To assess the diagnostic concordance of overactive bladder (OAB) and detrusor overactivity (DO) in male patients with predominant storage lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and evaluate their clinical and urodynamic profile according to DO presence and degree of obstruction.
Material and methodsEpidemiological, cross-sectional multicenter study. A 3-day bladder diary (3dBD), International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) and Bladder Control Self-Assessment Questionnaire (B-SAQ) questionnaires were analyzed. Prostate volume was determined by ultrasound. Urodynamic study (UDS) tests were performed. The prevalence of OAB and DO and the degree of clinical concordance (kappa index) were investigated. Descriptive analysis of clinical variables and UDS results was performed, followed by comparisons based on the presence of DO and degree of obstruction.
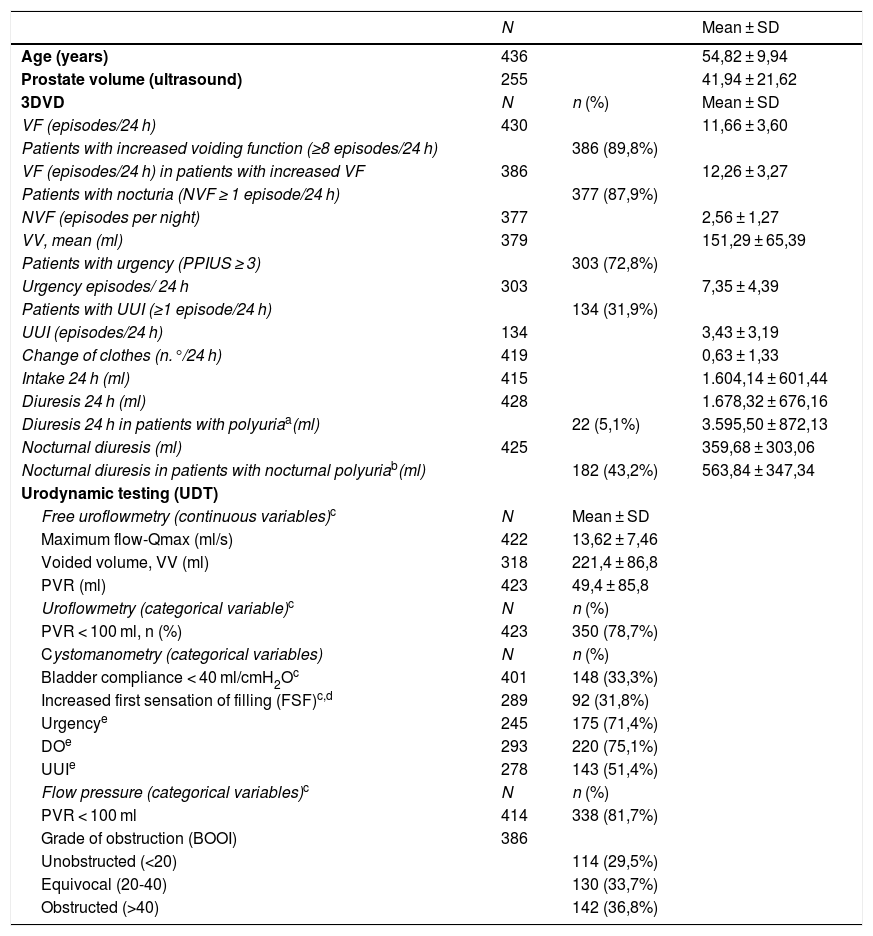
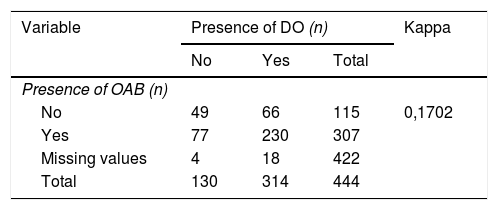
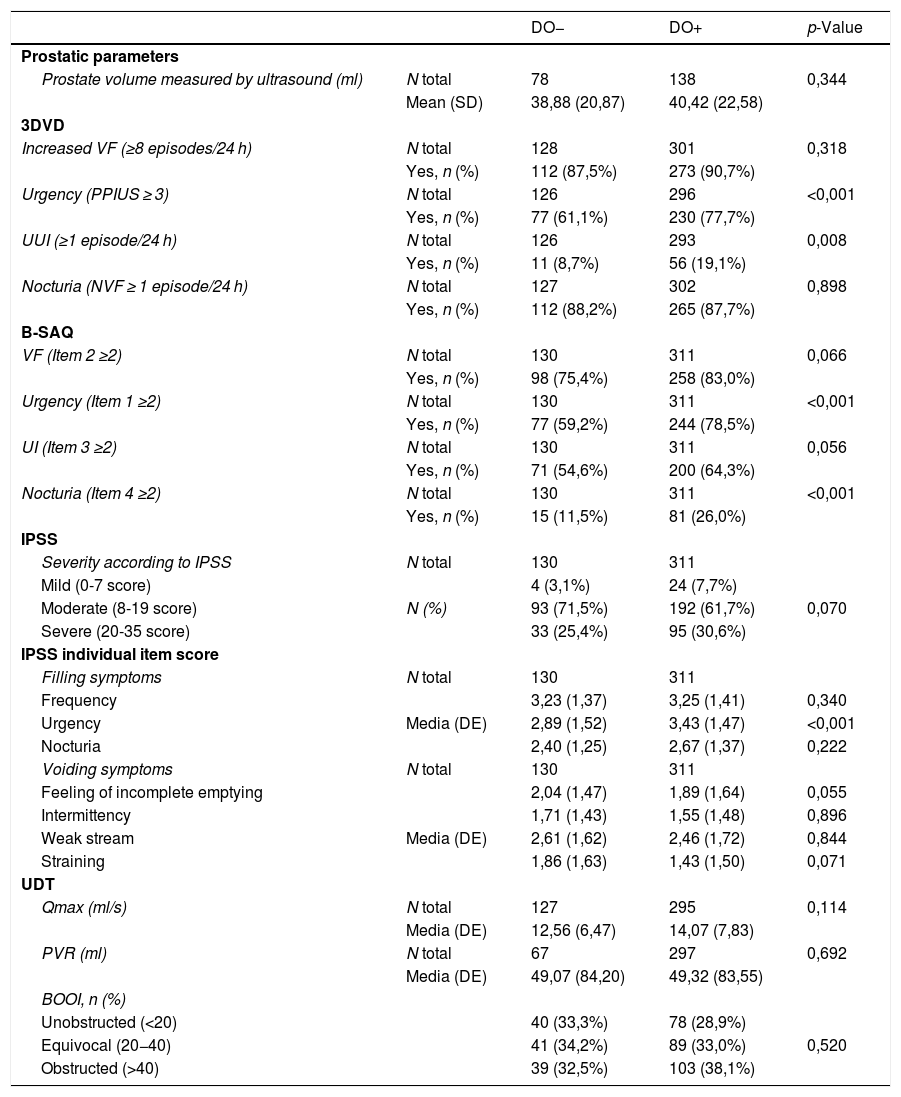
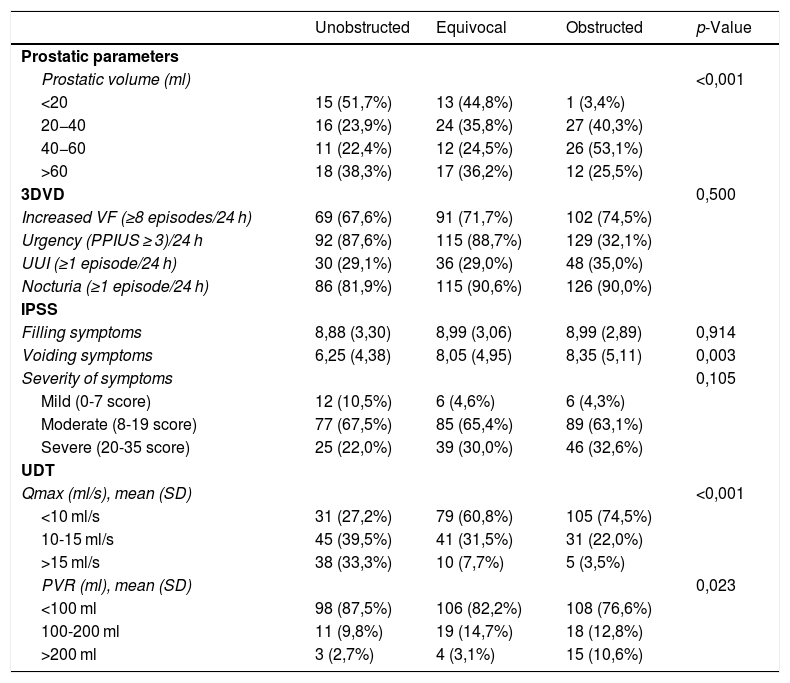
ResultsA total of 445 patients were included. The mean age was (SD) 54.8 (9.9) years. According to 3dBD, 89.9% presented increased urinary frequency, 87.9% nocturia, 72.1% urgency, and 31.9% urge urinary incontinence (UUI). Obstruction was present in 36.8%. Concomitant OAB and DO were present in 54.5%. The degree of diagnostic concordance between OAB and DO was low (κ = 0.1772). There were more patients with DO presenting urgency (3dBD and B-SAQ; p < 0.001), UUI (3dBD; p = 0.008) and nocturia (B-SAQ; p < 0.001). Differences were found in terms of prostate volume, IPSS-voiding, maximum flow (Qmax) and post-void residual (p < 0.05) according to the obstruction degree.
ConclusionsApproximately 50% of male patients aged 18–65 years old with predominant storage LUTS, referred to specialized units, have both OAB and DO. Obstruction is present on 1/3. Diagnostic concordance between OAB and DO is poor.
Estudiar el grado de concordancia diagnóstica entre vejiga hiperactiva (VH) e hiperactividad del detrusor (HD) en varones con síntomas del tracto urinario inferior (STUI) predominantemente de llenado, y el perfil clínico y urodinámico según presencia de HD y grado de obstrucción del tracto urinario inferior (OTUI).
Material y métodosEstudio epidemiológico, transversal, multicéntrico y nacional. Se cumplimentaron: diario miccional de 3 días (DM3d), International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) y Cuestionario de Autoevaluación del Control de la Vejiga (CACV). Se determinó el volumen prostático (Vp) por ecografía y se realizó estudio urodinámico (EUD). Se analizó la prevalencia de VH y HD y la concordancia (kappa). Se realizó un análisis descriptivo de características clínicas y urodinámicas; posteriormente se comparó su frecuencia según presencia de HD y OTUI.
ResultadosSe evaluaron 445 pacientes con edad media ± DE de 54,8 ± 9,9 años. Según el DM3d, un 89,8% presentaba frecuencia miccional aumentada, un 87,9% nicturia, un 72,8% urgencia y un 31,9% incontinencia urinaria de urgencia (IUU). Un 36,8% tenía OTUI. El 54,5% presentaba VH y HD. La concordancia diagnóstica entre HD y VH fue baja (κ = 0,1702). Más pacientes con HD que sin ella presentaron urgencia (DM3d y CACV; p < 0,001), IUU (DM3d; p = 0,008) y nicturia (CACV; p < 0,001). Hubo diferencias en IPSS-vaciado, flujo máximo (Qmax) y residuo posmiccional (p < 0,05) según el grado de obstrucción.
ConclusionesEn pacientes varones de 18 a 65 años con STUI predominantemente de llenado derivados a unidades especializadas, aproximadamente la mitad tienen coexistencia de VH y HD y un tercio tenía obstrucción. Hay baja concordancia diagnóstica entre VH y HD.