Overactive bladder (OAB) negatively impacts patient quality of life and may be associated with high resource use. Our aim was to describe the resource use, costs and persistence associated with mirabegron (MB) or antimuscarinic (AM) treatment in patients with OAB.
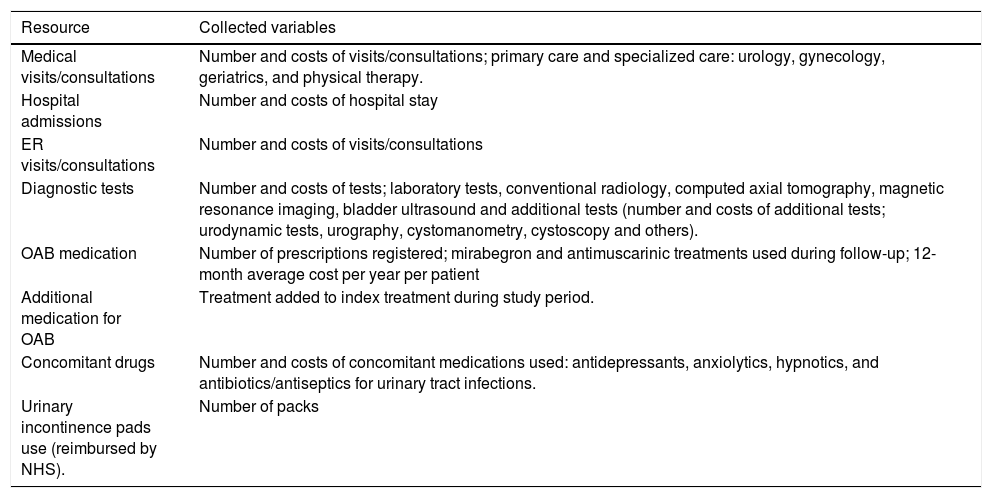
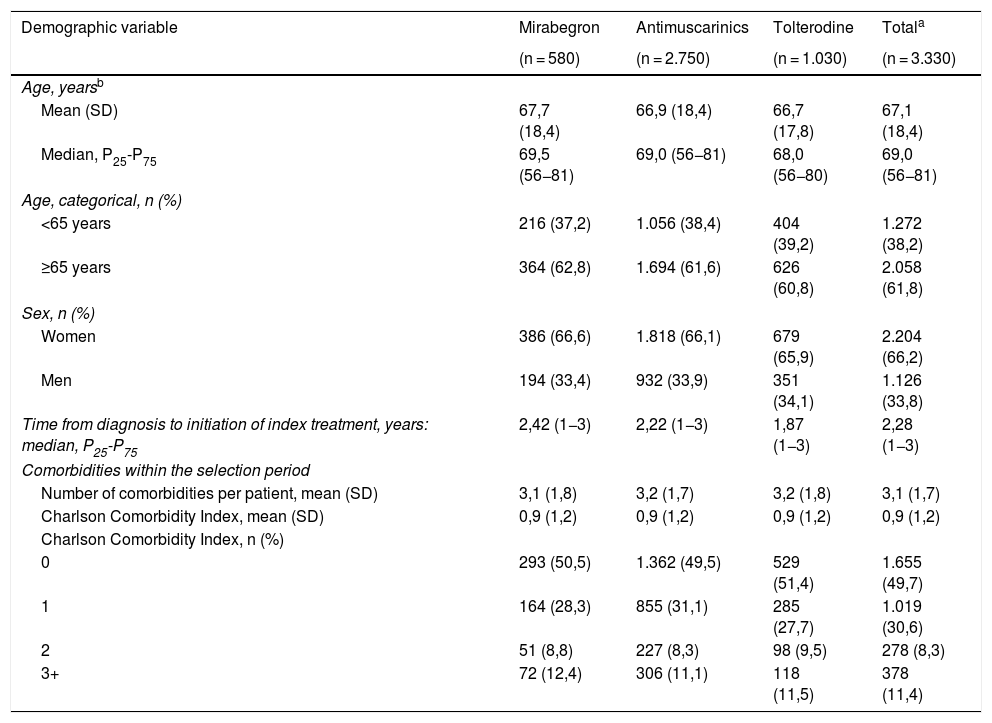
Materials and methodsObservational retrospective study of medical records in adult patients initiating OAB treatment with MB or AM in Catalonia. Healthcare resource use (visits, hospital stays, tests, medication, absorbent pads) in the first year after treatment initiation was collected. Associated costs were estimated (є, reference year 2019), as well as treatment persistence. Treatment discontinuation was defined as the absence of prescription for at least 45 days or treatment change.
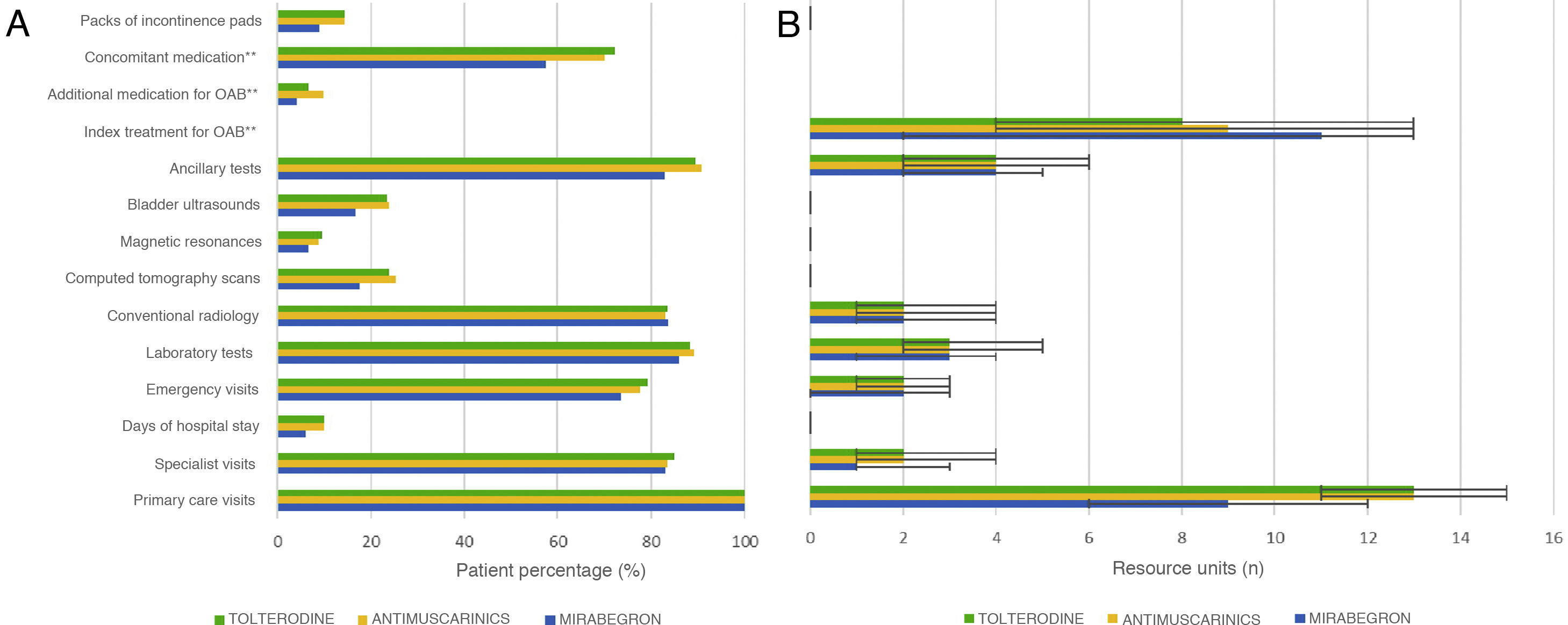
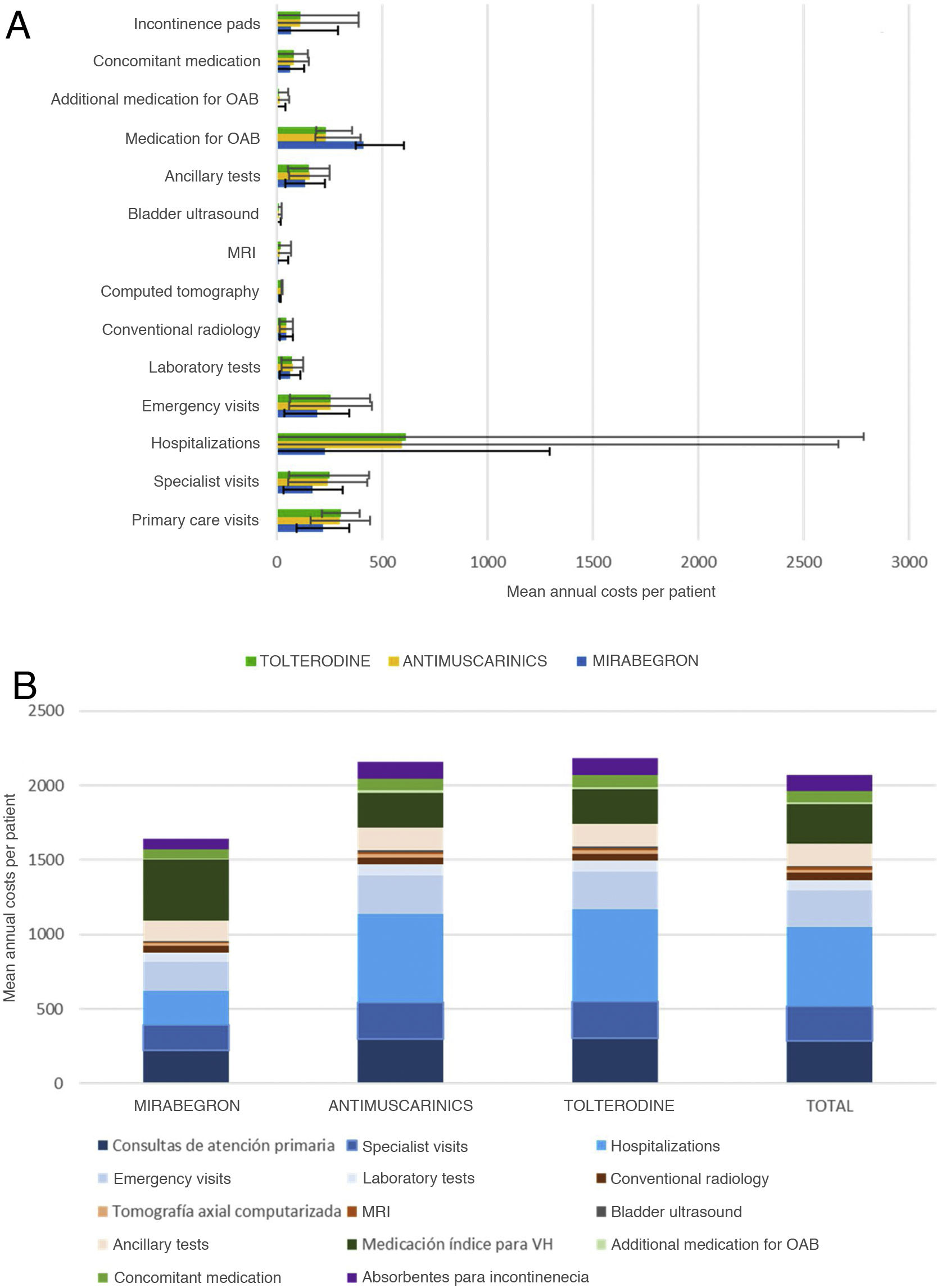
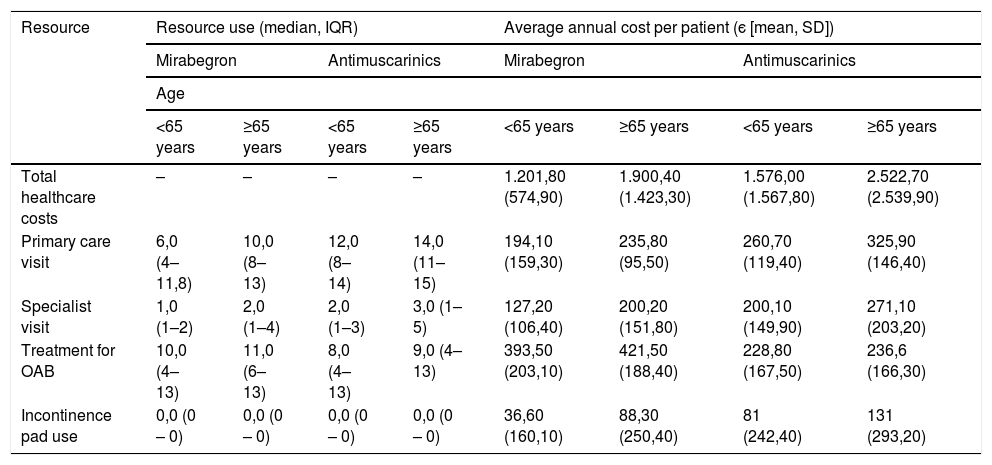
ResultsThe mean cost per patient (SD) was є 1,640.20 (є 1,227.60) with MB and є 2,159.20 (є 2,264.40) with AM; the associated healthcare resource use cost was lower with MB compared to AM, except for OAB drug costs. Persistence after 12 months of treatment initiation was higher in MB (42.1%) compared to AM (33.0%), as was the median time until treatment discontinuation: 299 (95% CI: 270–328) vs 240 days (95% CI: 230–250).
ConclusionsLower healthcare resource use was observed with MB compared to AM in the first year of index treatment, resulting in a lower mean direct cost per patient and year, despite its higher acquisition cost. Increased treatment persistence, as well as rational use of available treatments improves OAB management and, in return, patients’ quality of life.
La vejiga hiperactiva (VH) impacta negativamente en la calidad de vida de los pacientes y puede asociarse a un elevado consumo de recursos. Nuestro objetivo fue describir el uso de recursos, costes y persistencia asociados al tratamiento de la VH con mirabegrón (MB) o antimuscarínicos (AM).
Materiales y métodosEstudio observacional retrospectivo en registros médicos en adultos que iniciaron tratamiento para VH con MB o AM en Cataluña. Se analizó el uso de recursos sanitarios (visitas, hospitalizaciones, pruebas, medicación, absorbentes para incontinencia) el primer año tras el inicio del tratamiento, estimando sus costes asociados (є, 2019) y la persistencia terapéutica. Se definió abandono como la falta de prescripción durante ≥45 días o el cambio de tratamiento.
ResultadosEl coste medio por paciente (DE) con MB fue 1640,20 є (1227,60) vs. 2159,20 є (2264,60) con AM; el coste asociado al uso de recursos sanitarios fue inferior en MB vs. AM, exceptuando el coste del tratamiento farmacológico con MB. La persistencia al tratamiento a los 12 meses fue superior en MB (42,1% vs. 33,0%), así como el tiempo (mediana) hasta el abandono del tratamiento: 299 (95% CI: 270,11−327,89) vs. 240 días (95% CI: 230,46–249,54).
ConclusionesLos pacientes tratados con MB mostraron menor uso de recursos resultando en un coste medio por paciente/año más bajo, a pesar del mayor coste del fármaco respecto a AM. La mayor persistencia al tratamiento y el uso racional de las terapias disponibles mejoran el manejo de la VH y la calidad de vida de los pacientes.