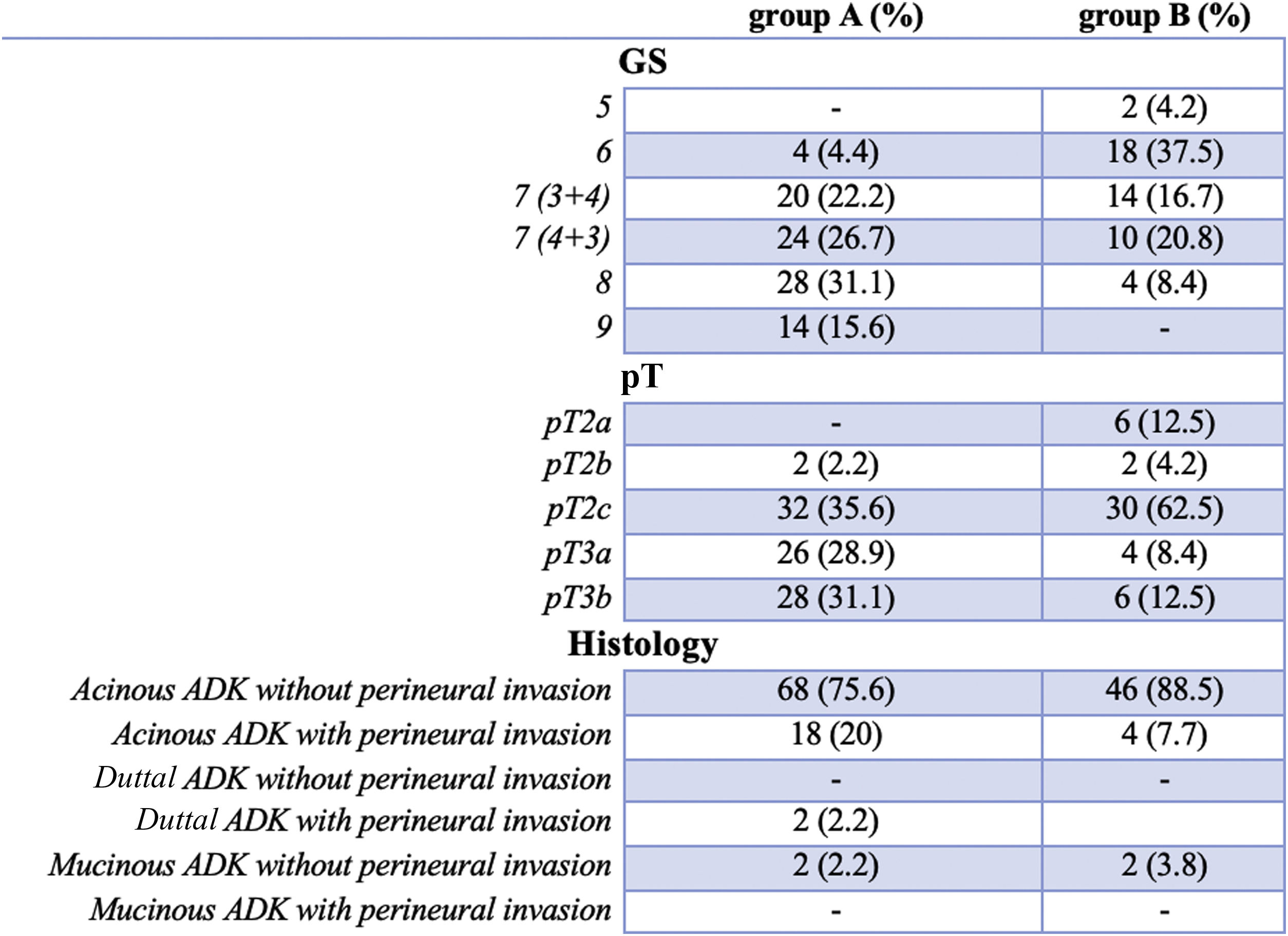
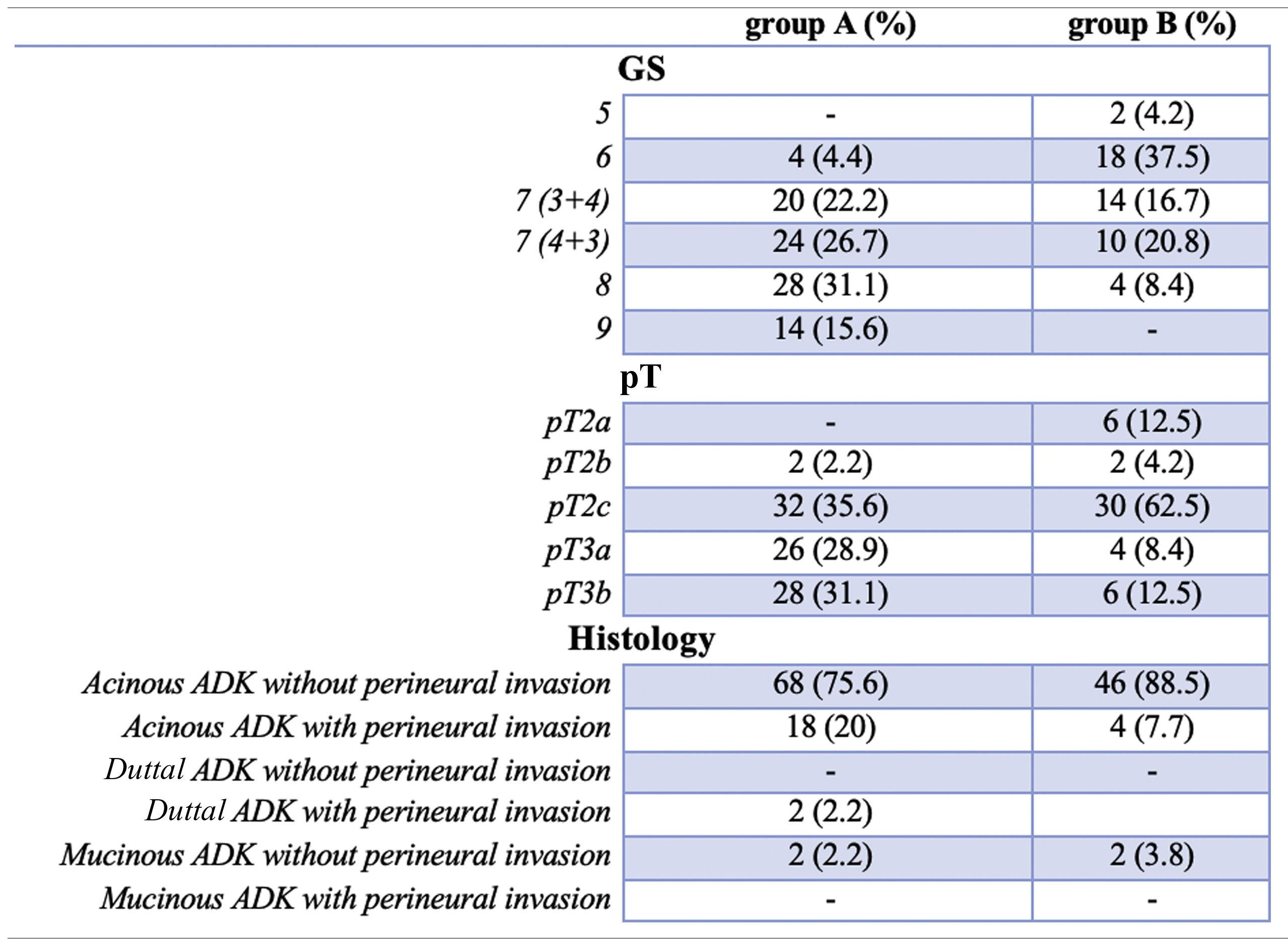
Materials and methodsWe identified two groups of patients based on presence (group A) and absence (group B or control group) of Bio-chemical Recurrence (BCR) after RP. A semi-automatic function able to recognize the typical attenuation values of adipose tissue was used for sub-cutaneous (SCAT), visceral (VAT), total (TAT) and periprostatic (PPAT) adipose tissues. For both groups of patients, a descriptive analysis of continuous variables and categorical variables was performed.
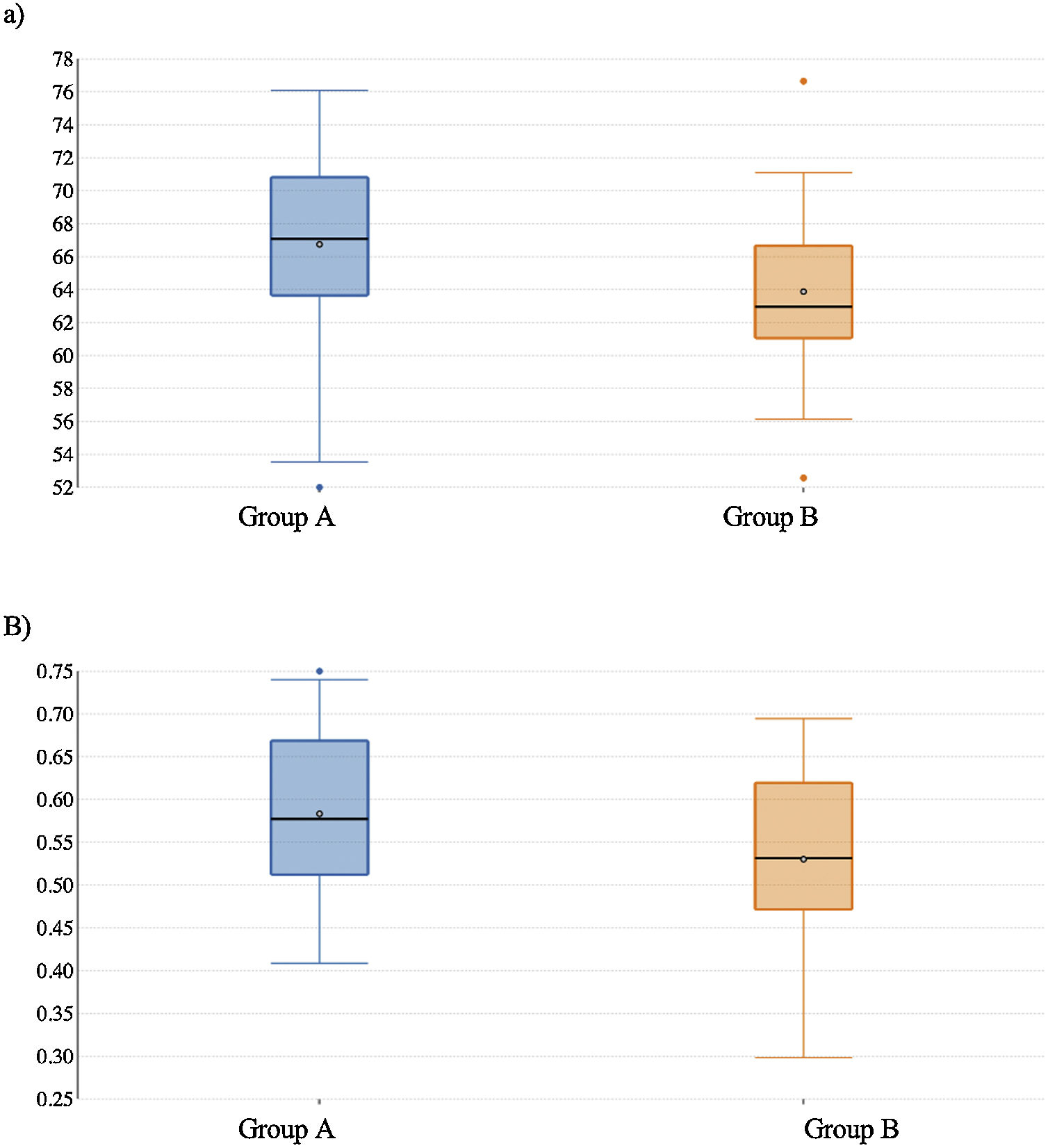
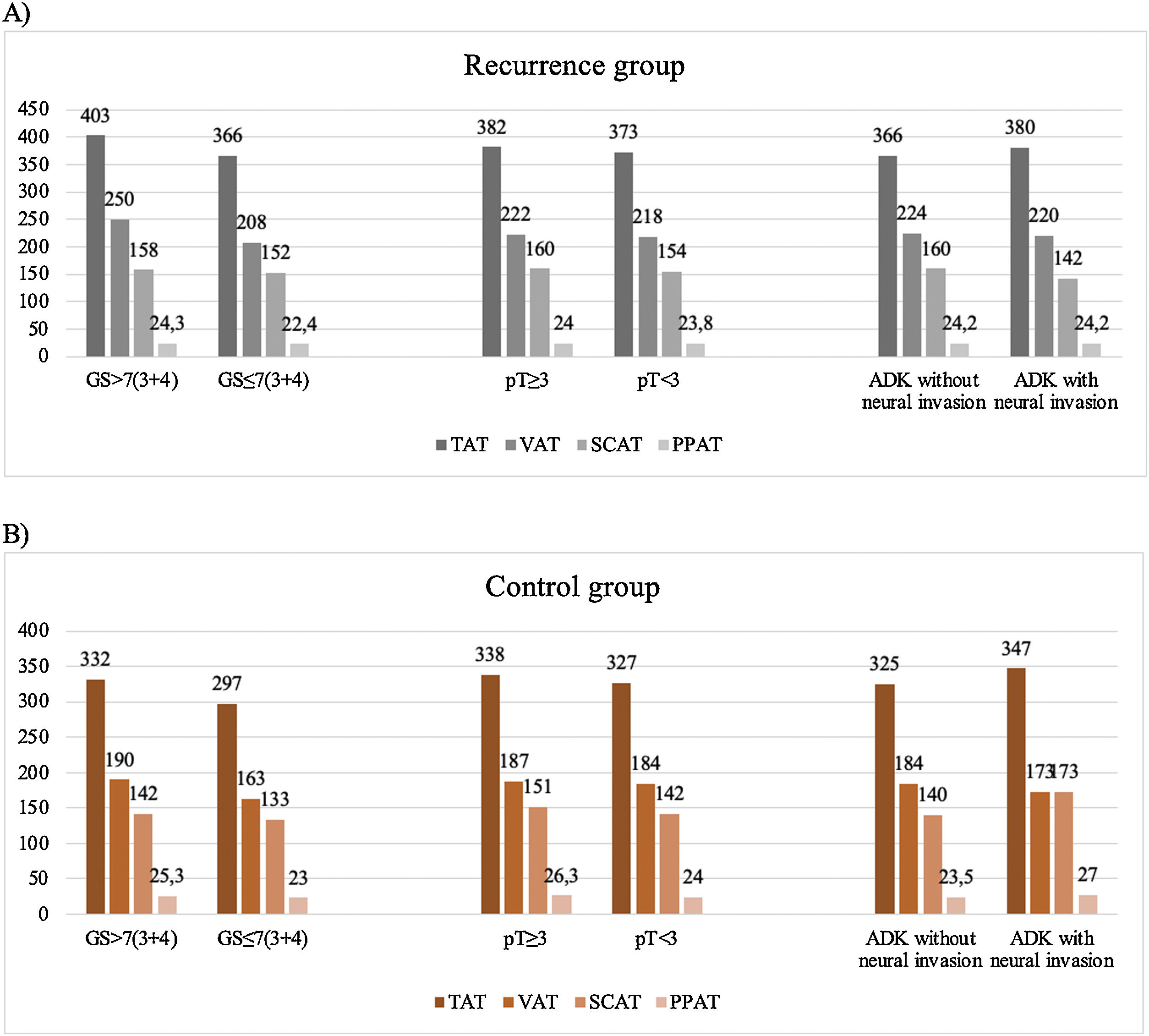
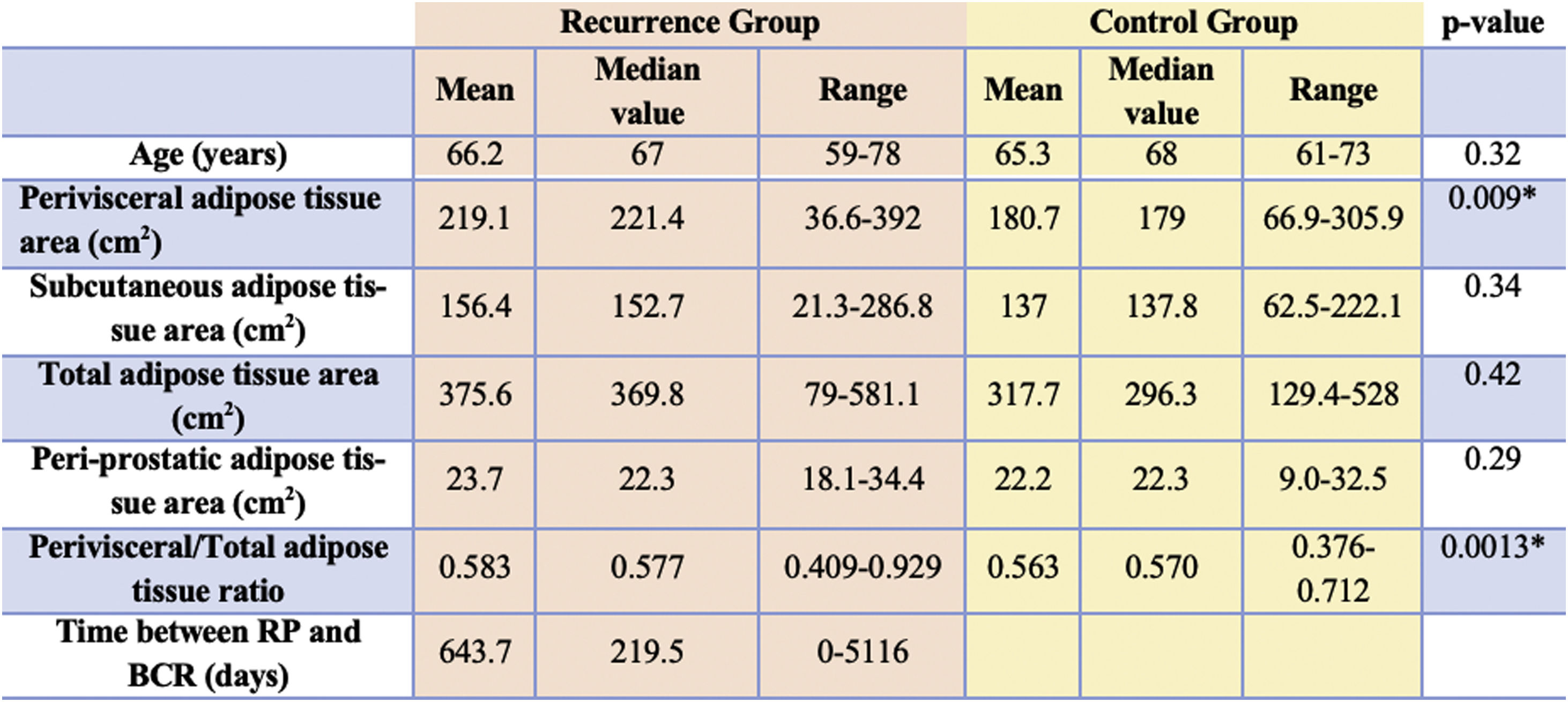
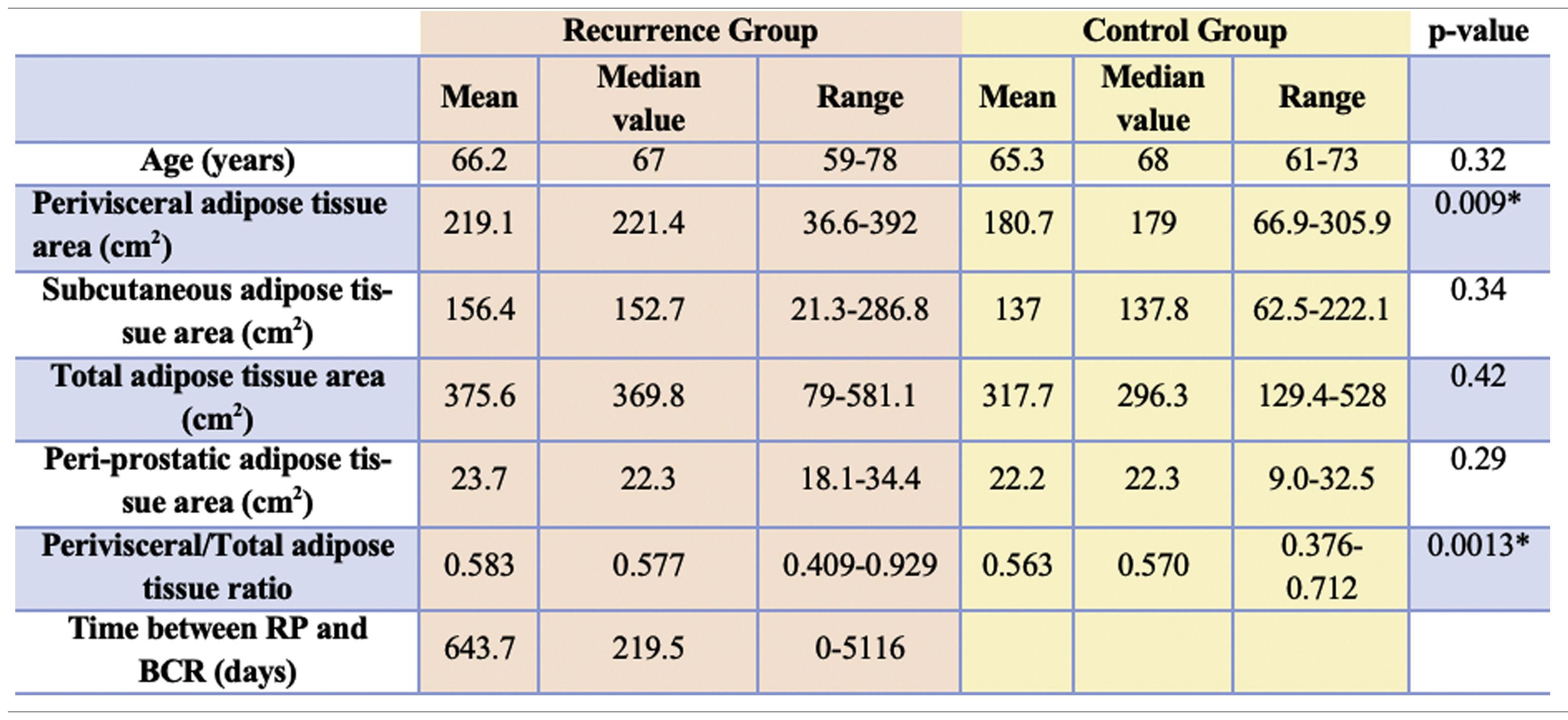
ResultsAfter comparing between groups, a statistically significant difference was found for VAT (p<0.001) and for VAT/TAT ratio (p=0.013). No statistically significant correlation was found for PPAT and SCAT, even if higher values were found in patients with high grade tumors.
ConclusionThis study confirms visceral adipose tissue as a quantitative imaging parameter related to oncological risk of PCa recurrence development, and the role of abdominal fat distribution measured with CT before RP as an important tool to predict the PCa recurrence risk, particularly in patients with high grade tumors.
El objetivo de nuestro estudio es correlacionar la distribución del tejido adiposo en la TC y el riesgo de recurrencia del cáncer de próstata (CaP) después de la prostatectomía radical (PR). Además, evaluamos la asociación del tejido adiposo y la agresividad del CaP.
Materiales y métodosIdentificamos dos grupos de pacientes en función de la presencia (grupo A) y la ausencia (grupo B o grupo de control) de recidiva bioquímica (RBQ) tras la PR. Se utilizó una función semiautomática capaz de reconocer los valores de atenuación típicos del tejido adiposo para el tejido adiposo subcutáneo (TAS), visceral (TAV), total (TAT) y periprostático (TAP). Para ambos grupos de pacientes se realizó un análisis descriptivo de las variables continuas y categóricas.
ResultadosAl comparar los dos grupos, hubo una diferencia estadísticamente significativa para el TAV (p<0,001) y para la proporción TAV/TAT (p=0,013). No se encontró una correlación estadísticamente significativa para el TAP y el TAS, aunque se encontraron valores más altos en los pacientes con tumores de grado alto.
ConclusiónEste estudio confirma que el tejido adiposo visceral es un parámetro de imagen cuantitativo relacionado con el riesgo oncológico de desarrollo de recidiva del CaP, y el papel de la distribución de la grasa abdominal en la TC antes de la PR como una herramienta importante en la predicción del riesgo de recidiva del CaP, particularmente en pacientes con tumores de alto grado.