To know the rate of nosocomial infections in open prostate surgery and to assess the application of pre-surgery preparation and preoperative antibiotic prophylaxis protocols at three public hospitals in the Autonomous Community of Madrid.
Materials and methodsProspective observational and multicentre study, including all the patients operated on at the services monitored and admitted for more than 48h between 1 January and 31 December 2009. They were monitored from admittance until their discharge.
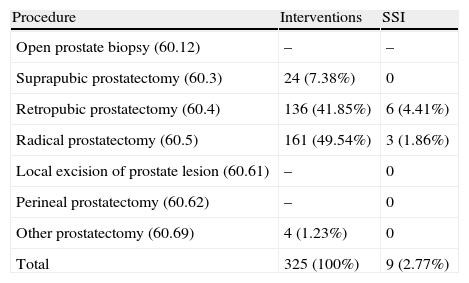
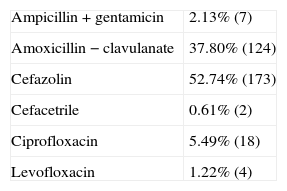
ResultsThe rate of hospital infection observed was 3.38%. The most frequent infection was surgical localization, with an incidence rate of 2.77% (superficial=1.23%; deep=0.31%; organ-space=1.23%). The percentage of appropriate surgical prophylaxis, both in the indication and in the selection of antibiotics, initiation and duration, with respect to all those patients that received it, was 47.42%. According to the data obtained from their clinical records, the percentage of patients in which the pre-surgery preparation protocol was correctly complied with, was 92%.
ConclusionsThe results obtained in this multicentre study can serve not only as a reference to other public hospitals but they are also comparable to other international monitoring systems. Monitoring and controlling infections associated with healthcare must be a key aspect in Patient Care and Safety programmes.
Conocer las tasas de infección nosocomial en cirugía abierta de próstata y valorar la aplicación de los protocolos de preparación prequirúrgica y profilaxis antibiótica preoperatoria establecidos en tres hospitales públicos de la Comunidad de Madrid.
Material y métodosEstudio prospectivo observacional multicéntrico, incluyendo a todos los pacientes intervenidos quirúrgicamente en los servicios sometidos a vigilancia e ingresados durante más de 48 horas, entre el 1 de enero y el 31 de diciembre de 2009. Fueron vigilados desde el ingreso hasta el alta.
ResultadosLa tasa de infección hospitalaria observada fue del 3,38%. La infección más frecuente fue la de localización quirúrgica, con una incidencia del 2,77% (superficial=1,23%; profunda=0,31%; órgano-espacio=1,23%). El porcentaje de profilaxis quirúrgicas adecuadas, tanto en indicación como en elección del antibiótico, inicio y duración, respecto a todos aquellos pacientes que la recibieron fue del 47,42%. Según los datos obtenidos de las historias clínicas el porcentaje de pacientes en los que se cumplió correctamente el protocolo de preparación prequirúrgica fue del 92%.
ConclusionesLos resultados obtenidos en este estudio multicéntrico, no sólo pueden servir como referencia a otros hospitales públicos, sino que también son comparables con otros sistemas de vigilancia internacionales. La vigilancia y control de las infecciones asociadas a la asistencia sanitaria deben ser un aspecto clave en los programas de calidad asistencial y seguridad del paciente.