Urinary incontinence (UI) is the involuntary loss of urine. It is highly prevalent in women and has a great biopsychosocial impact. Rehabilitation is established as the first-line treatment, although its use has not been protocolized.
ObjectiveTo identify which personal risk factors and type of treatment applied are statistically related to patient improvement.
Study designRetrospective cohort study.
MethodsRetrospective cohort study of female patients diagnosed with urinary incontinence who attended the Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Clinic of the Río Hortega University Hospital, receiving rehabilitation treatment during the year 2021. The minimum follow-up period was 12 weeks. The presence or absence of improvement was evaluated according to seven objective and subjective variables, and improvement was established as positive evolution in at least five of the seven variables.
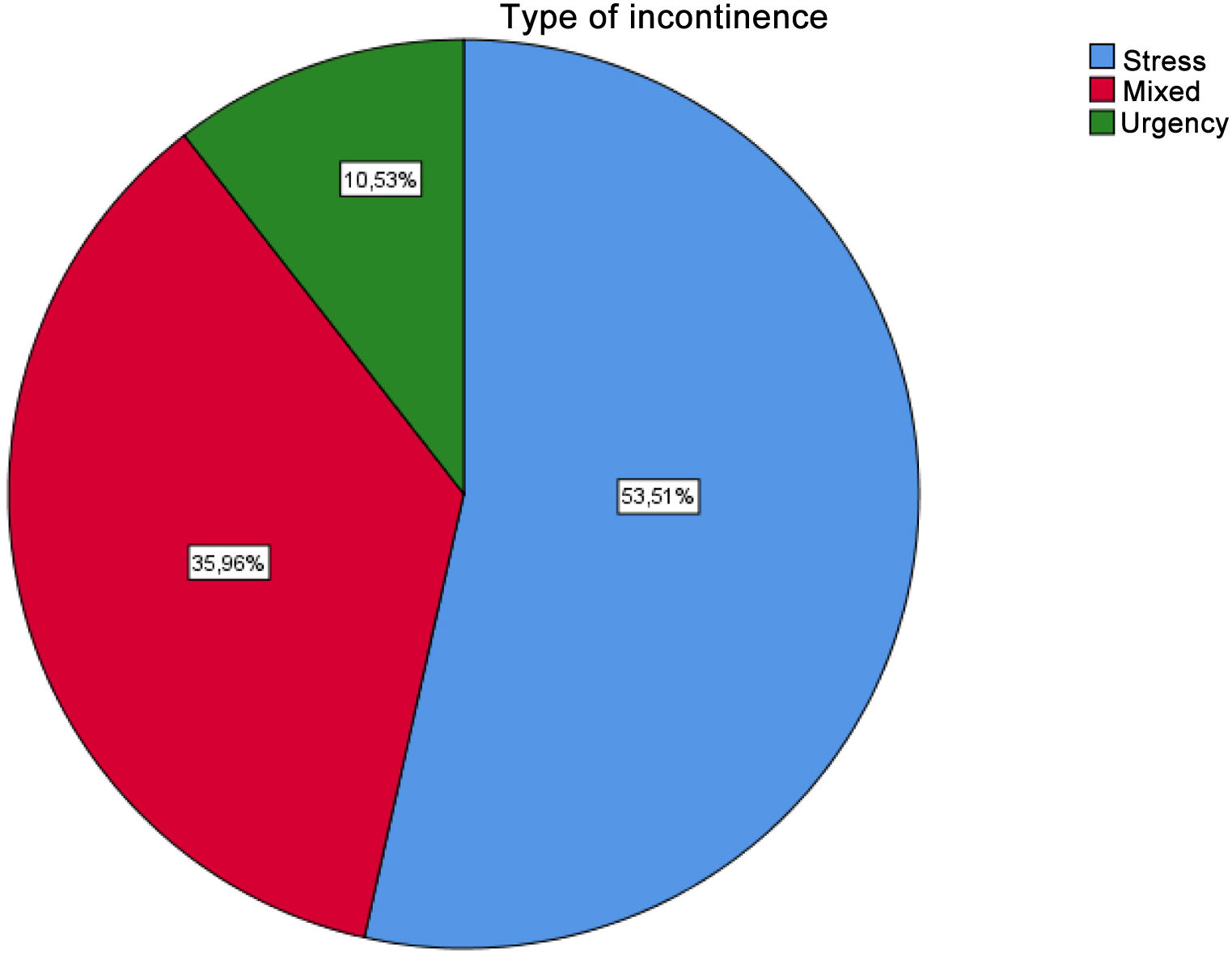
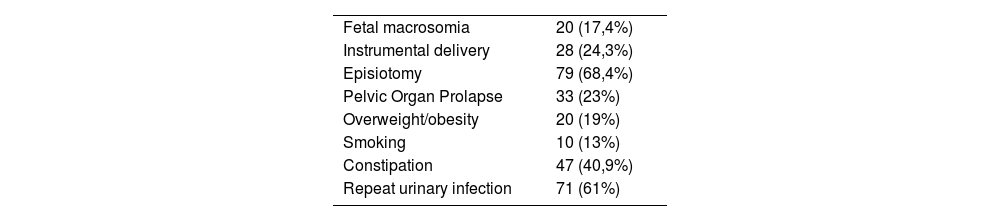
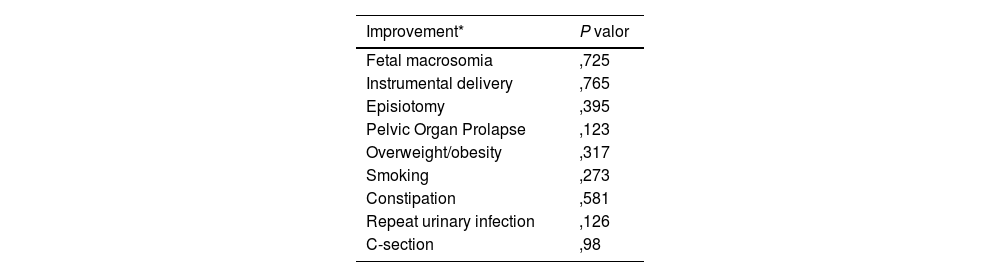
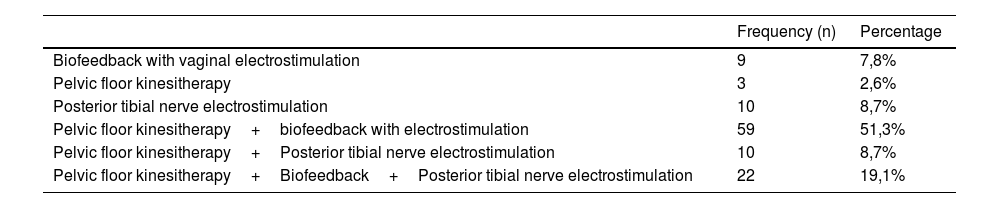
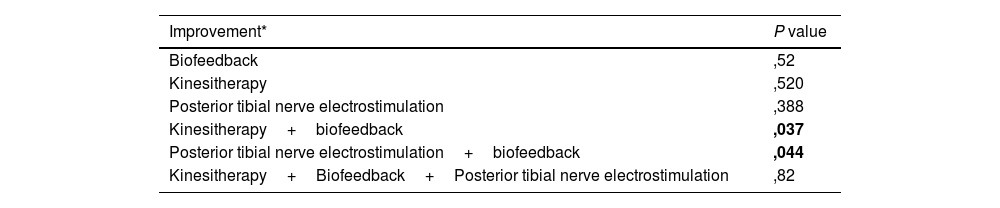
ResultsA total of 114 women with urinary incontinence were analyzed. The most frequent types of incontinence were stress (53%) and mixed (36%). The most important risk factors and associated pathology were episiotomy (68%), repeated urinary tract infections (61%), and constipation (40.9%). None of these factors showed a statistically significant relationship with patient improvement. The most used rehabilitative treatment was kinesitherapy+biofeedback (51%) which showed a statistically significant relationship with the improvement of these patients (P=.037) together with biofeedback+posterior tibial nerve electrostimulation (PTNS) (P=.044).
ConclusionBiofeedback combined with kinesitherapy or PTNS are established as the most effective rehabilitative procedures.
La incontinencia urinaria (IU) es la pérdida involuntaria de orina. Presenta una alta prevalencia en el sexo femenino y un gran impacto biopsicosocial. El tratamiento rehabilitador se establece como de primera línea, aunque su uso no ha sido protocolizado.
ObjetivoIdentificar qué factores de riesgo personales y tipo de tratamiento aplicado se encuentran relacionados estadísticamente con la mejoría de los pacientes.
Material y métodoEstudio de cohortes retrospectivas de las pacientes de sexo femenino diagnosticadas de incontinencia urinaria y que acudieron a la consulta de Rehabilitación de Suelo Pélvico del Hospital Universitario Río Hortega, recibiendo tratamiento rehabilitador a lo largo del año 2021. El periodo de seguimiento mínimo fue de 12 semanas, evaluando la mejoría o no acorde a siete variables objetivas y subjetivas, estableciendo la mejoría como la evolución positiva en al menos cinco de las siete.
ResultadosSe analizaron 114 mujeres con incontinencia urinaria. Los tipos de incontinencia más frecuente fueron: de esfuerzo (53%) y mixta (36%). Los factores de riesgo y patología asociada más importantes fueron la episiotomía (68%), infecciones de orina de repetición (61%), y el estreñimiento (40,9%). Ninguno de estos factores demostró una relación estadísticamente significativa con la mejoría de las pacientes. El tratamiento rehabilitador más empleado fue cinesiterapia+biofeedback (51%) que demostró una relación estadísticamente significativa con la mejoría de estas pacientes (P=,037) junto con biofeedback+electroestimulación del nervio tibial posterior (NETP) (P=.044).
ConclusiónEl biofeedback junto con la cinesiterapia o el NEPT se establecen como los procedimientos rehabilitadores más efectivos.